Axial Flux vs Radial Flux Motors: A Comprehensive Comparison
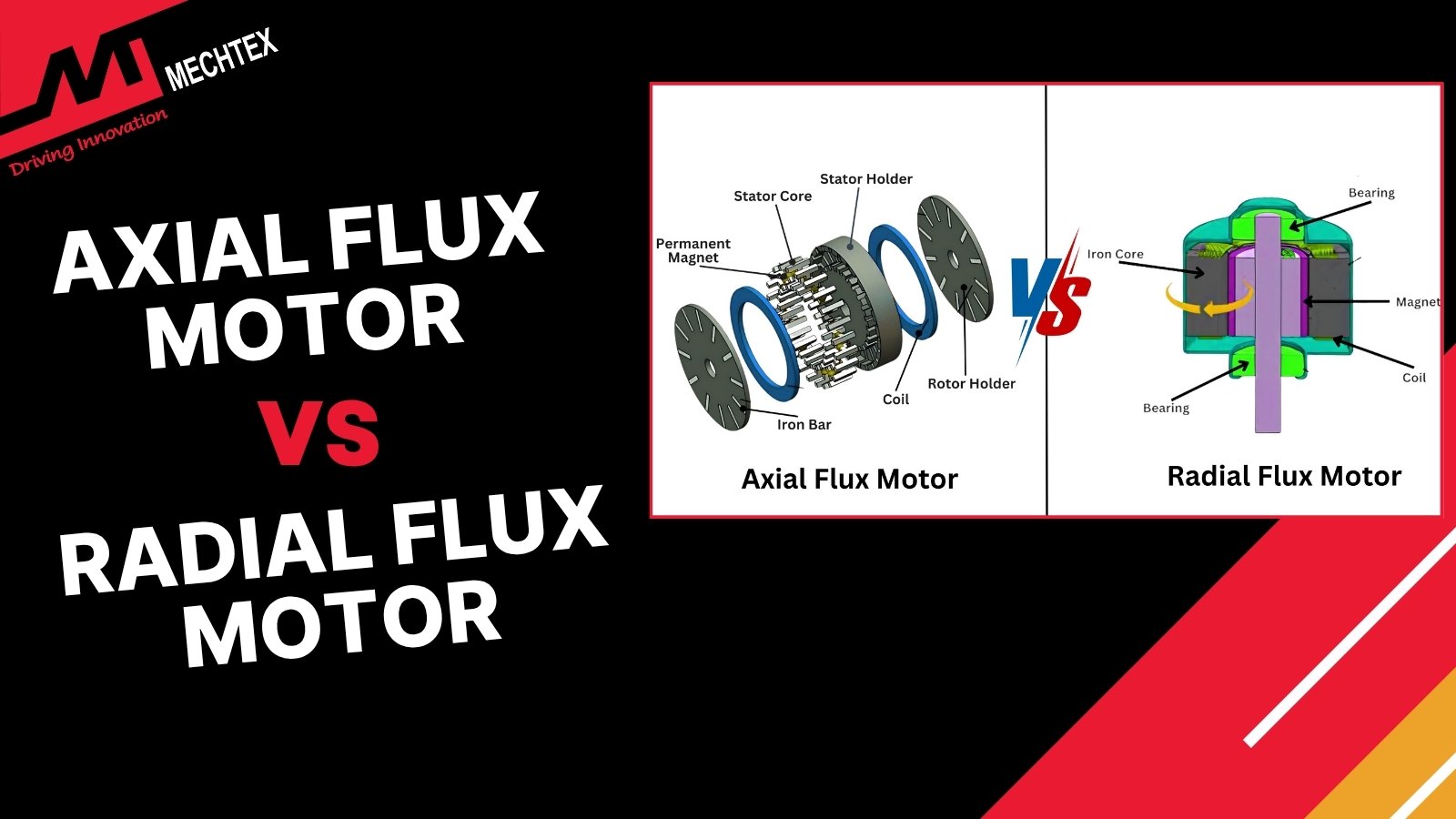
An axial flux motor is an electric motor in which the magnetic flux flows parallel to the axis of rotation, along the axial direction. In contrast, radial flux motors are electric motors where magnetic flux flows radially, i.e. perpendicularly to the axis of rotation.
Electric motors are the core component of modern automation, mobility and energy systems. While most of the motors have radial flux design, a new configuration called axial flux is gaining popularity due to its compact form factor and high torque density.
In this blog, we will explore radial flux and axial flux motors, their design, applications, and working principles, to gain a deeper understanding of both motor types and their uses.
What is Flux in a Motor?
In motors, the term “flux” refers to the magnetic flux, which is the measure of the magnetic field passing through a given area in the motor.
It is measured in Webers (Wb) and calculated as the product of the magnetic field strength (B) and the area (A) it passes through perpendicular to the field.
Mathematically, it is represented as
Φ = B × A
When current flows through the motor windings, it creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the magnetic flux from the permanent magnets or rotor poles and produces a force for rotation.
Efficient flux generation and its management are essential for high torque density, better power output, and motor performance.
What is Axial Flux Motor?
Axial flux motor is an electric motor in which the magnetic flux flows parallel to the axis of rotation, along the axial direction.
Unlike the radial flux motor, where the flux moves radially outwards, the axial flux motor generates torque through the interaction of the magnetic field aligned with the shaft axis.
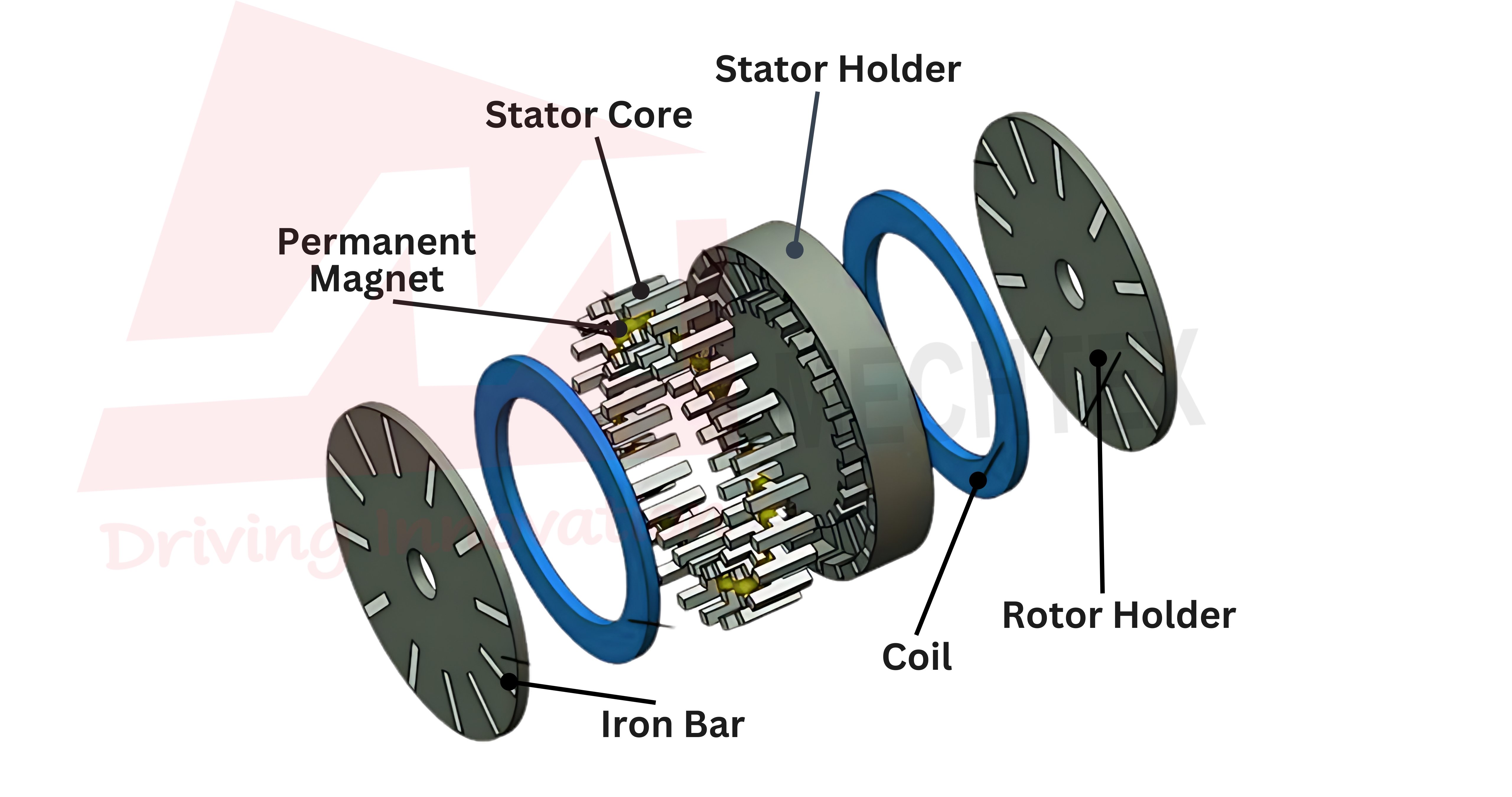
This flux motor consists of a flat disc-shaped structure. It typically consists of one or more rotor discs with permanent magnets and one or more stator discs with coil windings. The magnetic flux travels axially between the stator and rotor across the air gap to produce torque.
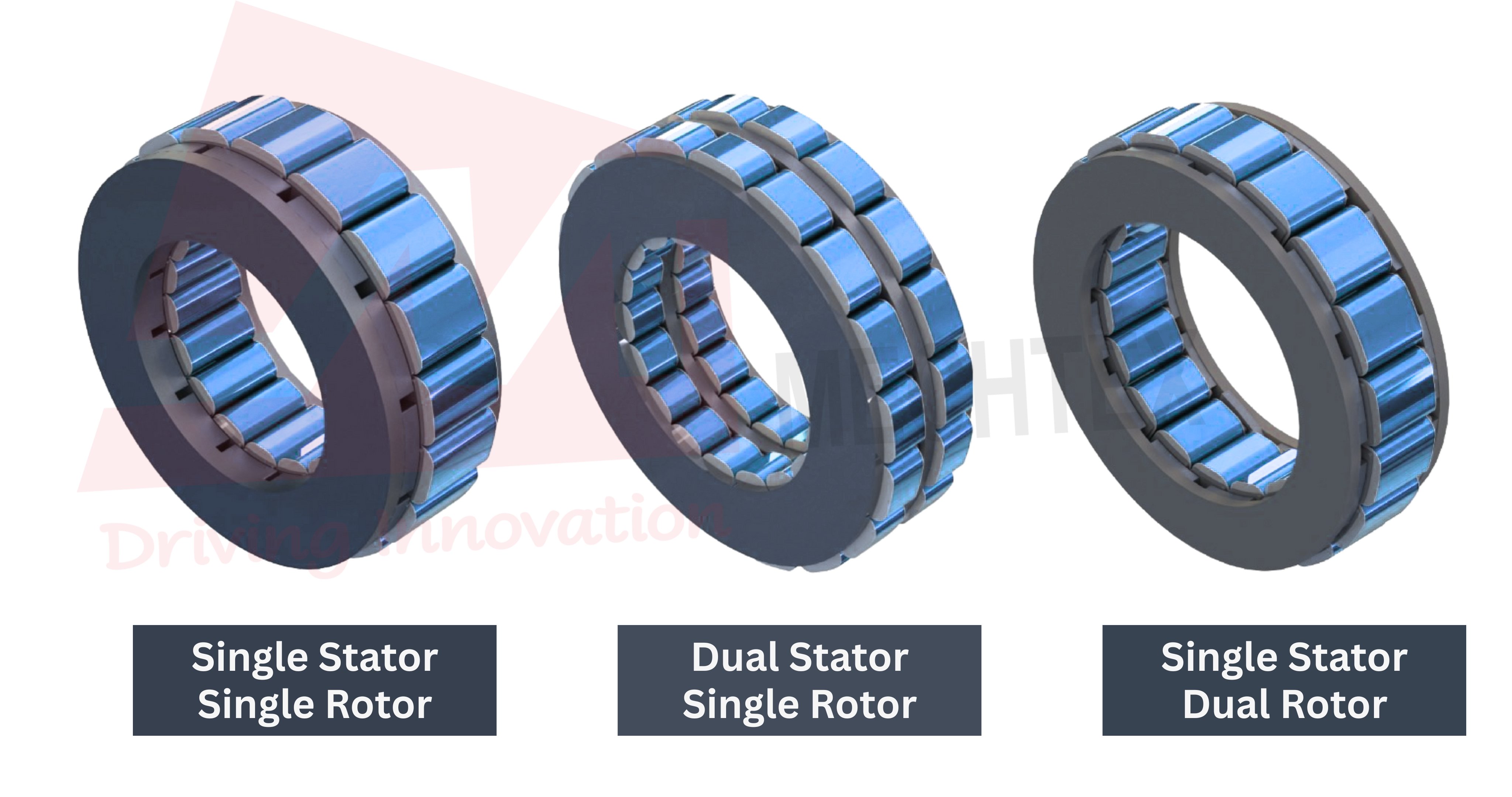
Axial flux motors can be configured into the following combinations:
- Single Stator - Single Rotor
- Dual Stator - Single Rotor (to produce more torque)
- Single Stator - Dual Rotor
Axial flux motor offers several advantages, such as high torque and power density, compact and lightweight design, Improved cooling mechanism, and high efficiency to drive applications smoothly.
These advantages make axial flux motors suitable for electric vehicles, aerospace, robotics, and high-performance motor sports, where compactness and weight savings are critical.
What is a Radial Flux Motor?
Radial flux motors are electric motors where magnetic flux flows radially, i.e. perpendicularly to the axis of rotation. These flux motors are the most common types of motors used in various applications such as electric vehicles (EVs), industrial machinery, robotics, and appliances.
In radial flux motor, the stator is positioned around the rotor, and the magnetic field lines extend from the rotor to the stator and vice versa.
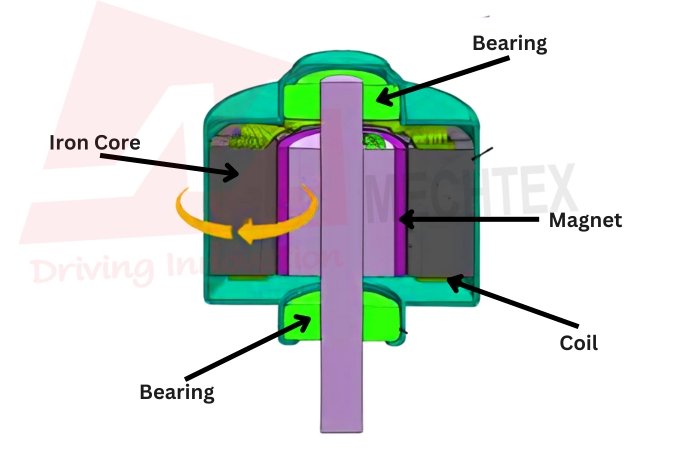
The rotor usually contains permanent magnets or is wound with coil, while the stator is equipped with windings that generate magnetic field. The torque is produced due to the interaction between the magnetic field of the stator and rotor.
Radial flux motors are classified into two types:
- Inner rotor design
In this design rotor is inside the stator, and it is the most common type of design for flux motors.
- Outer rotor design
In this design, the stator is placed inside and the rotor surrounds the stator. It is often used in applications that require high torque at low speeds.
Radial flux motor offers several advantages such as customised design, high torque density, and an effective cooling mechanism.
However, they also have some limitations in terms of compactness and power-to-weight ratio as compared to the axial flux motor.
Difference Between Axial Flux Motor and Radial Flux Motor
Electric motors are classified based on the direction of magnetic flux in relation to the axis of motion. Two prominent types of electric motors are axial flux motor and radial flux motor. Each motor has its own distinct characteristic, which makes them suitable for different applications.
Let’s take a look at some differences between axial flux motor and radial flux motor
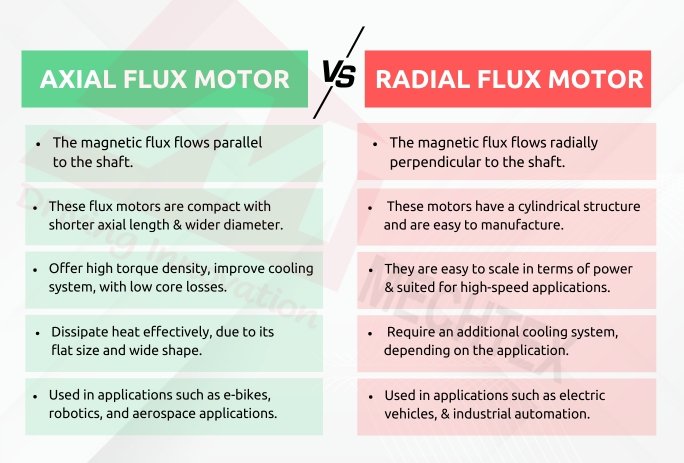
Magnetic Flux Orientation
- Axial Flux Motor
In this motor, the magnetic flux flows parallel to the shaft. These motors use a disc-shaped structure where the stator and rotor face each other.
- Radial Flux Motor
In this motor, the magnetic flux flows radially perpendicular to the shaft. The rotor and stator are arranged in a cylindrical layout, where the rotor is either inside or outside the stator.
Design and Construction
- Axial Flux Motor
These flux motors are compact with shorter axial length and wider diameter. They often use single or double rotors around the stator to enhance power usage.
- Radial Flux Motor
These motors have a cylindrical structure and are easy to manufacture with standardised components. They usually have long axial length.
Performance and Efficiency
- Axial Flux Motor
These motors offer high torque density, improve the cooling system, shorter magnetic path with low core losses and offer greater efficiency, especially at low speeds.
- Radial Flux Motor
These motors are easy to scale in terms of power and size, well optimised for high-speed applications, and well proven for the industrial sector.
Cooling and Thermal Management
- Axial Flux Motor
Axial flux motors generally dissipate heat effectively, due to their flat size and wide shape, which exposes more cooling areas.
- Radial Flux Motor
Radial flux motors require an additional cooling mechanism, depending on the applications and power rating.
Applications
- Axial Flux Motor
These motors are widely used in applications such as e-bikes, robotics, and aerospace applications.
- Radial Flux Motor
These flux motors dominate applications such as electric vehicles, industrial automation, and household appliances.
Conclusion
The choice between axial and radial flux motors depends on the application’s space constraints, torque requirements, efficiency goals, and manufacturing feasibility.
While radial flux motors are more common due to their mature technology and ease of production, axial flux motors offer a promising future with higher torque densities and improved energy efficiency, especially in compact and high-performance applications.
As motor technology continues to evolve, we are likely to see both types coexist, with axial flux motors gaining ground in niche and performance-driven sectors, and radial flux motors continuing to serve as the workhorse for mainstream industrial and commercial applications.