Material Selection for BLDC Motor Components: An Engineering Perspective
The construction of a BLDC motor consists of stator, rotor, bearings, housing, and other auxiliary components. Each component requires careful material selection to ensure maximum efficiency, minimal energy loss, and long service life.

BLDC motors are widely used in industrial automation, electric vehicles, robotics and aerospace applications due to their high efficiency, reliability and long lifespan. The performance and durability of the BLDC motor heavily depend on the selection of materials used to make its key components.
This blog explores the critical material choices for BLDC motor components, their impact on performance, and engineering considerations for optimal selection.
Key Components of a BLDC Motor and Their Material Selection
The construction of a BLDC motor consists of stator, rotor, bearings, housing, and other auxiliary components. Each component requires careful material selection to ensure maximum efficiency, minimal energy loss, and long service life.
Here are the key components of the BLDC motor and the type of material used in them:
- Stator
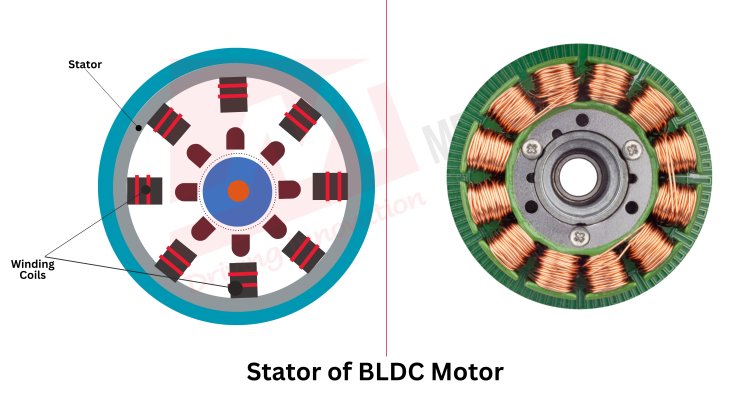
The stator houses the windings and provides the necessary electromagnetic field for operation. Primary materials include:
-
-
- Laminated Silicon Steel
-
The stator core is typically made from laminated silicon steel to reduce the eddy current losses. The silicon steel enhances electrical resistivity and minimises core losses.
-
-
- Copper Windings
-
Copper is preferred due to its high electrical conductivity, which ensures efficient power transmission and minimal resistive losses. In high-performance applications, oxygen-free copper (OFC) enhances conductivity and thermal stability.
-
-
- Insulation Materials
-
The winding insulation is usually made from polymer-based materials such as polyimide or epoxy coatings to provide electrical isolation and heat resistance.
- Rotor
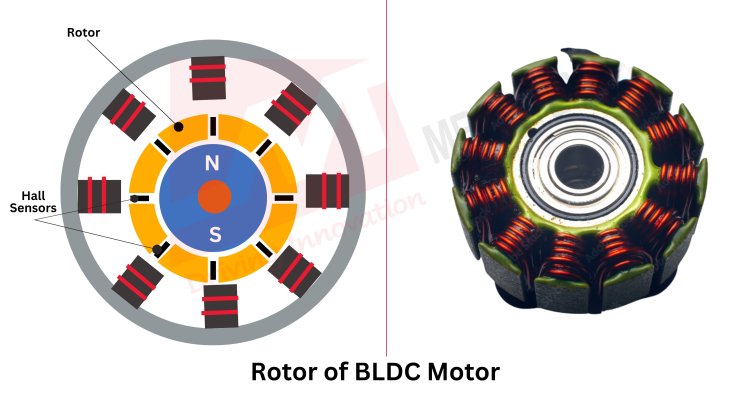
It is the rotating component that carries the motor’s magnetic field for smooth rotation. It interacts with the stator’s magnetic field to generate motion. Its design ensures efficient torque production, smooth operation, and precise speed control. Its materials include:
-
-
- Permanent Magnets
-
The choice of magnet material significantly impacts BLDC motor performance. Common materials used in permanent magnets of BLDC motor are:
-
-
-
-
- Neodymium-Iron-Boron (NdFeB): Offers the highest energy density, making it ideal for high torque BLDC motors.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Samarium-Cobalt (SmCo): Provides excellent thermal stability and corrosion resistance suitable for extreme environments.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Ferrite Magnets: Used in cost-sensitive BLDC motors where high power density is not required.
-
-
-
-
-
- Rotor Core
-
Typically made from laminated silicon steel to minimise eddy current losses and improve efficiency.
-
-
- Shaft Material
-
High-strength steels such as stainless steel or alloy steel provide mechanical integrity and resistance to wear.
- Bearings and Their Material Considerations
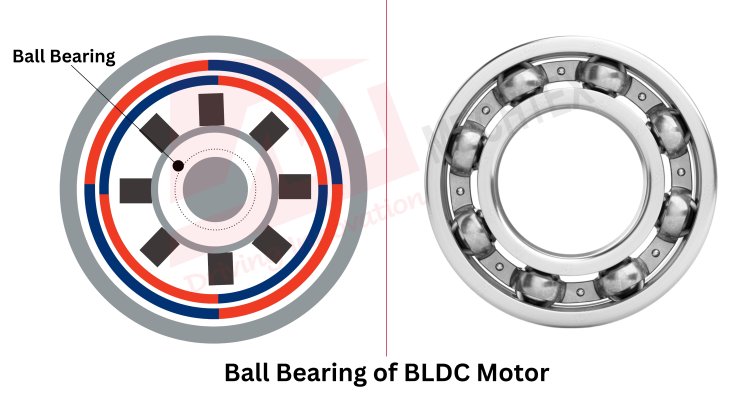
Bearings play a crucial role in reducing friction and ensuring the smooth operation of BLDC Motor. Materials include:
-
-
-
- Ball Bearings
-
-
Made from stainless steel or ceramic. Ceramic bearings are preferred in high-speed applications due to their low weight and high resistance.
-
-
-
- Lubrication
-
-
Grease or oil-based lubricants are used to reduce friction and enhance the life span of the BLDC motor. High-temperature grease is recommended for high-speed BLDC motors.
- Housing and Enclosure Materials
BLDC motor housing protects the internal components from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and heat. Materials used are:
-
-
- Aluminium Alloys
-
These alloys are lightweight, corrosion resistant and provide excellent thermal conductivity for heat dissipation.
-
-
- Stainless Steel
-
Used in harsh environments requiring high corrosion resistance.
-
-
- Polymer Composites
-
In lightweight applications, high-performance polymers such as PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) are used to reduce weight while maintaining durability.
- PCB and Electronics
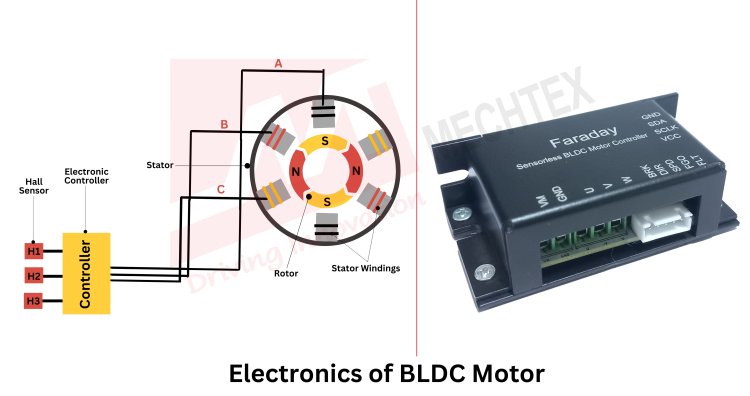
PCB and electronics control the operation of the BLDC motor by managing power distribution, commutation, and speed regulation. They enable precise control, high efficiency, and smooth operation in various applications. Its essential materials are:
-
-
-
- Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
-
-
Made from FR4 (glass-reinforced epoxy laminate) or high-temperature polyimide for thermal stability of BLDC motor.
-
-
-
- Hall Effect Sensors
-
-
Semiconductor materials such as silicon are used to provide accurate feedback about the rotor position.
Also Read
Engineering Considerations for Material Selection
Material selection for key components of the BLDC motor is driven by various engineering factors. Some of the key factors are:
- Thermal Management
Heat dissipation is crucial for BLDC motor longevity and efficiency. Materials with high thermal conductivity such as aluminium and copper, help in effective heat dissipation. Insulation material must withstand high temperatures without degradation.
-
Magnetic Properties
The choice of magnetic materials affects the BLDC motor’s torque and efficiency. High energy density materials such as NdFeB improve torque output, while laminated steel cores reduce hysteresis and eddy current losses.
-
Corrosion Resistance
In environments exposed to moisture or chemicals, corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel, anodised aluminium, and coated magnets to extend BLDC motor life.
-
Weight Reduction
Reducing weight is crucial in applications such as drones and electric vehicles (EVs). Lightweight materials like aluminium and polymer composites help achieve a high power-to-weight ratio.
-
Mechanical Strength
The BLDC motor components must withstand mechanical stress, vibrations, and other impacts. High-strength alloys and reinforced composites ensure structural integrity under dynamic loads.
Conclusion
The selection of materials for BLDC motor components plays a vital role in determining efficiency, durability, and performance. By considering factors such as electrical conductivity, magnetic properties, thermal stability and mechanical strengths, one can optimise the BLDC motor’s design for specific applications.
Advanced materials like NdFeB magnets, laminated silicon steel, high-strength alloys, and polymer composites contribute to the continuous improvement of BLDC motors in industrial and consumer applications.