Everything You Need to Know About Drones: Types, Physics & 2026 Real-World Uses
Explore our comprehensive breakdown of UAV types, how they fly, and the specialized applications transforming industries this year. Click for the full 2026 roadmap.

"Drones are revolutionising industries, transforming the way we work, and making the impossible possible"
Drones or Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are aircraft systems without a human pilot. These flying machines are changing the landscape of agriculture, surveillance, delivery services, and photography.
With advanced drone technology, they are becoming smarter, safer, and more accessible across various industries. In this blog, we will provide you with an overview of drones, their types, working, and uses in various industries.
What is a Drone?
A drone is an unmanned aircraft that can be either operated remotely or autonomously using GPS, sensors, and AI-driven software. They are also known as Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). These unmanned aerial vehicles are equipped with cameras, GPS Modules, Radar Control, Infrared, Inertial measurement units (IMUs) and sometimes LIDAR for obstacle detection and precision navigation. They are usually small or medium-sized and carry out a wide range of tasks.
The basic components of a drone (UAV) include drone motors, propellers, flight controllers, batteries, and remote control systems. The motor and propeller are necessary to provide thrust to lift the drone from the ground, while the flight controller is like the brain of a drone; it is responsible for processing data and controlling the movement of the drone.
The battery powers the electronic components of the drone, and remote control systems allow the operator to control the movement of the drone. The drone operates through a combination of electrical components and software algorithms.
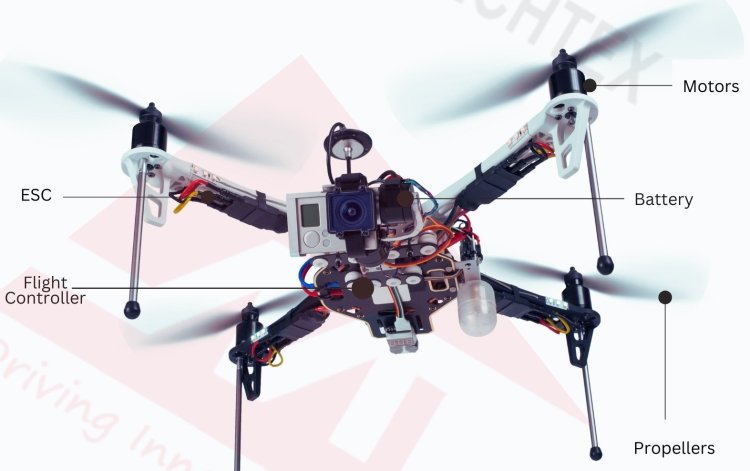

The defining feature of a drone is its ability to fly autonomously without any human intervention. This automation can range from simple, remote-controlled to fully automated missions. They are designed to perform tasks in the air with precision and reliability. Light in weight and compact in nature, these UAVs can reach areas that are difficult, dangerous and inaccessible to humans.
Drones (UAVs) are subject to national and international regulations that govern when, where and how drones can be flown. The rules and regulations are essential to maintain airspace safety, protect privacy, and avoid interference with manned aircraft. As the drone technology evolves, its usage and capabilities continue to expand and will make them an important part of the modern aerial landscape.
4 Types of Drones
Drones are also known as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). They come in various types, each type of drone tailored for specific applications and industries due to their unique capabilities and features.
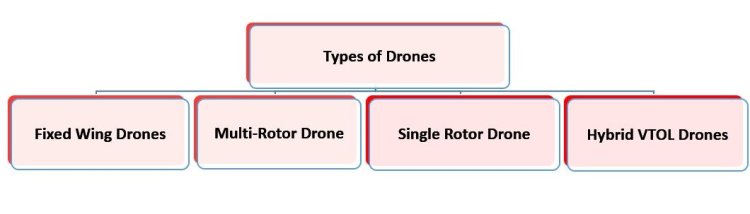
Here are 4 key types of drones:
- Fixed Wing Drones
These drones are similar to traditional aeroplanes with wings. They are efficient in flight and cover long distances. Fixed-wing drones are suitable for long-range mapping, agriculture spraying, and defence surveillance. Fixed-wing drones are generally used for aerial mapping, surveillance, and agriculture.
- Multi-Rotor Drones
Multi-rotor drones include quadcopters, hexacopters, and octacopters. These drones have multiple drones arranged in symmetrical patterns. They are highly efficient and capable of vertical takeoff and landing. It is the most common type of drone and is widely used in aerial photography, surveillance, inspection, and hobbyist applications. Quadcopter motors are specially designed to deliver optimal thrust and stability, ensuring smooth flight and precise manoeuvrability in these drones.
- Single-Rotor Drones
These drones consist of a single rotor and a tail rotor for better stability and control. They have a helicopter-like structure and are more efficient than multi-rotors for carrying heavier payloads. Single-rotor drones are less popular as compared to multi-rotor drones due to their high cost and complex design.
- Hybrid VTOL Drones
Hybrid VTOL drones are a combination of fixed-wing drones and multi-rotor drones. They have vertical take-off and landing capabilities along with efficient forward flight. They are suitable for aerial mapping, surveillance, and cargo delivery.
Other Types of Drones
- Photography Drones
These drones are designed to capture high-quality photos and videos. They are equipped with high-resolution cameras, GPS, and features like autopilot modes and obstacle avoidance.
Brushless gimbal motors are used in these drones to stabilise the camera, ensuring smooth and jitter-free footage even during dynamic flight movements.
- Military Drones
These drones are used by military forces for surveillance, intelligence gathering, and defensive activities. They come in various sizes and configurations, from small drones to large armed drones.
- Agricultural Drones
These drones are used for farming activities such as crop monitoring, pest detection, crop spraying, and precision irrigation. This helps the farmers to produce better yields and perform high-quality farming activities.
Brushless DC motors are used in these drones to provide reliable performance, higher efficiency, and the power needed for sustained agricultural operations.
- Emergency Response Drones
Emergency response drones are used by firefighters, police officers, and disaster management forces to assess disaster situations and provide medical supplies and communication equipment.
High-torque gimbal motors are utilised in these drones to stabilise cameras and sensors, ensuring clear visuals and accurate data collection in critical environments.
How do Drones Work?
Drones operate through a combination of electronic components, sensors, and software that enable drones to fly efficiently and perform precision tasks easily.
At the core of the drone, it is the flight controller that processes the data from various sensors such as gyroscopes, accelerometers, and GPS to maintain balance and direction. It also consists of motors and propellers, which generate lift and allow the drone to move by adjusting their speed. It also have an electronic speed controller which regulates motor performance based on input from the flight controller.
Drones (UAVs) are typically powered by lithium-polymer (Li-Po) batteries, which offer a good balance of weight and energy capacity. These batteries supply power to the motors, controller, and other systems of the drones. There are also communication systems such as radio, transmitters and receivers that connect the drone to the remote controller. The pilot sends commands like throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll to which help drones to execute tasks efficiently. Many drones use GPS modules for precise positioning and navigation.
In summary, drones work by using synchronised control of motor speed, sensor input, and programmed instructions to maintain stable flight and carry out designated operations, whether manually controlled or fully autonomous.
Also Read
A Comprehensive Guide on Drone Motors
What is a drone used for?
A drone is used for a wide range of applications across various industries due to its ability to reach hard-to-access areas, capture aerial data, and perform tasks with precision. Some of the common uses of drones are:
- Aerial Photography and Videography
Drones have revolutionised photography and filmmaking by providing a unique aerial perspective that was previously possible with helicopters and cranes. Equipped with high-resolution cameras, drones are now widely used in weddings, real estate, journalism, and movie production to capture cinematic shots from high altitudes to offer viewers a dynamic visual experience.
Brushless motors are used in these drones to ensure efficient operation, reduced noise, and extended durability, which offer dynamic live event coverage and cinematic aerial perspectives.
- Agriculture
Drones have revolutionised agriculture by offering precise data-driven insights about crop health and field conditions. Equipped with multispectral and thermal sensors, the UAVs capture detailed aerial images to identify issues like pest infestations, water stress, or nutrient deficiencies. This allows farmers to reduce manual efforts and increase efficiency to boost yields.
BLDC drone motors are used in these drones to provide high efficiency, reliable performance, and the power required for demanding farming operations.
- Search and Rescue
Drones have transformed search and rescue operations by enabling rapid, safe and efficient coverage of large and hard-to-access areas. Equipped with thermal imaging, GPS, and real-time video transmission, the UAVs help to locate missing persons even in darkness or under debris. It also use in forests, disaster zones, and remote regions to guide rescue teams with accurate visuals and enhance response time.
- Delivery Services
Drones have transformed the delivery landscape by enabling fast, contactless transportation of goods. Capable of navigating urban and remote areas, the UAVs deliver essentials such as medicines, food, and parcels with minimal human intervention.
By using GPS and an automated flight system, delivery drones reduce transit times and lower operational costs. The efficiency and speed of delivery drones make them a promising solution for last-mile logistics, especially in emergency or hard-to-reach locations.
Big drone motors are used in the delivery drones to handle heavier payloads and ensure stable flight over longer distances.
- Security and Surveillance
Drones have enhanced security and surveillance tasks by providing real-time aerial monitoring of large and sensitive areas. Equipped with high-resolution and night vision cameras, these UAVs offer continuous monitoring over borders, industrial zones, and public events.
Their ability to fly over difficult terrain and transmit live footage allows for quicker threat detection, situational awareness and security operations.
- Mapping and Surveying
Drones have revolutionised mapping and surveying operations by capturing high-resolution images and aerial data quickly and accurately. Using GPS and imaging technologies, these UAVs create detailed maps, 3d modules, and topographic surveys of land, construction sites, and infrastructure.
Their ability to access remote or hazardous areas makes mapping and surveying drones an efficient and reliable tool.
- Environment & Research
Drones have become valuable tools in environmental monitoring and scientific research by providing access to remote or fragile ecosystems without causing disturbance. They collect data on wildlife, vegetation, air quality, and climate conditions using specialised sensors and cameras.
Researchers use drones to track animal movements, monitor deforestation, and study environmental changes over time. Their efficiency, precision, and low environmental impact make them essential for sustainable observation and data collection.
The Future of Drone Technology: What’s Next?
The drone industry is evolving rapidly, powered by advancements in artificial intelligence, communication networks, and computing technologies. Here’s how the future of drone technology:
- AI-Powered Autonomy
Artificial intelligence is enabling drones to fly with minimal human intervention. With advanced machine algorithms, future drone technology will perform autonomous navigation, object recognition, and decision-making in real-time.
- Swarm Drone Coordination
Inspired by nature, swarm technology will allow multiple drones to work together in coordinated missions. Whether it's a search and rescue, environmental monitoring, or military operations, drone swarms will act as a collective system, increasing efficiency and reliability.
- Urban Air Mobility (UAM)
Urban air mobility is transforming drones into aerial transport vehicles. Cargo drones will soon redefine logistics and other transport. UAM (Urban Air Mobility) aims to decongest roads and enable safe and efficient air travel.





















