Brushed ESC vs. Brushless ESC - Key Differences Working Principles and Applications
Learn what an electronic speed controller (ESC) is and explore the key differences between brushed ESC and brushless ESC, including working principle, efficiency, control, and applications.
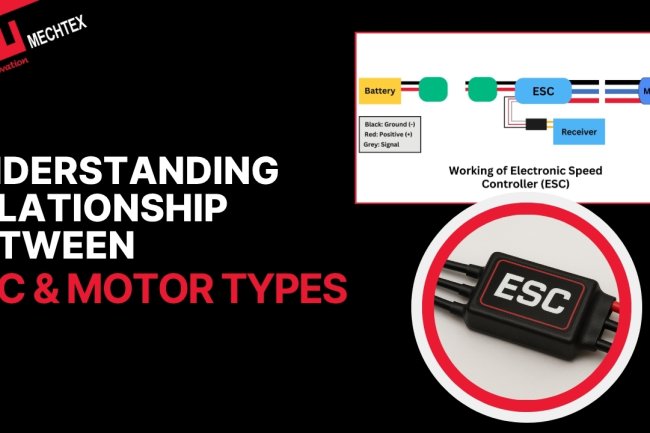
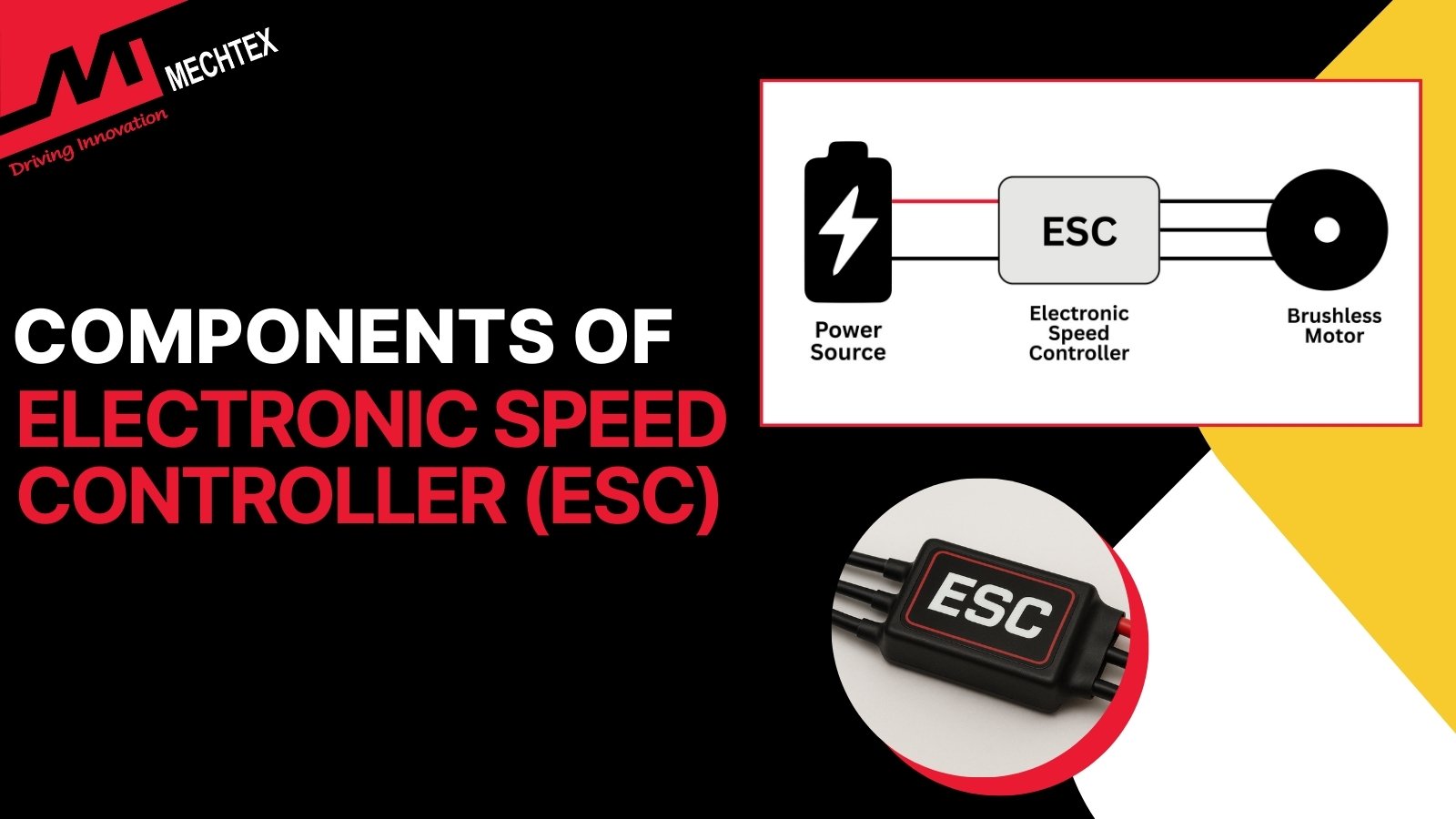
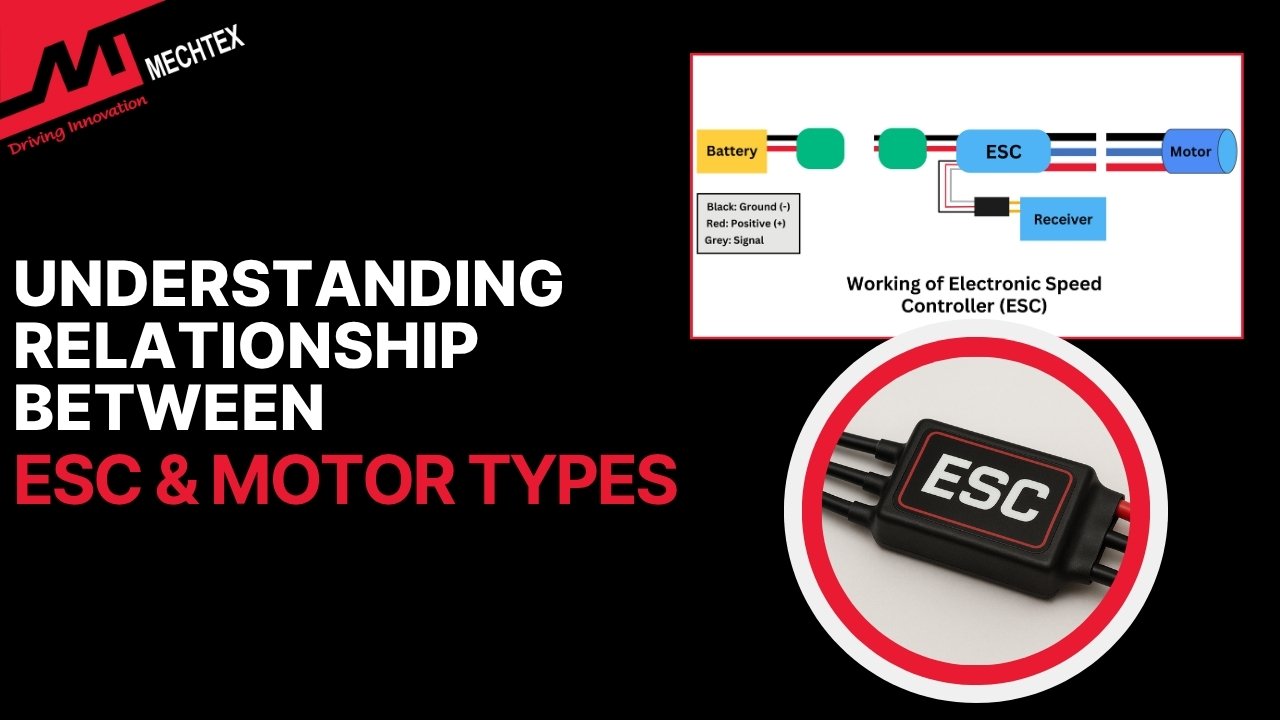
The Electronic Speed Controller (ESC) plays an important role in controlling speed, direction and braking of an electric motor. ESCs act as the interface between the power source and the electric motor to regulate the power of the motor.
Depending on different types of electric motors, ESCs are broadly classified into two types: Brushed ESC and Brushless ESC. Both types are used for the same purpose, but their operations, performance, and efficiency differ.
This blog provides a detailed comparison of brushed ESC and brushless ESC, which helps individuals select the right ESC for their application.
What is ESC (Electronic Speed Controller)?
An ESC (Electronic Speed Controller) is an electronic device used to control the speed, direction and braking of an electric motor. It interprets control signals and converts them into mechanical motion.
In an electric motor-driven system, the ESC receive low power signals from the controller and then adjusts the voltage and current by switching sequence between the windings. This allows for precise control over the speed and torque of the motor to ensure smooth and efficient operation.
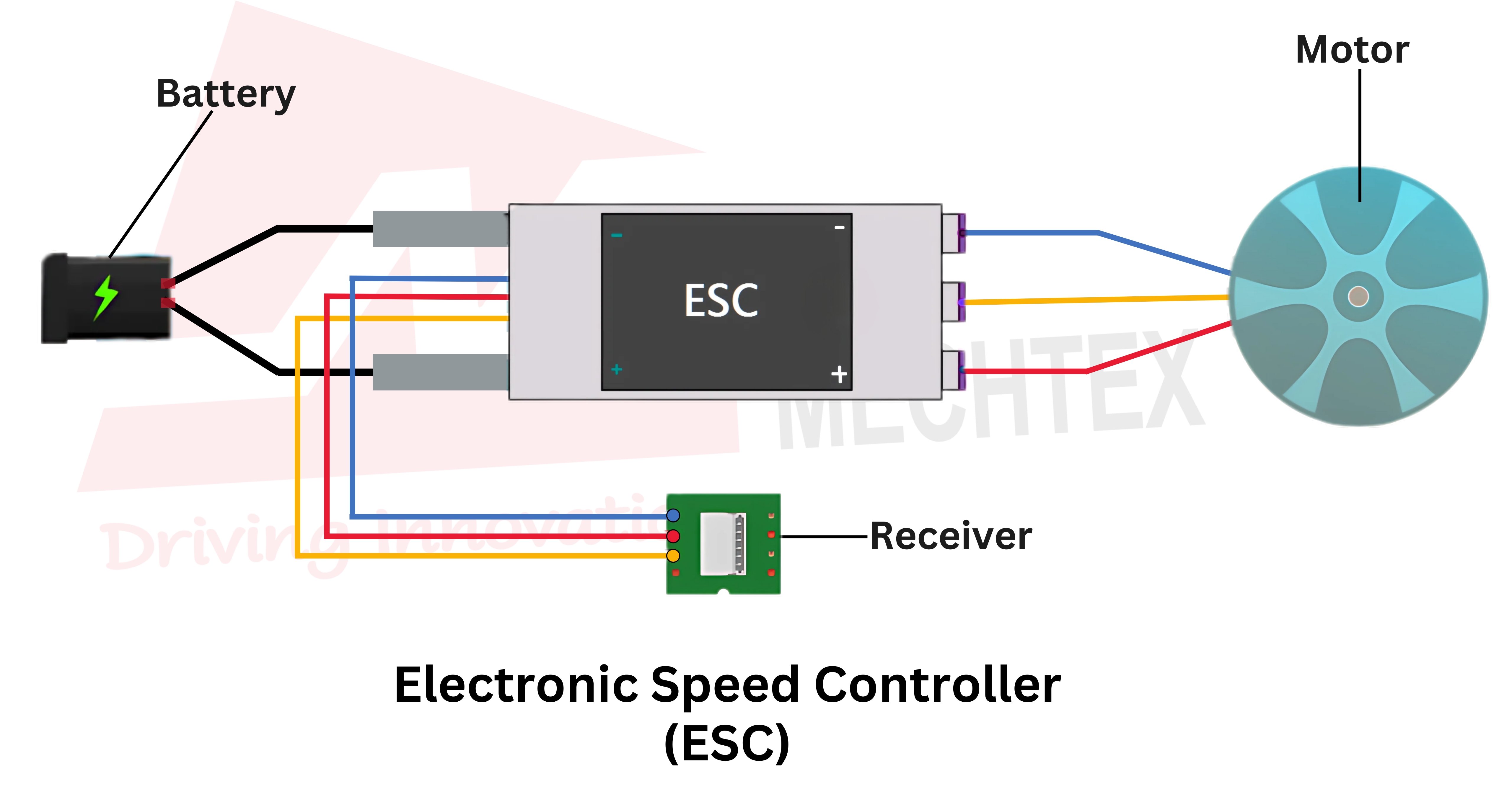
ESCs are also designed to manage high current and rapid switching of sequences to make them crucial for applications that demand quick responsiveness and reliable motor control.
Apart from speed regulation and direction control, the ESC also contains protective and monitoring functions such as over-current protection, thermal protection, and voltage cut-off. These functions protect the electric motor and power source from damage.
Therefore, ESCs are an essential device in an electric motor-driven system, which enables accurate motor control, improves system efficiency and enhances reliability for a wide range of applications.
What is Brushed ESC?
A brushed ESC is an electronic device used to control the speed, direction and braking of a brushed motor. It acts as an interface between the power source and brushed DC motor to convert signals into electrical output.
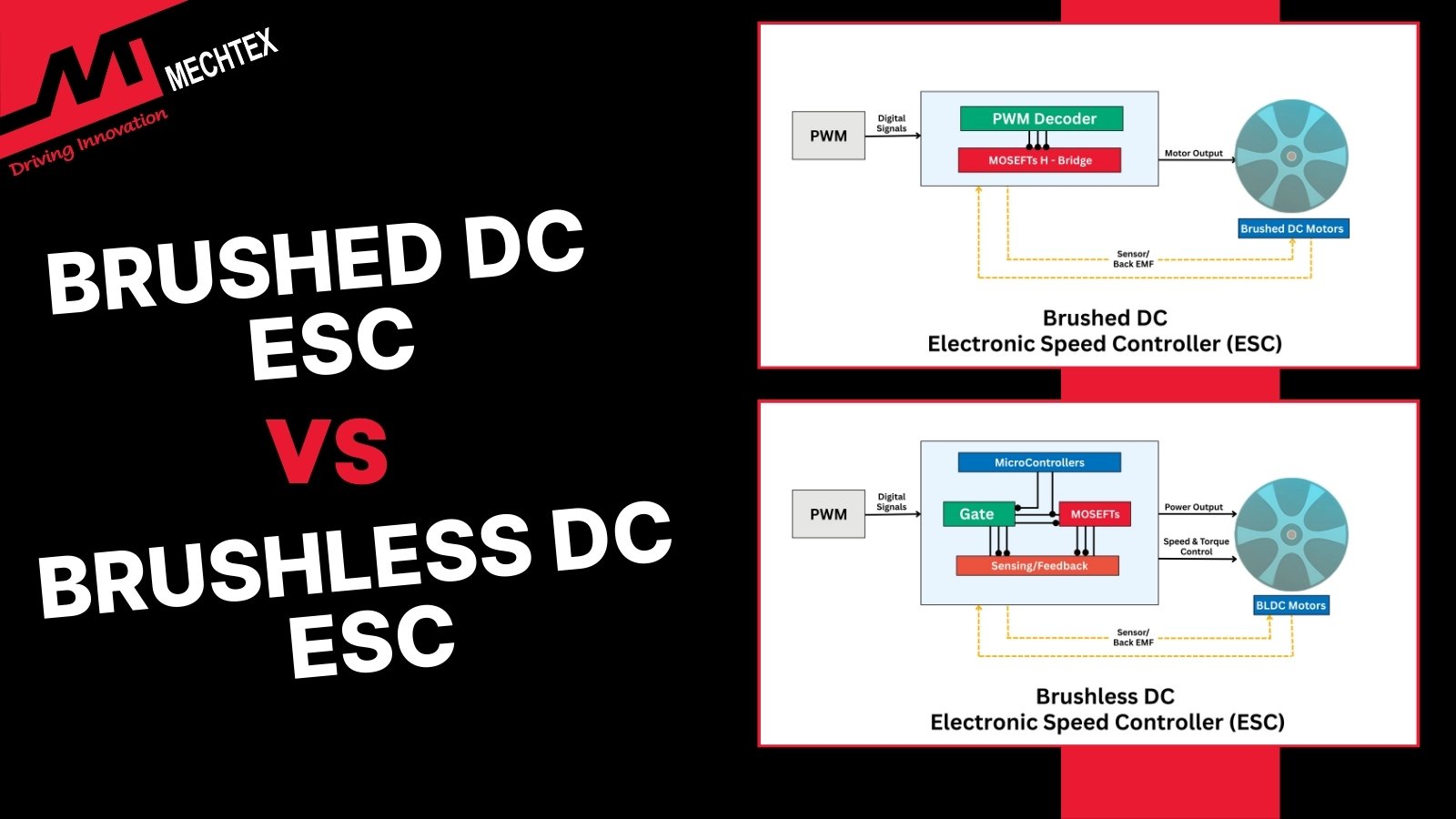
The main function of the brushed ESC is to manage the motor speed by adjusting the voltage and current provided to the motor. It is typically done using the pulse width modulation (PWM) technique, where the ESC sequentially switches the power supply to adjust the effective voltage of the motor.
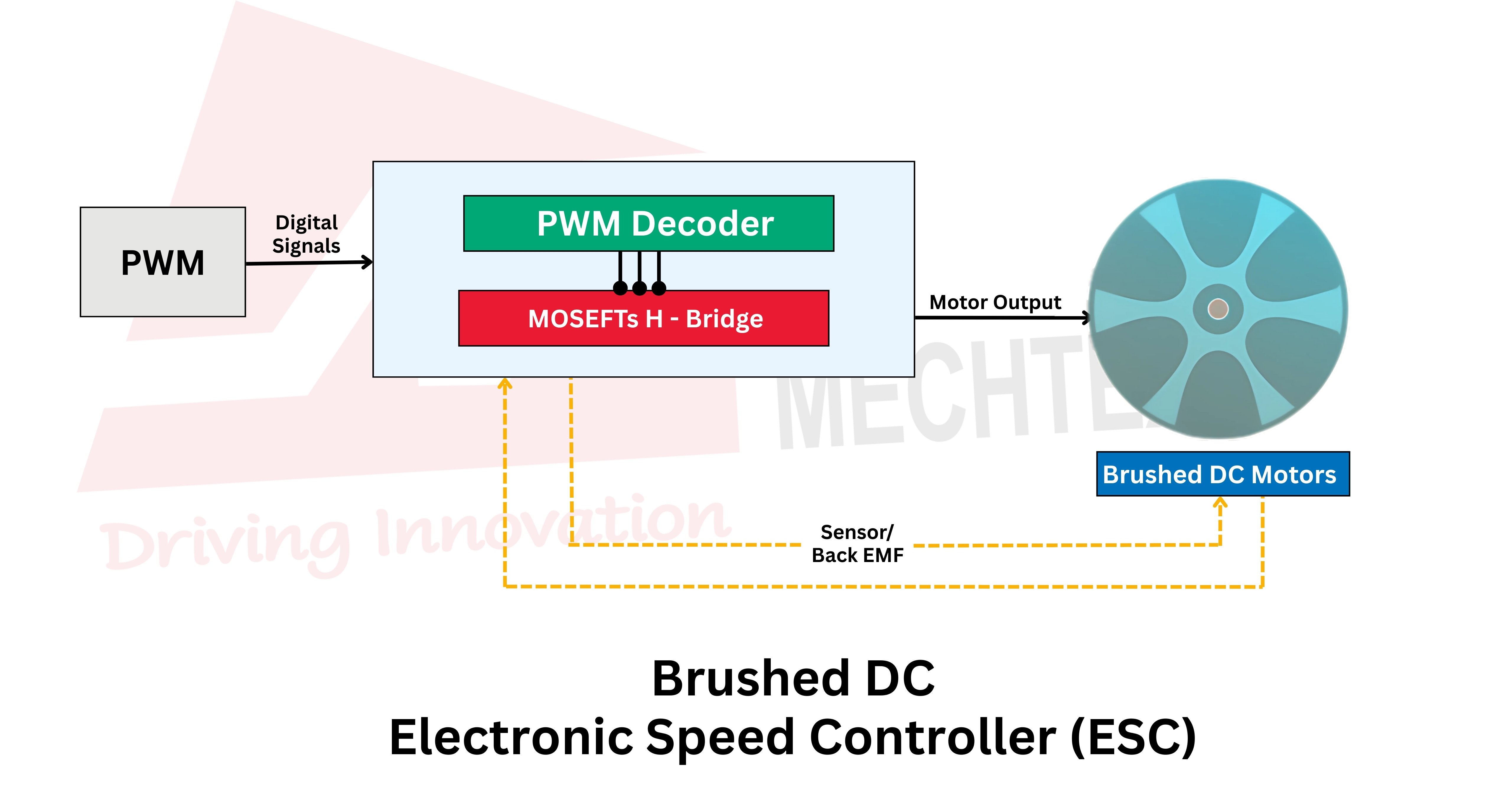
Since brushed DC motors rely on carbon brushes and a commutator for commutation. Brushed ESCs do not need any complex commutation and which makes them simple in design and reduces overall cost.
Most of the brushed DC motors also support forward and reverse direction by changing the polarity. Due to its simple design, low cost, it makes them suitable for a wide range of applications.
What is a Brushless ESC?
A brushless ESC (brushless electronic speed controller) is a motor control device designed to manage the speed, direction and braking of BLDC motors
Unlike brushed motors, brushless motors do not use commutators. Instead, a brushless DC motor uses electronic commutation for smooth movement.
The brushless ESC receives signals from controllers and converts power into a sequence of high signals required by the BLDC motor. By adjusting or switching the signals, it regulates the speed and torque of the BLDC motor with high accuracy. The brushless ESC enable smooth acceleration and quick responsiveness.
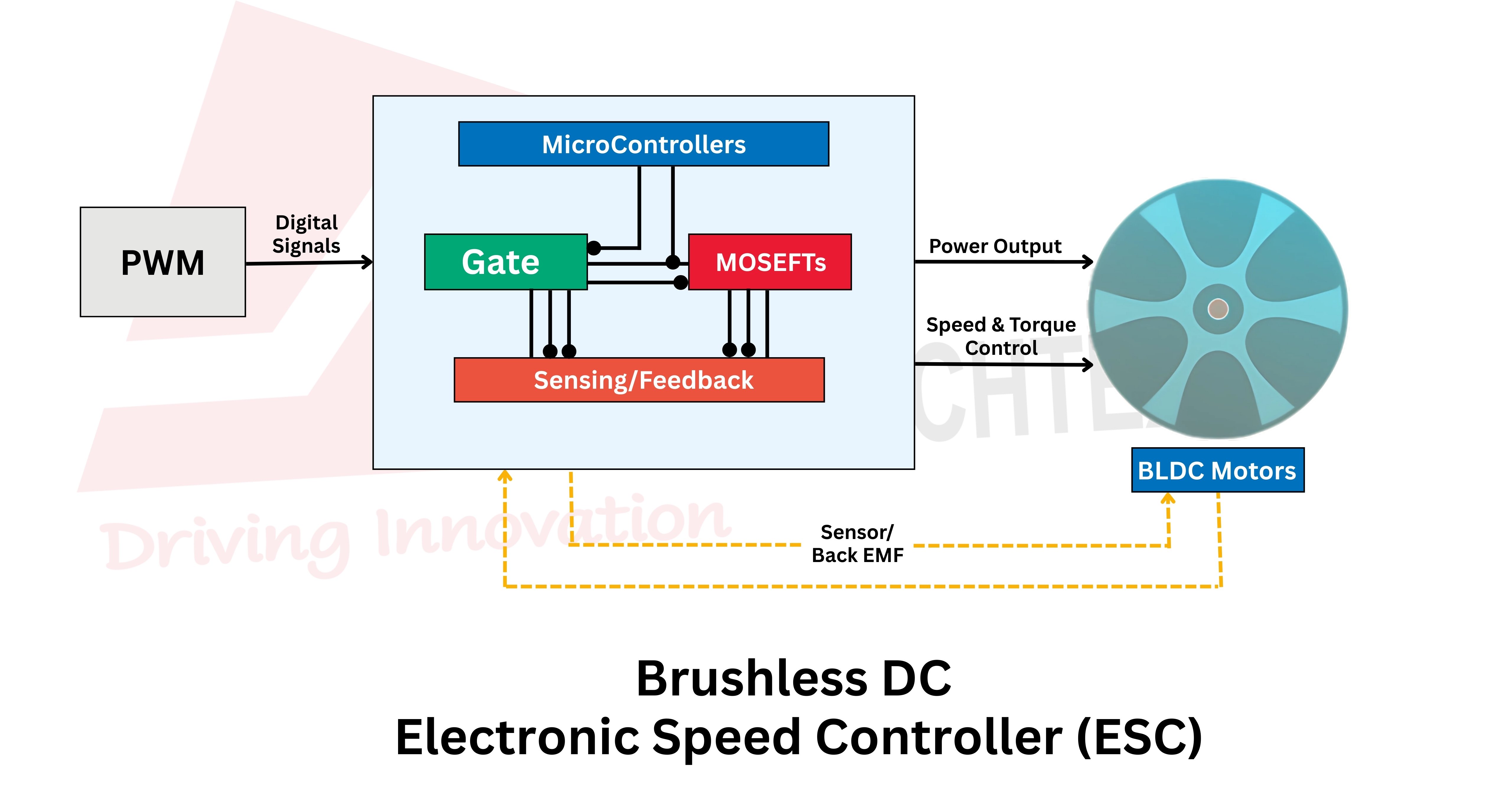
Brushless ESCs are equipped with a microcontroller, power MOSFETs, a gate driver, and sensing circuits. They operate either using sensor-controlled or sensorless control methods to determine rotor position.
Overall, brushless ESC is a crucial component in modern electronic systems to enable high efficiency, precise control, and smooth operation across various applications.
Key Differences Between Brushed and Brushless ESCs
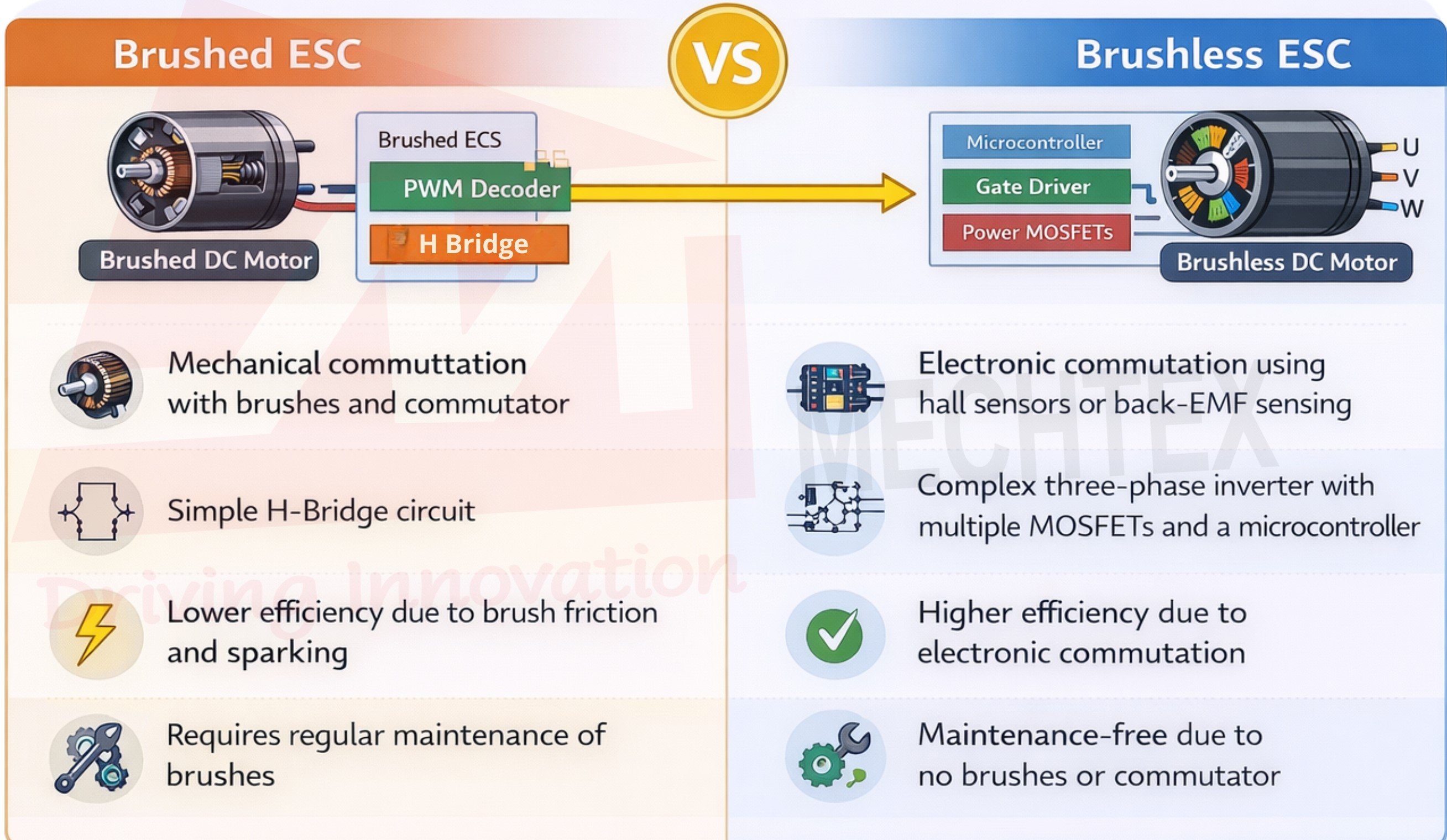
- Commutation Method
-
-
- Brushed ESC
-
-
Brushed ESCs depend on mechanical commutation for switching of current between windings. It is handled by physical brushes and commutators available inside the motor.
-
-
-
- Brushless ESC
-
-
Brushless DC motors do not have brushes. Therefore, the brushless ESC switches the current between the windings using hall sensors or the back-emf technique. This makes brushless ESCs a crucial part of the brushless DC motor rather than the controller.
- Circuit Complexity
-
-
- Brushed ESC
-
-
These ESCs have a simple circuit design using H-bridge configuration. It also has fewer power switches and easy-to-understand control logic.
-
-
-
- Brushless ESC
-
-
These ESCs are more complex than brushed ESCs. It consists of a three-phase inverter, multiple MOSFETs, gate drivers, microcontrollers, and protection circuitry. This adds complexity in design and increases overall cost.
- Efficiency
-
-
- Brushed ESC
-
-
The Efficiency of brushed ESCs is slightly lower due to brush friction, sparking, and electrical losses.
-
-
-
- Brushless ESC
-
-
Brushless ESCs are highly efficient, as electronic commutation reduces loss and heat generation for smooth operation.
- Speed and Torque Control
-
-
- Brushed ESC
-
-
Brushed ESCs offer basic speed control by varying the input voltages and PWM signals at high speed.
-
-
-
- Brushless ESC
-
-
Brushless ESCs provide precise speed and torque control through algorithms for smooth operation across a wide range of applications.
- Maintenance and Reliability
-
-
- Brushed ESC
-
-
Brushed ESCs require maintenance at regular intervals because brushes wear out, and the commutator degrades easily.
-
-
-
- Brushless ESC
-
-
It provides maintenance-free operation, as there are no wear-prone mechanical components such as brushes and a commutator, which results in long life.
Conclusion
Brushed and brushless ESCs serve distinct roles in motor control applications. Brushed ESCs remain relevant for simple, low-cost systems where ease of implementation is critical. However, as efficiency standards, performance demands, and reliability expectations increase, brushless ESCs have become the preferred choice across industries.
Understanding the fundamental differences in commutation, control strategy, efficiency, and system complexity allows engineers and designers to make informed decisions. Selecting the right ESC not only improves motor performance but also enhances system longevity and overall energy efficiency.