Differences Between Stepper Motor and Servo Motor
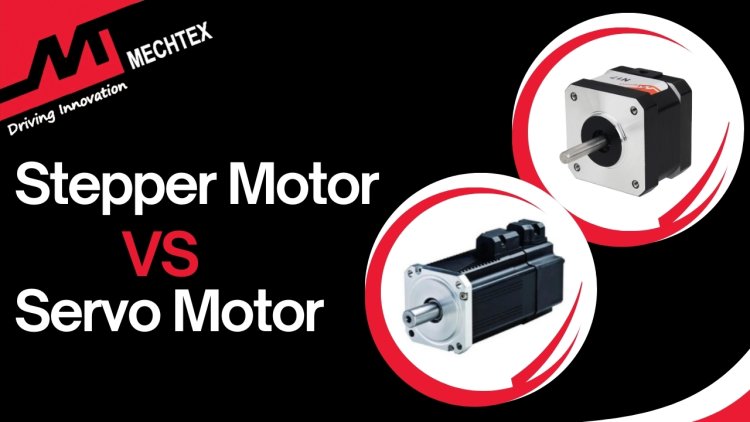
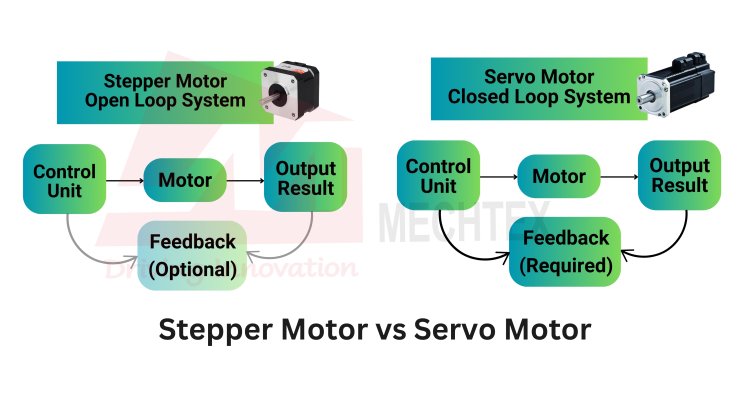
The Stepper Motor operates on an open-loop system without feedback mechanism, whereas the servo motor operates on a closed-loop system with feedback devices such as controllers for smooth and precise movement.
When choosing between a stepper motor and a servo motor for your application, understanding the fundamental differences between the two is crucial. Both motors are widely used in automation, robotics, and CNC machinery, but they operate on distinct principles and offer unique advantages.
A stepper motor is a brushless, synchronous electric motor that divides a full rotation into equal steps, making it ideal for precise positioning tasks. In contrast, a servo motor is a closed-loop system that includes a feedback sensor, enabling it to achieve high accuracy and speed by constantly adjusting its position. In this article we will explore the key differences between stepper and servo motors, helping you determine which is best suited for your specific needs.
What is a Stepper Motor?
A stepper motor is a brushless DC electric motor that converts electrical pulses into mechanical movements. Unlike traditional DC motors, which rotate continuously, stepper motors move in discrete steps. This characteristic makes stepper motors ideal for applications that require precise positioning and control in their operation.
There are three main types of stepper motor: Permanent Magnet (PM) Stepper Motor, Variable Reluctance (VR) Stepper Motor and Hybrid Stepper Motor. PM stepper motors are simple in design and offer moderate precision. Variable reluctance stepper motors offer high speed but low torque and hybrid stepper motors offer a combination of high speed with precision.
Also Read
The construction of a stepper motor consists of two main components: stator and rotor. The stator is the stationary part of the motor and consists of multiple coils arranged in groups called phases. These phases generate a magnetic field when current passes through it. The rotor is the rotating part of the motor and consists of permanent magnets. It interacts with the stator's magnetic field and causes the motor to rotate.
Watch the YouTube Video by "The Engineering Mindset" about Stepper Motors.
The working principle of the stepper motor is based on electromagnetic induction. When current passes through the stator coil, it creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the rotor and causes it to move in discrete steps at a specific angle. This angle is known as the step angle. The common step angle for a stepper motor is 0.9° or 1.8°.
Also Read
Working Principle of Stepper Motor
One of the primary advantages of a stepper motor is that it can hold position without any feedback system, making it an open loop system. Another advantage of stepper motors is they can produce high torque at low speeds which makes them suitable for applications where precise and slow movement is required.
Stepper motors are widely used in applications where precision is crucial. For example, in 3D printers, the stepper motor enables the accurate movement of the print head while in CNC machines they control the position of tools with high accuracy. Additionally, stepper motors are also used in medical devices where fine control is required.
What is a Servo Motor?
A servo motor is a closed-loop system device designed for precise control over the angular position, velocity and acceleration. Unlike other electric motors, servo motors have a feedback mechanism that continuously monitors the motor’s output to ensure the precision and accuracy of its motion. This feedback system makes servo motors ideal for applications where precision and control are essential.
Servo motors come in various types such as DC servo motors, AC servo motors, positional rotation servo motors, continuous rotation servo motors, and linear servo motors. DC servo motors are known for their precise control, while AC servo motors are robust and suitable for high-power applications. Positional rotation servo motor offers rotation up to 180°, Continuous rotation servo motor behaves more like a traditional DC motor while a linear servo motor provides linear motion and is useful in CNC machines.
Watch the YouTube Video by "LifeAda" about Servo Motors.
A Servo motor consists of four main components: motor, controller, feedback system, and drive circuit. The motor is usually AC or DC and generates mechanical motion. The controller sends pulse width modulation (PWM) to achieve the desired speed and torque. The feedback system consists of an encoder that provides real-time data on motor position. The drive circuit amplifies the control signals from the controller to a level suitable for driving the motor.
The working principle of the servo motor is based on a closed-loop control system. The controller sends signals to the motor to move to a particular position. As the motor moves, the feedback system monitors its position and sends it back to the controller. The controller then compares the motor’s actual position with the desired position. If there is any discrepancy, the controller adjusts the motor’s movement to correct the error, ensuring precision in movement.
One of the primary advantages of servo motors is high precision. The feedback system amplifies extremely accurate control movement of the motor. Another advantage of servo motors is fast response. These motors quickly respond to the changes in the control signal.
Servo motors find their uses in applications that require precise control of position, speed, and torque. For instance, in robotics to control the movements of the arms and legs, in CNC machines for precise control of cutting tools and in antenna systems for accurately aiming antennas in communication systems.
Differences Between Stepper Motor and Servo Motor
Stepper motors and Servo motors are both electromechanical devices that convert electrical pulses into precise control movements. Both these motors operate differently and are suited for different applications.
Here are the key differences between the stepper motor and the servo motor:
Control System
- Stepper Motor: It operates on an open-loop system, which means it moves in discrete steps in response to the input pulse. It does not rely on feedback systems for its movements.
- Servo Motor: It operates on the closed-loop system. Its movement is completely dependent upon the controller. The controller monitors the position of the motor via feedback systems and adjusts its movement to match the desired position of the motor.
Precision and Accuracy
- Stepper Motor: It provides high precision in positioning due to its ability to move in small (discrete) steps. However, without a feedback system, sometimes it loses its step under a heavy load, resulting in less accuracy.
- Servo Motor: It offers high accuracy with the help of the feedback system, which ensures that the motor reaches the exact position commanded by the controller. The Servo motor can achieve high precision even in heavy load conditions, which leads to high accuracy.
Speed and Torque
- Stepper Motor: It provides high torque at low speed but loses torque as the speed increases. This characteristic makes stepper motors suitable for applications that require low-speed and high-torque movement.
- Servo Motor: It is capable of maintaining high torque at a wide range of speeds. This makes servo motors suitable for applications that require both high torque and high-speed movement.
Response Time
- Stepper Motor: It has a slower response time than the servo motor due to the absence of a feedback system. It completely relies on sequential step movement. Therefore, stepper motors are not suitable for applications that require rapid acceleration and deceleration.
- Servo Motor: It has a fast response due to the feedback system, which allows it to quickly accelerate and decelerate as needed. This makes them suitable for applications that require rapid acceleration and deceleration.
Holding Torque
- Stepper Motor: It naturally provides high-holding torque even in a stationary position. It makes them suitable for applications where maintaining the position is more important than speed and power.
- Servo Motor: It requires continuous power to maintain holding torque. Further, this torque is controlled by the feedback system. Therefore, they are not suitable for applications where maintaining a position is required.
Conclusion
In summary, stepper motors operate in an open loop control system, which allows accurate positioning without the need for complex feedback mechanisms. They also have an ability to hold positions without continuous power added, making stepper motors well-suited for tasks such as 3D printing, and CNC machining, where reliability and cost-effectiveness are key.
While servo motors operate on a closed-loop control system, consisting of feedback systems to ensure exceptional precision and adaptability. Servo motors also offer high speed, substantial torque, and dynamic adjustments with the position of the motor. This makes them ideal for robotics, advanced automation, and high-performance CNC machinery.
Therefore, understanding the strengths and limitations of each motor type enables engineers and designers to select between stepper motors and servo motors for their specific needs while optimising performance and efficiency in their systems.




















