Understanding NEMA Frame Sizes: A Beginner’s Guide
NEMA frame size refers to the standardised sets of dimensions and mounting configurations. It is a code that tells us about the NEMA motor’s size, mounting, and shaft dimensions. It plays a crucial role in ensuring that motors can be easily replaced or upgraded without modifying the mounting setup.
When selecting a NEMA motor for the application, one crucial factor that is often overlooked is the NEMA frame size. Choosing the right frame size ensures that your motor fits correctly, aligns perfectly, and operates efficiently within the machinery. For beginners, terms like “NEMA 56C” or “NEMA 143T” might sound technical, but understanding them is simpler than they appear.
In this blog, we will explore the basics of NEMA frame sizes, their significance, how to interpret frame numbers, and key considerations when selecting a frame size for NEMA motors.
What Is a NEMA Frame Size?
A NEMA frame size refers to the standardised sets of dimensions and mounting configurations established by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) for electric motors, primarily in North America. These frame sizes ensure mechanical interchangeability among the motors of the same designation, regardless of the manufacturer.
A NEMA frame size code typically includes numbers (like 56, 143T, or 182T) and sometimes letters, which indicate various attributes such as shaft height, bolt pattern, shaft diameter, and overall dimensions.
Watch the YouTube Video by "Zikodrive" to get a deep insight into NEMA Frame Sizes.
This frame size plays a crucial role in ensuring that motors can be easily replaced or upgraded without modifying the mounting setup. This is important in industrial and commercial applications, where downtime must be minimised.
While the frame size governs the physical and mounting dimensions, it does not directly define the motor's power, speed, or electrical characteristics—these depend on the internal design.
In summary, NEMA frame sizes offer a consistent and industry-wide reference for motor dimensions, promoting compatibility and simplifying design. Engineers and technicians rely on these standards to ensure that the right motors fit correctly into machinery and perform reliably in the application.
How to Read NEMA Frame Numbers?
NEMA Frame Number (like 56C, 145T, etc.) is a standardised code that tells us about the motor’s size, mounting, and shaft dimensions. Here’s how to decode it:
-
First Two (or Three) Digits – Frame Size
-
- The first two or three digits represent the shaft height and foot mounting dimensions.
- To find the shaft centerline height, divide the first two or three digits by 16 to get the approximate motor mounting height in inches.
-
Example,
For NEMA 56,
56 → 56 ÷ 16 = 3.5 inches
-
Last Letter(s) – Mounting and Shaft Features
-
- C: Face-mounting with a standard flange.
- T: Standard motor frame introduced for modern motor designs.
- Y: Special mounting dimensions (custom or unique applications).
- Z: Special shaft dimensions.
- S: Short shaft length.
- U: Older design (used before "T" frame standardisation).
- C: Face-mounting with a standard flange.
-
Letters usually provide mounting or design information critical for compatibility.
-
Additional Notes
-
-
- "S" sometimes indicates a short shaft.
- Frame numbers like 182T or 184T mainly differ by shaft diameter or length.
- Footless motors or round body motors also use specific suffixes.
- "S" sometimes indicates a short shaft.
-
Common NEMA Frame Sizes
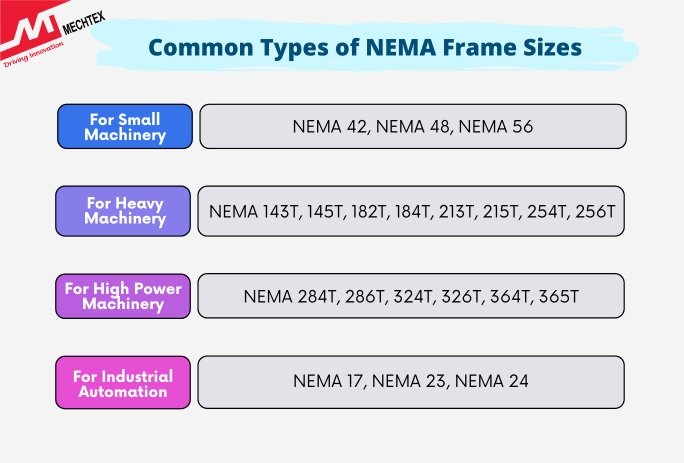
- NEMA 42, 48, 56:
-
- Commonly for small machinery, pumps and fans.
- NEMA 56 is a widely used frame size.
-
NEMA 143T, 145T, 182T, 184T, 213T, 215T, 254T, 256T-
- T-frame indicates motors built after the 1964 standard revision
- Used in conveyor, HVAC, or compressors.
-
- NEMA 284T, 286T, 324T, 326T, 364T, 365T
-
- For high-power applications in heavy industry
- Flange and foot mounting options are available.
-
- NEMA 48Y, 56C, 143TC, etc.
-
- "Y" and "C" indicate special mounting: Y = OEM/custom, C = Face mount
-
- NEMA 17, 23, 24
Selecting the Right NEMA Frame Motor
When choosing a motor based on NEMA frame size, consider the following:
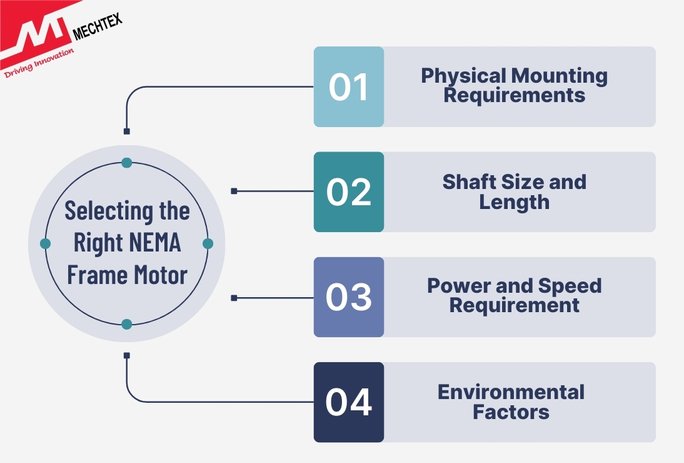
- Physical Mounting Requirements
Determine if your machinery requires face, foot or combination mounting. The correct mounting ensures mechanical stability, alignment and ease of installation without any major modifications.
- Shaft Size and Length
Shaft diameter and length must align with couplings, pulleys or gear trains in your system. Mismatched shafts can lead to misalignment, vibration, or failure.
- Power and Speed
Ensure NEMA motors deliver sufficient power and operate at the required speed for the load. Frame size alone does not guarantee performance. Check motor specs to avoid underpower or oversized selection.
- Environment
For harsh environments like dust, moisture, and others. Select a NEMA motor with a proper enclosure (TEFC, ODP, or Explosion-proof) and protection ratings to ensure safety, longevity, and compliance with environmental demands.
Conclusion
NEMA frame sizes are not just arbitrary numbers — they are a standardised, practical way to ensure motors physically fit into the machinery they drive.
Understanding frame numbers allows beginners and engineers alike to confidently select, replace, and install NEMA motors without worrying about mechanical mismatches.
Whether you are replacing a motor in a conveyor, installing a pump, or specifying a motor for a new design, being fluent in NEMA frame sizes can save you time, reduce downtime, and ensure a perfect fit every time.


















