Comprehensive Guide on Magnetic encoder
A magnetic encoder is an electromechanical device which converts motion into digital signals using a magnetic field. It provides feedback about position, speed, and direction to the controller.
In today’s modern world of automation, position accuracy and feedback are important to ensure accuracy and reliability in every performance. This positional accuracy is achieved by the various types of encoders.
Among these encoder technologies, magnetic encoders have emerged as a versatile and prominent solution for various applications where dust, vibration and temperature play a vital role in the application.
What is a Magnetic Encoder?
A magnetic encoder is an electromechanical device which converts motion into digital signals using magnetic field. It is a crucial component in modern control systems, by providing feedback about position, speed, and direction to the controller.
Unlike optical encoders, which rely on light, magnetic encoders use the interaction between magnetic fields and sensors to detect motion and provide feedback to the controller.
These encoders are used in a wide range of applications such as industrial automation, robotics, and other areas where precision and accuracy are essential. Magnetic encoders are known for their compact design, non-contact sensing method, and resistance.
Depending upon the application and industry requirements, magnetic encoders are available in two types: incremental encoders and absolute encoders. Each type of encoder provides a different level of information about the movement.
An incremental encoder offers relative movement data, while an absolute encoder provides a unique position value for each movement. The choice between these types of encoders depends upon accuracy, resolution and application requirements.
Construction of Magnetic Encoder
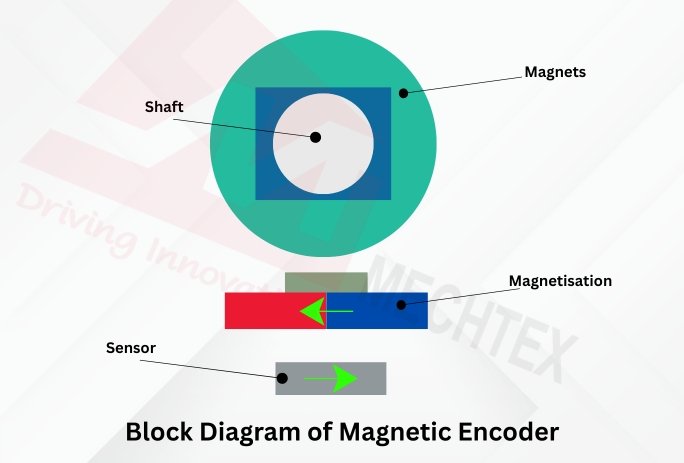
The construction of the magnetic encoder depends upon the interaction between the magnetic field and sensing elements that detect the motion and provide feedback.
It typically consists of the following components: magnetic disc, sensor array, signal conditioning circuitry and output interface.
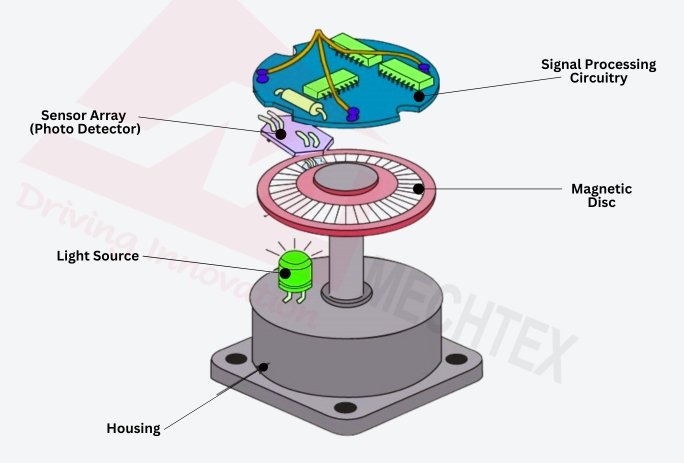
- Magnetic Disc
The magnetic disc is embedded with north and south poles. This magnetic pattern acts as a reference for the detecting motion. The magnetic disc is mounted on a rotating shaft, while the strip is attached along the linear path.
- Sensor Array
The sensor array depends upon the Hall-effect sensor and is positioned close to the magnetic surface. As the magnetic poles pass by, the sensor identifies changes in the magnetic field and generates electrical signals. These signals are raw signals and need to be processed to identify the position and other feedback.
- Signal Conditioning Circuitry
Signal conditioning circuitry processes, filters, and converts these signals into digital pulses for interpreting the feedback to the control system.
- Output Surface
The output interface, such as TTL, RS422, or other analogue output, transmits the data to the controllers to regulate the speed, direction and other parameters of the motor for better performance.
In some designs of magnetic encoders, there are shielding layers to minimise electromagnetic interference and housing to ensure durability.
Working Principle of Magnetic Encoder
The magnetic encoder works by detecting the variations in the magnetic field, which is caused by motion. Then convert these variations into the electrical signals to detect the position, speed and direction of the motor.
This encoder operates through the interaction between the magnetic disc and the magnetic sensor array placed nearby.
Watch the YouTube Video by "Training in Automation - By Lab4sys" to know more about the working of magnetic encoder
As the magnetic disc moves, the magnetic poles pass in front of the sensors. These sensors detect the changes in the magnetic field and produce the signal. Each change produces a signal that corresponds to the movements of magnetic poles.
These signals are sent to the signal conditioning circuitry, where they are processed, filtered, and converted into digital signals. These signals are further processed to detect the position, speed and direction of the motor.
The magnetic encoder continuously sends data to the controller, which is further used to monitor and improve the performance of the motor. Since the sensing is non-contact, there is minimal wear and tear and a long operational life.
Advantages of Magnetic Encoder
Magnetic encoders are the popular choice in industrial automation, robotics and other motion systems due to their accuracy, reliability, and long life. Some major advantages are:
- High Durability
Magnetic encoders are resistant free from dust, moisture, and other environmental parameters, which makes them ideal for harsh industrial environments where optical encoder fails.
- No-Contact Operation
There is zero contact between the sensors and the magnetic field, which reduces the wear and tear and increases the life of the magnetic encoder.
- Compact and Cost-Effective
Magnetic encoders are small in design, compact in structure, and easy to integrate into compact systems where space is constrained.
- Absolute and Incremental Capability
Magnetic encoders can provide both incremental and absolute feedback, which makes them suitable for various applications such as robotics, CNC machines, and automation systems.
Conclusion
Magnetic encoders stand out as a robust, efficient, and cost-effective alternative to traditional optical encoders, particularly in industrial and environmental conditions.
By leveraging magnetic sensing principles, they ensure accurate position and speed detection even in the presence of dust, moisture and vibration.
As industries continue to demand greater reliability and compactness in motion control systems, magnetic encoders will play an important role in automation, robotics, and renewable energy systems.