Construction of BLDC Motor
The construction of a BLDC motor contains several key components such as the stator, rotor, electronic controller and many others which ensure the efficient performance of BLDC motors.
What is a BLDC Motor?
A BLDC motor is a synchronous electric motor powered by direct current. These brushless DC motors are known for their efficiency and performance. Unlike traditional brushed DC motors, which use mechanical commutation to switch the direction of current in the motor winding, BLDC motors use electronic commutation to switch the current direction. This means instead of relying on brushes and commutators, BLDC motors use electronic controllers to control the flow of current.
These controllers precisely manage the timing of electrical current into the motor winding to ensure optimal performance and low wear and tear. This modern approach to commutation not only enhances the BLDC motor’s efficiency but also contributes to the quiet operation.
The construction of the BLDC motor includes stator and rotor. The stator is the stationary part of the motor and contains winding. The rotor is a rotating part of the motor and contains permanent magnets. The interaction between the magnetic field of the stator and the rotor produces torque and causes the rotor to spin.
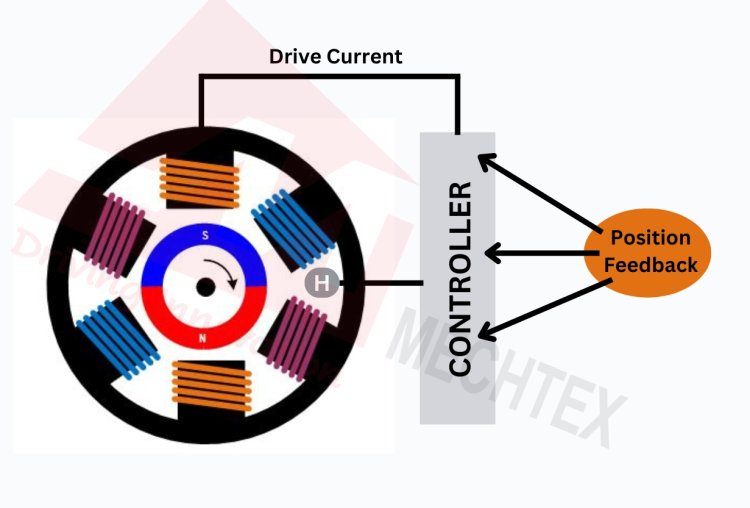
The working of the BLDC motor relies on the principle of electromagnetism. The electronic controller generates a rotating magnetic field by sequentially energising the stator’s winding in a specific pattern. This rotating magnetic field interacts with the permanent magnets of the rotor and causes the rotor to rotate. The controller adjusts the flow of current into the stator’s winding based on the rotor’s position which causes smooth and precise rotation of the rotor.
Brushless DC motors also known as BLDC motors offer several advantages. These brushless motors are more efficient than brushed motors due to the absence of brushes in their structure which optimised the flow of current in windings and ensures efficient performance. These motors are also more durable as there is less wear and tear as compared to brushed motors. Additionally, these motors provide better speed, torque and power density which results in efficient operation.
Due to these benefits, BLDC motors are used in a wide range of applications such as electric vehicles, drones, industrial automation machinery and medical devices. BLDC motors are the best alternative to traditional brushed DC motors by offering efficiency, durability, and performance across a wide range of applications.
Construction of BLDC Motor
The construction of a BLDC motor contains several key components such as the stator, rotor, electronic controller and many others which ensure the efficient performance of BLDC motors.
Some of the main components of BLDC motors are:
- Stator
Stator is the stationary part of the BLDC motor. It is made up of laminated steel sheets to reduce the energy loss due to circulating currents. It consists of windings which are important to generate the magnetic field to drive the rotation of the rotor. The windings are generally made up of copper wire and arranged in either Star (Y) configuration or Delta (Δ) configuration.
The stator also has slots and teeth that hold the windings. The precise design of slots and teeth helps in optimising the magnetic flux and reduces the cogging torque to ensure efficient operation.
- Rotor
Rotor is the rotating part of the BLDC motor. It contains permanent magnets which are usually made up of rare-earth materials like neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) or samarium-cobalt (SmCo) to provide a strong magnetic field. These permanent magnets are arranged in various configurations such as surface-mounted or interior-mounted, depending on the BLDC motor’s design.
The core of the rotor is also made up of laminated steel sheets to minimise the current loss. The laminations are insulated from each other to prevent the short-circuiting of current and make BLDC motors energy efficient.
- Electronic Controller
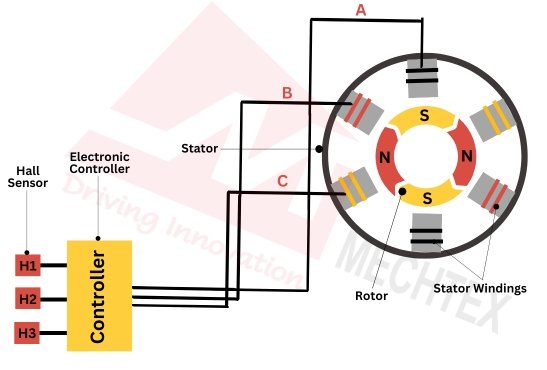
The Electronic controller is the crucial component of the BLDC motor. It distinguishes BLDC motors from traditional brushed DC motors. The controller performs the role of commutation by switching the direction of current in the stator’s winding based on the rotor’s position.
The electronic controller consists of several components such as hall sensor, microcontroller, and inverter circuit.
Hall sensor or encoder detects the position of the rotor and provides feedback to the controller to ensure a timely supply of current into the stator’s winding.
The microcontroller collects the feedback from the hall sensors and controls the switching of transistors in inverter circuits. This switching ensures that the magnetic fields in the stator are correctly aligned with the rotor magnets, resulting in smooth and efficient rotation.
Based on the switching frequency and pattern controlled by the microcontroller inverter circuit converts the DC power supply into a three-phase AC output.
Other Components
- Bearings
High-quality bearings are used to support the rotor and ensure its smooth rotation with minimal friction. This ensures the durability and efficient performance of the BLDC motor.
- Housing
Housing provides structural support and protection to the integral components of BLDC motors. It is made up of materials like aluminium or steel to ensure durability and heat dissipation.
Working Principle of BLDC Motor
BLDC motors operate on the principle of electromagnetism. It involves interaction between the rotating magnetic field of the stator and the permanent magnets of the rotor with the help of an electronic controller.
The electronic controller energises the stator’s electromagnets (windings) in a specific sequence and creates a rotating magnetic field. This field interacts with the permanent magnet of the rotor and causes the rotor to rotate with the stator’s magnetic field.
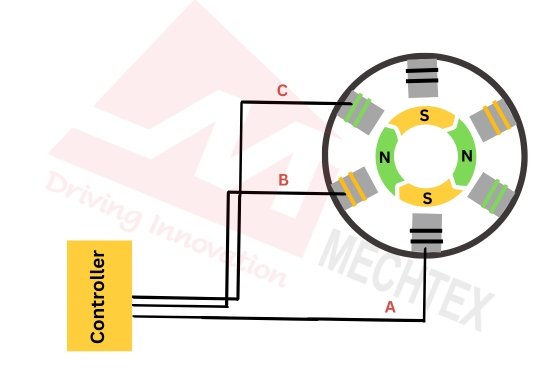
To maintain the rotation of the rotor, the controller must know the position of it. This is achieved by using the hall sensors. Hall sensors detect the position of the rotor and send it to the controller. Based on the hall sensor's data, the controller energises the next set of stator coils with a timely flow of current. This process repeats rapidly and ensures smooth and continuous rotation of the rotor.
This electronic commutation system allows Brushless DC motors to operate efficiently and precisely, by converting electrical energy into mechanical motion without physical contact between stator and rotor.
Also Read
Working Principle of BLDC Motor
Applications of BLDC Motor
BLDC motors are used in a wide range of applications due to their efficiency, reliability, and controllability. Some of the applications are:
- Electric Vehicles
BLDC motors power the propulsion system of electric vehicles (EVs) by providing efficient and reliable torque delivery for driving the vehicles.
- Industrial Automation
BLDC motors are used in robotics, CNC machines, conveyor systems and other automated machinery where precise speed and torque control are essential.
- HVAC System
HVAC systems use BLDC motors in fans and ventilation pumps to maintain temperature.
- Medical Devices
BLDC motors power medical pumps, respirators and surgical tools where reliability and precise movement are crucial.
- Renewable Energy
BLDC motors are used in solar tracking systems to adjust the panel orientation for capturing the maximum energy.