Bipolar Stepper Motor vs Unipolar Stepper Motors
Bipolar stepper motors offer superior torque and compactness while unipolar stepper motors provide simplicity and cost-effectiveness. By carefully evaluating torque requirements, budget, and system complexity, one can select the right type of stepper motor that aligns with goals.

Stepper motors are vital components in various applications from CNC machines to 3D printers where precise control is crucial. Among the types of stepper motors, bipolar stepper motors and unipolar stepper motors are most commonly used. Choosing the right type depends upon specific application requirements including torque, complexity, and cost.
In this blog, we will provide an in-depth comparison of bipolar and unipolar stepper motors and help you to make an informed decision.
What is a Stepper Motor?
Stepper motor is an electromechanical device that converts electrical pulses into precise mechanical movements. These motors are known for their ability to provide positioning and control without a feedback system. This makes them ideal for applications requiring precision and reliability.
Working of the stepper motor involves energising the windings of the stator to generate a magnetic field and interact with the rotor. This interaction causes the rotor to move in a fixed angular step.
Watch the YouTube video by "Sabins Civil Engineering" to learn about the working of stepper motors.
The size of these steps is determined by the stepper motor’s design. The common step angles are 0.9° to 1.8° per step. By controlling the sequence and timing of the electrical pulses, the stepper motor can achieve highly controlled motion.
Stepper motors are valued for their open-loop control system which eliminates the need for the feedback mechanism. They also deliver high precision, and high torque at low speed making them suitable for applications such as 3D printers, and CNC machines, where accurate positioning is crucial.
Also Read
Bipolar Stepper Motors
A bipolar stepper motor is a type of stepper motor designed with two windings which allow the current to flow in both directions through each winding. This helps the bipolar stepper motor to generate high torque and precise motion which makes it suitable for applications requiring accuracy and reliability.
The bipolar stepper motor windings are straightforward as they lack the centre tap which is found in unipolar stepper motors. This design requires full current reversal in each phase of winding to produce precise motion. To achieve this, bipolar stepper motors use H-bridge circuits, which manage the direction of current flow and allow for efficient polarity switching.
Bipolar stepper motors are known for their superior performance compared to unipolar stepper motors. By utilising the entire winding during the operation, these stepper motors deliver high torque. They are commonly available in two-phase or four-phase configurations, depending on application requirements.
These stepper motors are widely used in applications such as robotics, CNC machines, and industrial automation, where precision and compact design are crucial.
Unipolar Stepper Motors
A unipolar stepper motor is a type of stepper motor with windings which include a centre tap that allows the current to flow in one direction through each half of the windings. This design simplifies the driving circuitry and makes these stepper motors ideal for various industrial applications.
The winding configuration of the unipolar stepper motor consists of two coils per phase, each with a centre tap. The centre tap connects to the common voltage and enables the energising of each half of the windings. This arrangement eliminates the need for current reversal and reduces the complexity of the driving circuit.
Unipolar stepper motors are commonly found in applications requiring moderate torque and simpler control systems such as printers, small automation systems, and basic robotics applications.
Bipolar Stepper Motors vs Unipolar Stepper Motors
Bipolar and unipolar stepper motors differ in their winding configuration, power requirements, and control mechanisms, leading to distinct performance characteristics. Here are some key differences between these stepper motors as follows:
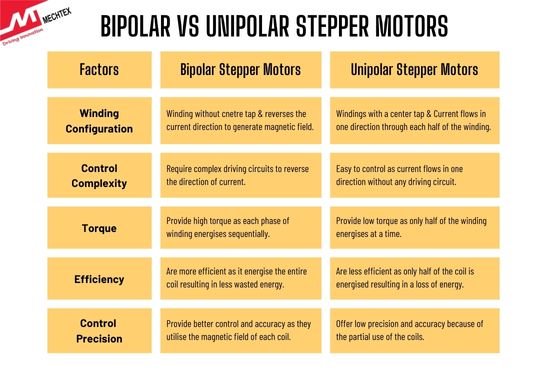
- Winding Configuration
Bipolar Stepper Motors: Each phase has two windings, without a center tap. Each phase reverses the current direction in each coil to generate the magnetic field. This results in higher torque output.
Unipolar Stepper Motors: Each phase has two windings, with a center tap. Current flows in one direction through each half of the winding. This results in lower torque output.
- Control Complexity
Bipolar Stepper Motors: Require complex driving circuits as current needs to be reversed to energise the coils.
Unipolar Stepper Motors: Easy to control as current flows in one direction which reduces the complexity of driving circuits.
- Torque
Bipolar Stepper Motors: Provide high torque as each phase of winding energises sequentially to produce motion.
Unipolar Stepper Motors: Provide low torque as only half of the winding energises at a time to produce motion.
- Efficiency
Bipolar Stepper Motors: Bipolar stepper motors are generally more efficient than unipolar motors since they use the entire coil for each step, resulting in less wasted energy.
Unipolar Stepper Motors: Unipolar stepper motors are less efficient as only half of the coil is energised for each step resulting in a loss of energy and affecting the performance.
- Control Precision
Bipolar Stepper Motors: Bipolar stepper motors provide better control and accuracy as they allow for fine adjustment in movements by utilising the magnetic field of each coil. This can be particularly useful in applications requiring high precision.
Unipolar Stepper Motors: Unipolar stepper motors offer low precision and accuracy because of the partial use of the coils. However, these stepper motors are still suitable for many applications where high precision is not a critical requirement.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Bipolar or Unipolar Stepper Motor
When selecting between bipolar and unipolar stepper motors, some factors need to be considered as per the needs of your application. Here’s a detailed explanation of each factor to consider when choosing between bipolar and unipolar stepper motors:
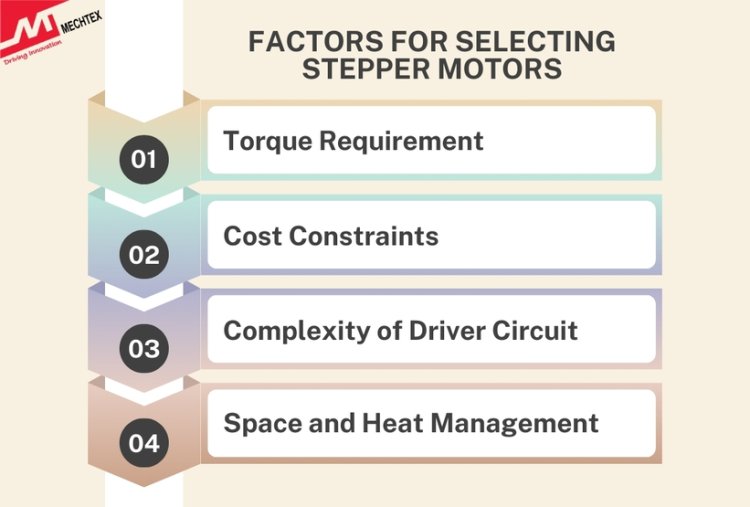
- Torque Requirement
Bipolar Stepper Motors: Provides high torque compared to unipolar stepper motors as these motors utilise all windings in both directions by allowing current to flow throughout the motor winding.
Unipolar Stepper Motors: Provides less torque as the current flows through half of the winding coils at a time which makes them suitable for low torque applications such as small-scale printers, scanners, or light-duty conveyors.
- Cost Constraints
Bipolar Stepper Motors: Provides high performance and tends to be more expensive as they require complex driver circuitry to alternate the current between the two motor windings.
Unipolar Stepper Motors: They tend to be more cost-effective than bipolar stepper motors due to their simpler driver requirements which reduces manufacturing costs. This makes them a more budget-friendly option for applications where the performance demands are less stringent.
- Complexity of Driver Circuit
Bipolar Stepper Motors: Have a more complex driver to handle the reversed current through the windings which makes its circuitry design more complex.
Unipolar Stepper Motors: These are easier to drive as they require simple control electronics making them a better choice for applications where ease of implementation and low cost are key priorities.
- Space and Heat Management
Bipolar Stepper Motors: They have a compact design and require additional cooling systems due to their higher power requirements and the generation of more heat during operation.
Unipolar Stepper Motors: Generate less heat and require less cooling, which makes them ideal for small-scale systems or environments where heat dissipation is a concern.
Conclusion
The choice between bipolar and unipolar stepper motors depends on the application's specific needs. Bipolar motors offer superior torque and compactness at the expense of driver complexity, making them ideal for high-performance applications. Conversely, unipolar motors provide simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making them perfect for basic tasks and budget-friendly projects.
By carefully evaluating torque requirements, budget, and system complexity, one can select the motor type that aligns with goals. Whether it's a precision-driven CNC machine or a simple automation project, understanding these differences ensures optimal performance and reliability.