Differences Between Brushed DC Motor & Brushless DC Motor
Brushed DC and Brushless DC Motor are two types of DC motors. They differ in their construction, working principle and applications, where they are used. Here are the top 5 differences between a brushed DC motor and a brushless DC motor.

What is a Brushed DC Motor
A brushed DC motor is a type of electric motor powered by direct current and operates with the help of brushes. This motor is known for its simple design, ease of control and reliability in operation.
A brushed DC motor consists of several components such as stator, rotor, commutators and brushes. Stator is the stationary part of the motor and consists of a permanent magnet or electromagnet to create the magnetic field. The rotor is the rotating part of the motor and consists of coils of wire wound around its iron core. The commutator is a cylindrical structure attached to the rotor. It is typically made up of conductive material such as copper. The brushes are the stationary carbon or metal contacts that press against the commutator.
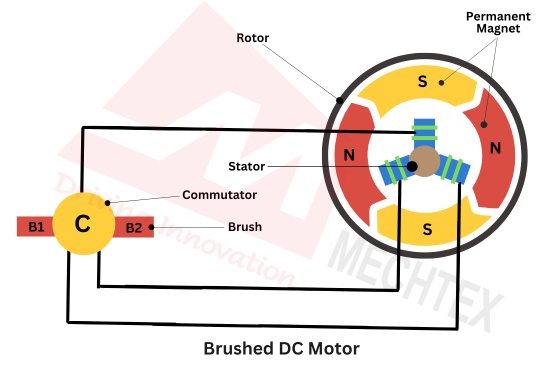
When direct current is applied to the brushed DC motor, the current flows through the brushes and commutator in the rotor winding. This current generates the magnetic field around the rotor. This magnetic field interacts with the magnetic field of the stator and produces a torque that causes the rotor to rotate.
As the rotor rotates, the commutator makes segments and breaks contact with the brushes. The brushes reverse the direction of current through rotors winding at appropriate times. This process is known as commutation. It ensures that the torque generated by the motor continues in the same direction and allows for continuous rotation.
Brushed DC motors are known for their simple design and cost-effectiveness. These motors provide good torque at low speeds making them suitable for applications such as automotive starters, household appliances, and small tools. Additionally, these motors are highly efficient and easy to control.
Brushed DC motors have some disadvantages. The mechanical contact between brushes and commutators leads to wear and tear and requires frequent maintenance. The friction between components also generates heat and noise, which reduces the overall efficiency and lifespan of the brushed DC motor.
What is a Brushless DC (BLDC) Motor
A brushless DC motor is a type of electric motor powered by direct current and operates with the help of commutation. Unlike brushed DC motors, which rely on mechanical brushes to switch the direction of current in motor winding, BLDC motors use an electronic controller to switch the direction of current, resulting in high efficiency and low maintenance cost.
A BLDC motor consists of three main components: stator, rotor and electronic commutation system. The stator is the stationary part of the motor and consists of multiple windings. The rotor is the rotating part of the motor and is made up of permanent magnets. The key component of a brushless DC motor is the electronic commutation system. This system is a combination of hall sensors and electronic controllers to manage the flow of the current into windings.
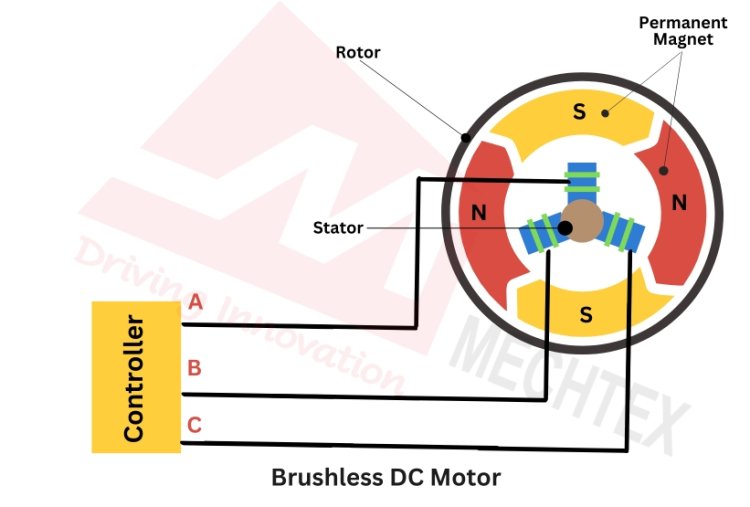
Brushless DC motor also known as a BLDC motor operates on the principle of electromagnetism. The hall sensors detect the position of the rotor and send signals to the electronic controller. The electronic controller receives the signal and determines the position of the rotor. Based on the rotor’s position, the electronic controller energises the winding of the stator and creates a rotating magnetic field.
This rotating magnetic field interacts with the magnetic field of the rotor and causes the rotor to rotate. By continuously energising the windings of the stator, the controller maintains a rotating magnetic field and keeps the rotor rotated in continuous motion. It ensures the smooth and efficient operation of the BLDC motor.
BLDC motors offer several advantages over brushed DC motors. BLDC motors are more efficient due to the elimination of friction from brushes. These motors have a longer lifespan since there are no brushes to wear out. These motors offer precise control over speed and position and produce less noise during operation. This makes them ideal for applications like electric vehicles, drones, and HVAC systems.
Also Read
Advantages and Disadvantages of BLDC Motors
Top Differences between Brushed DC Motor and Brushless DC Motor
Brushed DC and Brushless DC Motor are both different types of DC motors. They differ in their construction, working principle and applications where they are used.
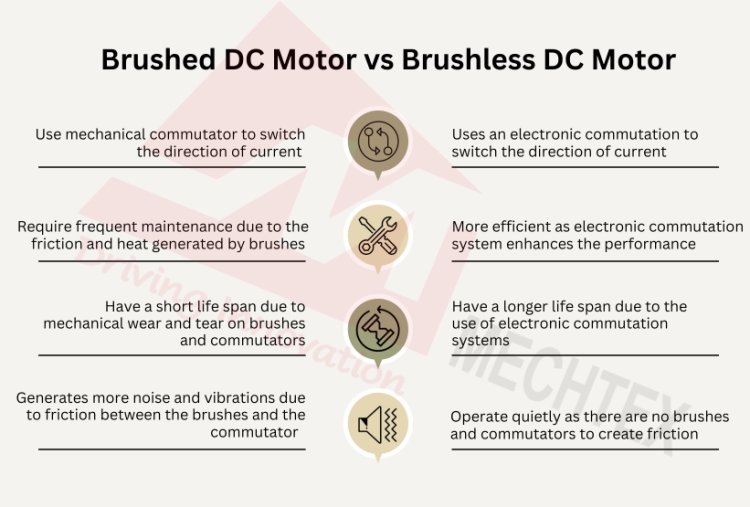
Here are the top differences between brushed DC motor and brushless DC motor:
Commutation Method
- Brushed DC Motor: It uses a mechanical commutator and brushes to switch the direction of current in windings. The physical contact between the commutator and brushes causes wear and tear and increases maintenance costs.
- Brushless DC Motor: It uses an electronic commutation system consisting of hall sensors and an electronic controller to switch the direction of the current in windings. It eliminates the use of commutators and brushes and increases the efficiency of the motor.
Maintenance
- Brushed DC Motor: These motors are less efficient as compared to brushless DC motors due to energy loss from the friction and heat generated by brushes. It affects the overall performance of the brushed DC motor.
- Brushless DC Motor: Brushless DC motors are more efficient than brushed DC motors as they use an electronic commutation system rather than brushes and commutators. The electronic commutation system enhances the performance and efficiency of BLDC motors, especially at high speeds.
Life Span
- Brushed DC Motor: Brushed DC motors have a short life span due to mechanical wear and tear on brushes and commutators. It creates frequent maintenance and replacements and increases the overall cost of the motor.
- Brushless DC Motor: Brushless DC motors have a longer life span due to the use of electronic commutation systems instead of brushes and commutators. It extended their life span and improved the overall performance of the motor.
Noise and Vibration
- Brushed DC Motor: These motors generate more noise and vibrations due to friction between the brushes and the commutator.
- Brushless DC Motor: These motors operate quietly as there are no brushes and commutators to create friction which causes noise and vibration. This makes it suitable for applications that require quiet operation.