Harmonics in Synchronous Motors: Causes, Effects, and Mitigation
Harmonics in synchronous motors refer to the voltage and current waveform that deviates from the fundamental frequency and introduces unwanted distortions. It arises due to various electrical and mechanical factors leading to inefficiencies. Understanding their root causes and implementing mitigation strategies enhance motor performance.

What is Harmonics in Synchronous Motor?
Harmonics in synchronous motors refer to the voltage and current waveform that deviates from the fundamental frequency, introducing unwanted distortions. These harmonics arise due to the non-sinusoidal nature of the magnetic field and electrical waveforms in synchronous motor operation.
In an ideal scenario, the supply voltage and current should be purely sinusoidal. However, synchronous motors operate under practical conditions where the magnetic flux distribution in the air is not perfectly uniform. This leads to harmonic components in the generated electromotive force (EMF) and stator currents.
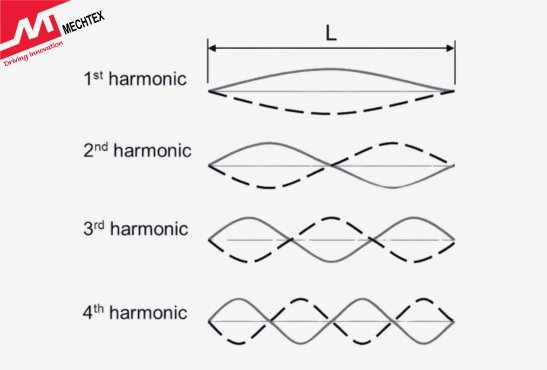
A key characteristic of harmonics in synchronous motors is their influence on torque production. Harmonics can generate pulsating torque, which may lead to unwanted mechanical vibrations.
Additionally, harmonic distortions contribute to heating due to an increase in core losses,, which affects synchronous motor efficiency. The severity of harmonic distortion depends on the synchronous motor’s design, winding configuration, and supply waveform quality.
Harmonics are analysed using Fourier series decomposition, where the waveform is broken down into its fundamental and harmonic components. Engineers use this analysis to understand the harmonic spectrum and design synchronous motors with optimised winding configurations to minimise their impact.
Causes of Harmonics in Synchronous Motors
Harmonics in synchronous motors arise due to various electrical and mechanical factors. These harmonics can negatively affect motor performance, leading to inefficiencies, vibrations, and overheating. The primary causes of harmonics in synchronous motors include:

- Slotting Effect
The presence of stator and rotor slots disrupts the uniform magnetic field, which leads to generating harmonics components in air gap flux. This results in torque pulsations and additional losses.
- Saturation of Magnetic Core
When the magnetic core of a synchronous motor operates near saturation and introduces non-linearity in the magnetic circuit. This nonlinearity distorts the sinusoidal waveform and produces odd and even harmonics in synchronous motor voltage and current.
- Unequal Air Gap
An uneven air gap between the stator and rotor, due to improper alignment or mechanical imperfections, causes asymmetry in the magnetic field. This asymmetry generates additional harmonic components.
- Winding Configuration
The type and arrangement of stator winding impact the harmonic generation. Improperly distributed windings are non-ideal windings which lead to an imbalance in induced EMF and contribute to unwanted harmonic frequencies.
- Supply Frequency Variations
Fluctuation in power supply due to unstable grid conditions introduces harmonics components in synchronous motor operation. This is especially prevalent in industrial environments with fluctuating loads.
Effects of Harmonics in Synchronous Motors
Harmonics in synchronous motors refer to voltage and current waveforms that deviate from the fundamental frequency due to non-linear loads or distortions in the power supply. These harmonics introduce several adverse effects on motor performance, efficiency, and reliability. Some effects are as follows:
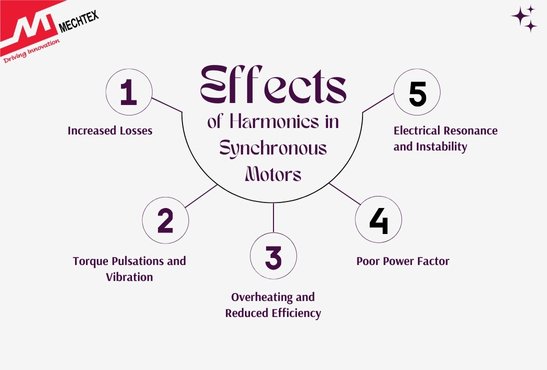
- Increased Losses
Harmonic current causes additional losses in the stator and rotor, leading to increased copper losses and iron losses. This results in excessive heating and reduces the synchronous motor's lifespan and efficiency.
- Torque Pulsations and Vibration
Harmonic components generate unwanted torque pulsations, causing fluctuations in synchronous motor speed. These pulsations lead to mechanical vibrations and increased noise levels and potentially cause damage to synchronous motor bearing and coupling.
- Overheating and Reduced Efficiency
High-order harmonics induce circulating currents in the rotor and lead to excessive heating. If overheating is not controlled, it can degrade insulation material and reduce synchronous motor efficiency and life.
- Poor Power Factor
Harmonics can cause reactive imbalances, which lead to a poor power factor. This results in increased demand for power factor correction devices.
- Electrical Resonance and Instability
Harmonics can excite electrical resonance conditions within the motor and power system, which leads to voltage distortion and instability in synchronous motor operation. This can result in erratic performance or even damage to the power supply system.
Harmonics Mitigation Techniques for Synchronous Motors
Harmonics in synchronous motors arise due to non-linear loads, distorted supply voltages, and unbalanced operating conditions. These harmonics can lead to excessive heating, increased losses, and reduced efficiency. Effective mitigation techniques include:

- Use of Filters
Passive Filters: Comprising inductors, capacitors and resistors, passive filters eliminate specific harmonic frequencies
Active Filters: These filters dynamically counteract harmonics by injecting compensating currents and offer better adaptability.
- Improved Motor Design
Fractional Slot Windings: These windings reduce harmonic content in the air gap flux
Short-Pitch Windings: These windings minimise harmonic orders.
- Harmonic Suppression Through Supply Quality Improvement
Phase Shifting Transformers: It reduces triplen harmonics by phase cancellation.
Isolation Transformer: It blocks high-frequency harmonics from reaching the synchronous motor.
- Power Factor Correction (PFC) Techniques
Well-designed power factor correction capacitors can filter out harmonics and improve the efficiency of synchronous motors.
Conclusion
Harmonics in synchronous motors pose challenges that can degrade efficiency, increase operational costs, and reduce lifespan. Understanding their root causes and implementing mitigation strategies such as harmonic filtering, optimised winding design, and improved power correction can significantly enhance motor performance. By addressing harmonics effectively, industries can ensure reliable and efficient motor operation, minimising downtime and maintenance costs.