Open-Loop vs Closed-Loop Stepper Motors: A Comparative Guide
Open loop stepper motor operates by following a series of predefined electrical pulses without any feedback system. While a closed-loop stepper motor incorporates a feedback system (encoder or sensor) to monitor the motor’s actual position. Read ahead to learn about their functionality, advantages, & limitations.

Stepper motors are specialised electric motors that provide precise rotational control through discrete steps. Unlike traditional motors that rotate continuously, stepper motors move incrementally, allowing for precise controlled positioning and repeatability without a feedback system.
Due to this inherent precision, stepper motors are ideal for applications requiring exact positioning, such as 3D printers, CNC machines, and robotic arms. There are two distinct types of stepper motors: open-loop and closed-loop.
In this blog, we will discuss each type of stepper motor, examining its functionality, advantages, limitations, and ideal applications to help one make informed decisions.
Open Loop Stepper Motor
Open loop stepper motor operates by following a series of predefined electrical pulses to control its movement without any feedback system. The term “open-loop” means the motor does not receive any signal about its actual position or speed, instead, it assumes each step, moves the stepper motor in a fixed amount and enables its incremental rotations.
In an open-loop configuration, the stepper motor receives steps and direction signals from a controller or pulse generator. Each pulse corresponds to a movement of step which is determined by the motor’s step angle.
The open-loop stepper motor’s internal magnetic coils are energised in a specific sequence to create a rotating magnetic field that pulls the rotor to fixed increments steps. This stepping sequence allows the open-loop stepper motor to maintain a specific position as long as there is sufficient torque.
Open-loop stepper motors are widely used in applications where precision is critical, yet external feedback is unnecessary, such as in printers, basic robotics, and CNC machinery.
Advantages of Open-Loop Stepper Motor
- Cost Effective
Open-loop stepper motor consists of fewer components which makes them more affordable
- Simple Design
The absence of a feedback system simplifies the design and reduces maintenance requirements for the open-loop stepper motor.
- Suitable for Light Loads
In low-torque and constant load, open-loop stepper motors can deliver high performance without any feedback system.
Close-Loop Stepper Motor
A closed-loop stepper motor is a type of stepper motor that incorporates a feedback system (encoder or sensor) to monitor the motor’s actual position. Unlike open-loop stepper motors, closed-loop stepper motors can correct positioning errors which makes them ideal for applications where precision and reliability are critical such as robotics or CNC machines.
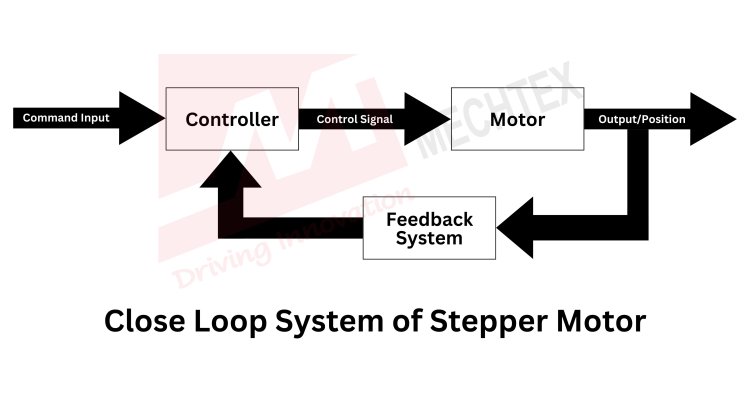
In a closed-loop stepper motor, the controller sends pulses to the motor to create a movement similar to the open-loop stepper motor. However, with each movement, the encoder detects the motor’s position and sends real-time feedback to the controller. This feedback allows the system to check if the stepper motor has reached its position. If any deviation occurs, the controller can adjust the current to correct the position or compensate for any lost steps, ensuring the motor operates as intended.
Advantages of Closed-Loop Stepper Motor
- Enhanced Accuracy
Feedback allows for precise adjustments and reduces the chances of lost steps.
- Improved Efficiency
The closed-loop stepper motor system adjusts current based on load to optimise power consumption and improve efficiency.
- High Torque at High Speed
With a feedback system to monitor the speed, a closed-loop system can maintain torque at high speed better than an open-loop stepper motor.
Open-Loop Stepper Motor vs Closed-Loop Stepper Motor
Due to their precise control and positioning capabilities, stepper motors are widely used in various applications. They are generally classified into two types: open-loop and closed-loop stepper motors. Understanding the differences between these two types is crucial for selecting the right motor for specific applications.
Watch the YouTube Video by "Science Channel" to know how open loop & closed loop stepper motors work.
Feedback Mechanism
- Open-Loop Stepper Motor
These motors operate without any feedback mechanism. They execute commands solely based on input given to them. This system makes its design simple but limits the motor’s ability to detect errors.
- Closed-Loop Stepper Motor
These motors use an encoder-based feedback system. This allows the stepper motor to monitor its speed and position in real time. By continuously monitoring the position, the close-loop stepper motor can make corrections to ensure smooth and efficient operation.
Precision
- Open-Loop Stepper Motor
The precision in an open-loop stepper motor is limited to the accuracy of command signals. Since there is no feedback system, any loss of step can lead to inaccuracies in positioning especially at high speed.
- Closed-Loop Stepper Motor
Closed-loop stepper motors offer high precision due to the availability of the feedback system. The encoder provides immediate feedback and enables the stepper motor to maintain its position even under high speed.
Torque at High Speed
- Open-Loop Stepper Motor
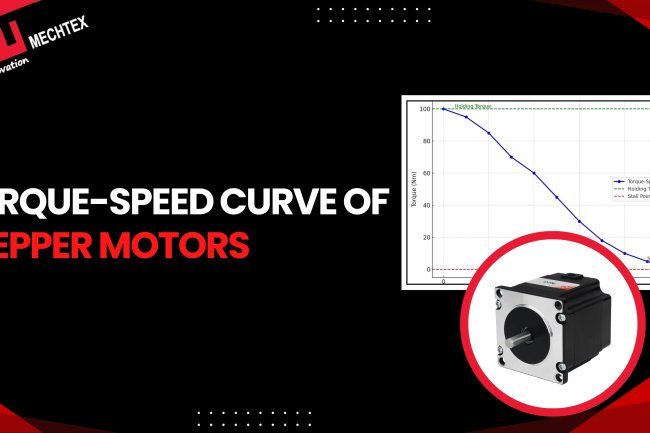
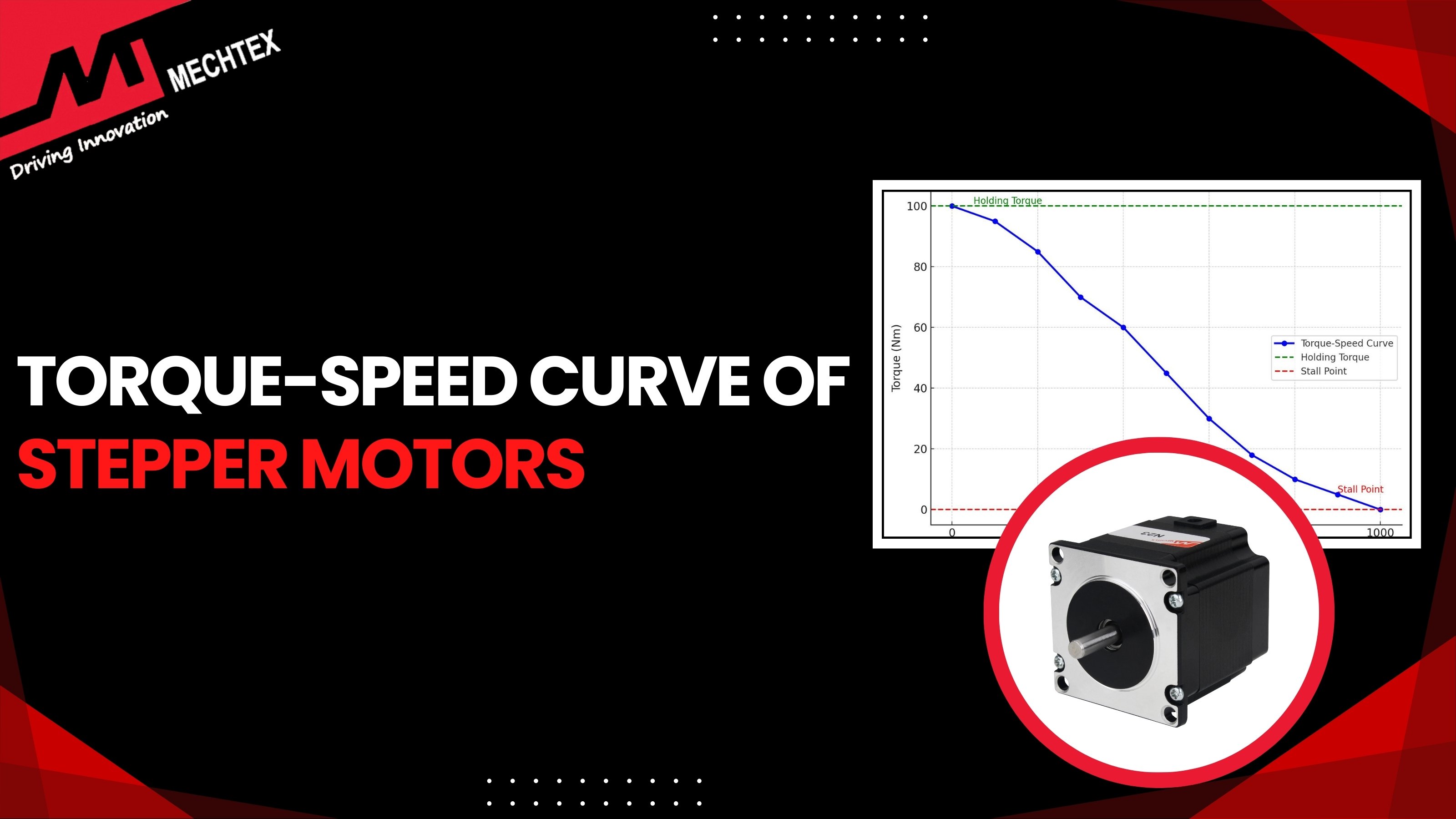
Open-loop motors tend to experience a decline in torque at high speeds. It restricts its use in high-speed applications where consistent torque is required.
- Closed-Loop Stepper Motor
The closed-loop motor can maintain consistent torque at high speeds. The feedback from the encoder allows the close-loop stepper motor to optimise its performance and ensure consistent torque at various speed ranges.
Efficiency
- Open-Loop Stepper Motor
It consumes more power regardless of the load it drives. This leads to unnecessary energy usage, reduces its efficiency and affects the overall performance.
- Closed-Loop Stepper Motor
These stepper motors are more efficient as they can optimise the power consumption based on feedback from the encoder. By adjusting the power usage, the closed-loop stepper motor reduces energy consumption which is particularly beneficial in applications where the load may vary frequently.
Reliability
- Open-Loop Stepper Motor
It offers good reliability in low-speed, constant conditions. However, this stepper motor can struggle in applications with varying loads, where step loss can occur more frequently.
- Closed-Loop Stepper Motor
It offers high reliability, especially in variable load conditions. The feedback mechanism allows these motors to adapt to changes made in operating environments, making them suitable for demanding applications such as robotics and CNC machining.
Conclusion
Both open-loop stepper motors and close-loop stepper motors have unique advantages tailored to specific applications.
Open-loop stepper motors are viable solutions for simple and cost-effective systems where the load needs to be constant and the precision requirement is moderate.
Closed-loop stepper motors with their advanced feedback system offer high-precision, and consistent performance for industrial applications, where accuracy, efficiency, and reliability are paramount.
By carefully evaluating the application’s load variability, budget, precision needs, and environmental conditions, one can make an informed decision to enhance performance and ensure the long-term reliability of its application.