Impacts of Gear Reduction on Speed and Torque of DC Gear Motors
Gear reduction in a DC motor refers to the use of a gearbox to decrease the motor’s output speed while increasing its torque. It is widely used to DC gear motors making them ideal for precise and heavy-load applications.

DC gear motors are widely used in automation, robotics, and industrial machinery due to their simplicity and controllability. But what really makes them a prominent solution and enhances their functionality is gear reduction.
Gear reduction plays a crucial role in shaping the motor’s output speed and torque. Understanding how it works can help engineers, technicians and others to select the most efficient DC gear motor for their applications.
In this blog, we will explore what gear reduction is, how it affects the speed and torque of DC gear motors, and provide practical examples.
Understanding Gear Reduction in DC Motors
Gear reduction in a DC motor refers to the use of a gearbox to decrease the motor’s output speed while increasing its torque. It achieves this by connecting gears of different sizes - typically small gears on the motor's input shaft to drive large gears. It results in lower rotational speed at the output shaft, which significantly increases the torque.
The gear ratio defines the relationship between input speed and output speed. For example, a 10:1 gear ratio means the motor turns 10 times for every 1 rotation of the output shaft. It is useful when the application requires high torque at low speed, such as in robotics, conveyors, or solar tracking systems.
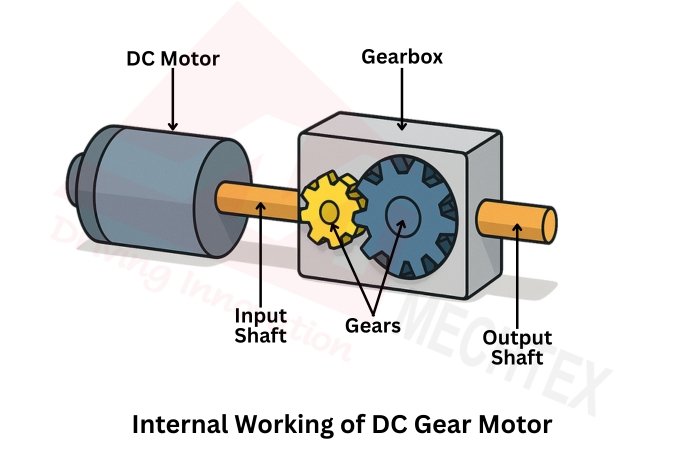
One key advantage of gear reduction is that it improves load handling capacity. A small DC motor, when paired with an appropriate gearbox, can drive heavy loads without stalling. Additionally, gear reduction can enhance positioning accuracy and system stability in applications that require precise motion control.
Effect of Gear Reduction on Speed
One of the primary impacts of gear reduction is speed reduction. It significantly reduces the output speed of the DC motor. When gears are arranged, the small gear drives the large gear, which results in the output shaft rotating more slowly than the motor shaft. This ratio between input and output speed is called the gear ratio.
Speed Reduction Formula:
Output Speed = Motor Speed/Gear Ratio
For example, a 10:1 gear ratio means the motor shaft must complete 10 revolutions for the output shaft to complete 1 revolution. Thus, if the DC motor runs at 1000 RPM with a gear ratio of 10:1, then the output speed will be 100 RPM.
Effect of Gear Reduction on Torque
Gear reduction increases the output torque of a DC gear motor while reducing its speed. This occurs through the gearbox that allows a smaller gear to drive a larger gear, which results in a mechanical advantage that multiplies the torque delivered at the output.
Torque Increase Formula:
Output Torque = Motor Torque x Gear Ratio x Efficiency
For example, a DC motor produces 0.5 Nm torque and is paired with a 10:1 gearbox with 90% efficiency.
Output Torque = 0.5 x 10 x 0.9 = 4.5 Nm
This increase in torque allows the gear motor to handle heavier loads, climb inclines, or move precision systems with high resistance.
It is vital for applications requiring high force to move or lift loads, such as robotic arms, electric actuators, and mobility systems.
Real-World Applications
Gear reduction in DC gear motors is widely used to enhance torque and reduce speed, making them ideal for precise and heavy-load applications. Here are some real-world applications:
- Robotics
DC gear motors play a crucial role in enabling controlled movement and delivering high torque to various robotics applications such as robotic joints, grippers, and wheels.
The gear reduction allows for slower, more precise movement, which is essential for applications requiring accurate positioning and the ability to handle varying loads.
- Automated Gates and Barriers
DC gear motors are commonly used in automated gates and barrier systems where controlled, powerful motion is required. The gear reduction helps generate sufficient torque to move heavy gate panels while maintaining a safe and manageable speed.
- Conveyor Systems
In conveyor systems, DC gear motors are essential for transporting products at a consistent and controlled speed. The reduction mechanism allows the motor to produce the torque required to move loads along production lines while preventing overheating or slippage.
In medical equipment such as surgical robots and infusion pumps, DC gear motors deliver the fine control necessary for sensitive operations. Gear reduction enables slow, deliberate movements and provides the torque required for pushing fluids or manoeuvring delicate instruments.
Key Factors Influencing Gear Reduction Choice
When selecting the right gear ratio, several factors must be considered:
- Required Torque Output
The primary reason for using a gear reduction is to increase torque. The gear ratio should be selected based on the torque needed to move or lift the intended load without straining the motor.
- Desired Output Speed
Gear reduction reduces motor speed. The required rotational speed at the output shaft determines the optimal gear ratio. Applications needing slow, controlled motion (like robotics or conveyor systems) often require higher reduction ratios.
- Load Characteristics
The type of loads, such as constant, variable or intermittent, affects the gear selection. Heavier or irregular loads need higher torque and stronger gearsets.
- Duty Cycle and Operational Time
Motors that run continuously or under frequent start-stop cycles need gearboxes that can handle heat and wear. Gear selection must consider thermal load and mechanical durability.
Conclusion
Gear reduction plays a transformative role in how DC gear motors perform. By converting high-speed, low-torque input into low-speed, high-torque output, gearboxes expand the usability of DC motors across countless industries. However, the key lies in selecting the right gear ratio to suit your application’s torque and speed demands—balancing efficiency, load requirements, and motor limitations.
Whether you're designing automation systems, robotics, or energy equipment, understanding the impact of gear reduction helps optimise performance, increase durability, and ensure cost-effective motor operation.


















