Types of BLDC Motors: Inrunner, Outrunner, Sensorless & More
Discover the main types of BLDC motors, including inrunner, outrunner, axial flux, sensored and sensorless designs and learn how design and control methods affect performance.

What is a BLDC Motor?
A brushless DC (BLDC) motor is an electric motor that uses the electronic commutation method instead of brushes to switch the direction of current. Unlike traditional DC motors, which rely on brushes and commutators to switch the direction of the current, BLDC motors use an electronic controller to switch the direction of the current. This brushless design eliminates friction and wear and tear and makes the BLDC motor efficient and reliable for various industrial applications.
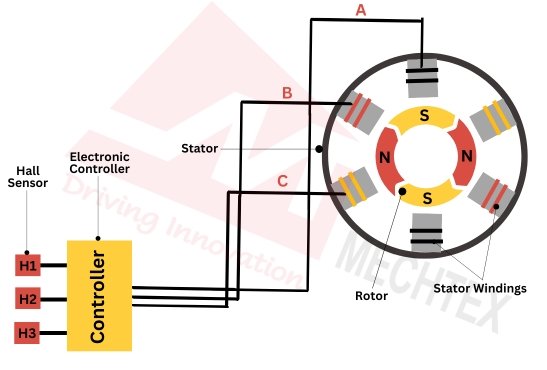
Construction of the BLDC motor consists of two main components: stator and rotor. The stator is a stationary part of the BLDC motor. It consists of windings that create a rotating magnetic field. The rotor is the rotating part of the BLDC motor. It consists of a permanent magnet and its movement is controlled by the electronic controller.
Watch the YouTube Video by "Lesics" to know more about the BLDC motors.
A BLDC motor operates on the principle of Lorentz force where the controller sends the current to stator windings and generates a magnetic field. The rotor consists of permanent magnets that interact with the magnetic field and start to move. The sensor detects rotor movement and sends a signal to the controller to switch the direction of current in stator windings to maintain continuous rotation.
BLDC motors are used across a wide range of applications due to their high efficiency and reliability. They are commonly used in electric vehicles, HVAC systems, actuators, industrial automation and other industrial applications.
Also Read
Construction of BLDC Motor
The construction of the BLDC motor consists of several components that work together to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy and offer high efficiency and reliability in operation. Some of the key components of BLDC motors are:
- Stator
It is made up of a laminated steel sheet consisting of winding coils. These windings are arranged in star (Y) or delta (Δ) configuration.
- Rotor
It consists of permanent magnets that interact with the stator magnetic field and start rotating.
- Electronic Controller
An electronic controller replaces the function of brushes. It uses feedback mechanisms such as hall sensors, or back EMF to detect the rotor’s position and switch the direction of current in stator windings.
Types of BLDC Motors
BLDC motor is an electric motor that operates without brushes and commutation and provides high efficiency and reliability in operation. BLDC motors come in various types based on their design, application, and commutation method. Here are the main types of BLDC motors:
Inrunner BLDC Motor
Inrunner BLDC motor is also known as an inrunner BLDC motor. In inrunner BLDC motors, the rotor comprises a permanent magnet and is situated inside the stator. The stator is enclosed with windings and is responsible for generating the magnetic field necessary for operation.
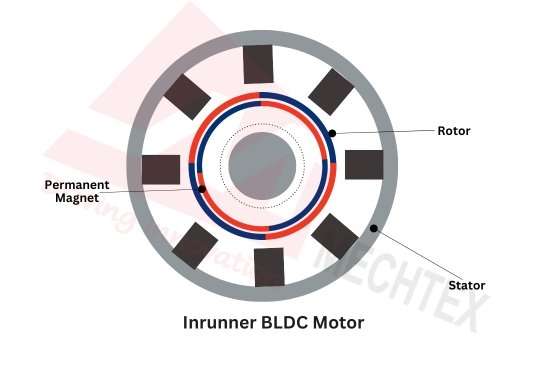
Inrunner BLDC motors provide high torque due to the increased rotor inertia which results in a powerful performance. Additionally, heat dissipation is achieved because the stator that produces the heat during the operation is positioned outside. This design enhances the efficiency and performance of the inrunner BLDC motor.
Inrunner BLDC motors are used in industrial machinery, electric vehicles, and other high-speed applications where powerful and reliable performance is required.
Outrunner BLDC Motor
In the outrunner BLDC motor, the rotor is positioned outside the stator. The permanent magnets of the rotor are attached to the inner surface surface of the rotor, which allows the rotor to rotate around the stator.
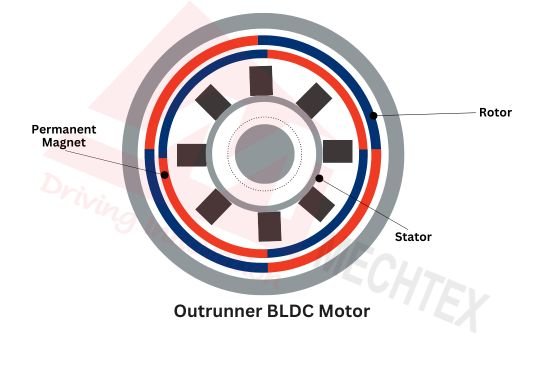
This design results in lower rotational inertia leading to more smooth and efficient movement. Additionally, outrunner BLDC motors are more compact in structure which results in a high torque to volume ratio. Due to the above characteristics, outrunner BLDC motors are used in applications such as fans, drones, and electric scooters, where compactness and smooth operation are crucial.
Axial Flux BLDC Motor
In axial flux BLDC motors, the magnetic flux flows parallel to the axis of the rotation, unlike traditional radial flux motors where magnetic flux is perpendicular to axis rotation. The rotor and stator of axial flux BLDC motors are arranged face-to-face resulting in a flat pancake-like design.
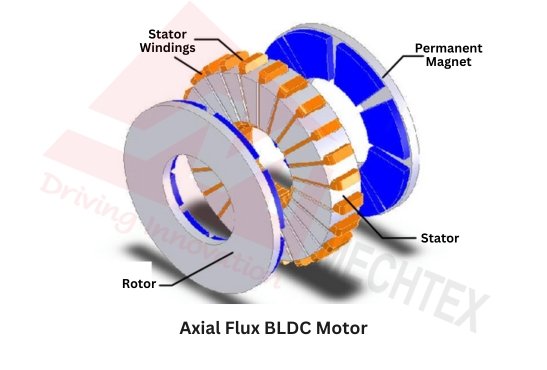
This design allows axial flux BLDC motors to achieve high power density while maintaining the compact design. Additionally, this design also helps to reduce magnetic leakage which improves the overall efficiency of the motor. Due to these advantages, axial flux BLDC motors are widely used in electric vehicles, aerospace applications, and compact industrial equipment where space and efficiency are critical factors.
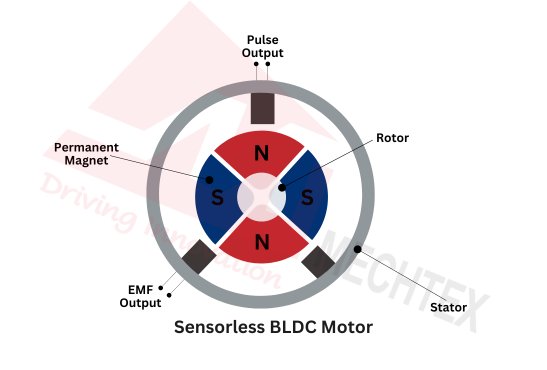
Sensorless BLDC Motor
Sensorless BLDC motors are motors that operate without the physical position sensors such as hall sensors. They utilise back EMF feedback to detect the rotor position and eliminate the need for additional sensors.
This design makes sensorless BLDC motors more affordable with low maintenance requirements. However, this motor may struggle with performance at low speed and high precision applications. Due to the simple construction and cost-effectiveness, sensorless BLDC motors are used in fans, pumps, and basic drives where cost-effectiveness is required.
Also Read
Sensorless Control Techniques for BLDC Motors
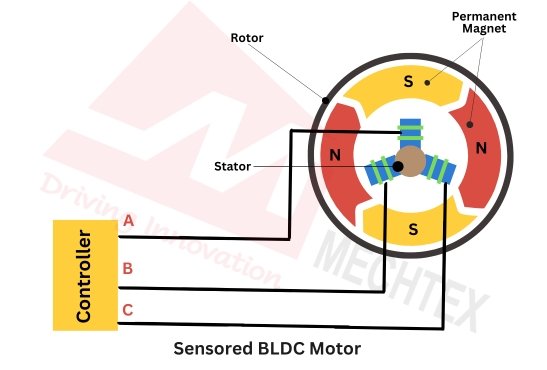
Sensored BLDC motors
Sensored BLDC motors consist of hall sensors that detect the rotor position and provide feedback to the controller. This sensor feedback allows for precise control of the motor’s operation, particularly at low speeds where precision is essential.
Sensored BLDC motors are used in applications that require accurate position control such as robotics, electric vehicles, and industrial automation, where precision and performance are key requirements.
Conclusion
When selecting the right BLDC motor, it's essential to consider factors like power requirements, efficiency, control precision, and environmental conditions. Each type of BLDC motor offers unique benefits tailored to different applications, but the right choice depends on understanding these needs. Consider factors like the required torque, speed, and form factor, along with cost constraints and maintenance considerations will guide you in selecting the most suitable BLDC motor, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency of your application.