NEMA vs IEC Motor Standards: A Comprehensive Guide
NEMA stands for National Electrical Manufacturers Association, which develops standards for electrical equipment to ensure safety, performance, and operability. IEC stands for International Electrotechnical Commission, which prepares and publishes international standards for electrical, electronic and related technologies.

Electric motors power a vast array of industrial and commercial applications worldwide, from pumps and compressors to conveyor and robotics. Two prominent electric motor standards that dominate the global market are NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) and IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission).
Both standards aim to ensure quality, performance and safety; they both differ significantly in terms of dimensions, specifications, testing protocols and market demand.
In this blog, we explore the key differences between and NEMA and IEC motor standards to help OEM manufacturers and engineers to make informed decisions when selecting motors for specific applications.
What is NEMA?
NEMA stands for National Electrical Manufacturers Association, a U.S.-based organisation that develops standards for electrical equipment to ensure safety, performance, and operability. Founded in 1926, NEMA brings together manufacturers of electrical products, including motors, enclosures, lighting, and many more.
One of the most recognised contributions of NEMA is the standardisation of motor frame sizes, especially for stepper motors and AC/DC motors. NEMA frame sizes, such as NEMA 17, NEMA 23, and NEMA 34, refer to the physical dimensions of the motor's mounting face and bolt hole pattern.
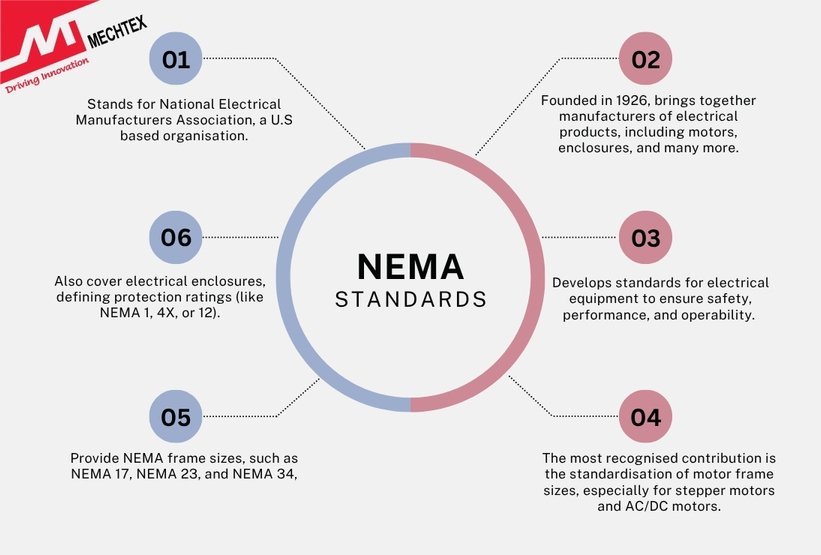
NEMA standards also cover electrical enclosures, defining protection ratings (like NEMA 1, 4X, or 12) that indicate resistance to dust, water and corrosive environments. These ratings are vital for selecting electric motors suitable for industrial, outdoor, or hazardous locations.
Globally, NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) is compared with IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standards.
Overall, NEMA plays a crucial role in ensuring compatibility, safety and quality across the electrical manufacturing industry. By adhering to NEMA standards, manufacturers can assure reliable performance and easier integration of electrical components across various applications.
What is IEC?
IEC stands for International Electrotechnical Commission, a global standards organisation that prepares and publishes international standards for electrical, electronic and related technologies. Founded in 1906, the IEC’s headquarters are in Geneva, Switzerland, and include members from over 80 countries.
IEC standards cover a wide range of industries, including power generation, automation, robotics, electronics, renewable energy, and medical equipment. These standards ensure operability, safety, environmental compatibility, and efficiency across international markets.

In motor and electrical system design, IEC is known for defining motor frame sizes, efficiency classes (IE1 to IE4), and protection ratings (IP codes).
For example, an IEC frame size like 90S or 122M denotes specific mounting and shaft dimensions. Unlike NEMA, which uses inch-based measurement, IEC uses the metric system, making it widely used in Europe, Asia and other international regions.
The IEC also defines IP (Ingress Protection) ratings such as IP54, IP55 or IP67, which specify the degree of protection against dust and water. These ratings are critical for selecting equipment used in harsh or outdoor environments.
In summary, the IEC plays a vital role in harmonising global electrical standards, facilitating international trade, innovation, and product safety across borders. =
NEMA vs IEC Standards
-
Frame Size and Mounting Dimensions
-
-
- NEMA Standards
-
-
-
-
-
- NEMA motors are identified by numbers such as 56, 143T, 182T, etc.
- The frame size is directly related to the motor height, shaft diameter and mounting dimensions.
- Dimensions vary non-linearly, and replacement with a different size requires reengineering the mount.
-
-
-
-
-
- IEC Standards
-
-
-
-
-
- IEC frame sizes use numbers such as 63, 80, 100, 132, indicating the shaft height in millimetres from the mounting surface.
- Frame size and mounting dimensions are standardised using metric units.
- Interchangeability across various manufacturers is easy due to standardised global specifications.
-
-
-
-
Efficiency Standards
-
-
- NEMA Standards
-
-
-
-
-
- Defines efficiency levels under NEMA Premium, Energy Efficient, and Standard Efficiency categories.
- Use IEEE 112 testing protocols.
- Compliance with Department of Energy (DOE) regulations is mandatory in the U.S.
-
-
-
-
-
- IEC Standards
-
-
-
-
-
- Defines efficiency classes such as IE1 (Standard), IE2 (High), IE3 (Premium), and IE4 (Super Premium).
- Uses IEC 60034-30-1 for classification.
- Testing based on the IEC 60034-2-1 method.
-
-
-
-
Service Factor and Overload Capability
-
-
- NEMA Standards
-
-
-
-
-
- Include a service factor (SF) typically 1.15, which allows motors to operate at 15% overload without damage.
- Useful in applications where occasional overloads are expected.
-
-
-
-
-
- IEC Standards
-
-
-
-
-
- Does not traditionally define the service factor.
- Instead, IEC motors are rated for Continuous Duty (S1) or specified duty cycles such as S2, S3, etc.
-
-
-
-
Global Usage and Availability
-
-
- NEMA Standards
-
-
-
-
-
- Preferred in North America and in some parts of Latin America.
- Replacement parts and motors are harder to find in other regions.
-
-
-
-
-
- IEC Standards
-
-
-
-
-
- It is a global standard and is used across the globe - Europe, Asia, the Middle East, and Africa.
- Motors and other parts are easily available in the international market.
-
-
-
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between NEMA and IEC motor standards is essential for selecting the right motor for your application. While both offer quality and reliability, the choice ultimately depends on the application environment, geographic location, regulatory requirements, and performance needs.
For domestic U.S. applications, NEMA motors offer familiar configurations and built-in overload capabilities. In contrast, IEC motors provide metric-based sizing, higher interchangeability, and global conformity, making them the go-to choice for internationally distributed systems.
By evaluating your project requirements through the lens of these standards, you can ensure optimal motor performance, cost efficiency, and ease of integration.