Hall Sensor vs. Sensorless BLDC Drivers
A hall sensor BLDC driver is an electronic controller designed to operate a BLDC motor equipped with hall sensors. A sensorless BLDC driver is an electronic controller used to operate BLDC motors without hall sensors or other position feedback devices.
BLDC motors are widely used in industrial automation, robotics, drones, and electric vehicles due to their high efficiency, reliability, and low maintenance. Electronic drivers play a crucial role in controlling the speed and torque of BLDC motors. These drivers are broadly classified into two types: Hall sensor-based and sensorless drivers. Both have their own unique characteristics, advantages, and applications.
In this blog, we will explore the working principles, advantages and key differences between each electronic driver, which will help us to select the right electronic driver for our application.
BLDC Motor Commutation
Commutation in a BLDC motor refers to the process of switching current through the motor winding to generate continuous rotational movement. Unlike brushed DC motors, which use mechanical brushes and a commutator, BLDC motors rely on electronic commutation using a hall effect sensor or a sensorless technique.
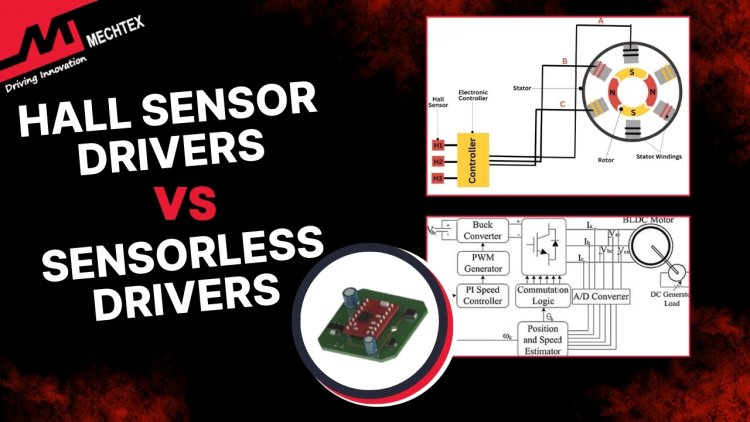
BLDC motors have three stator windings and a permanent magnet rotor. During the operation, the rotor’s position is detected by the hall sensor, which sends signals to the motor controller. The controller uses these signals to energise the appropriate windings in sequence to create a rotating magnetic field. This field interacts with the rotor magnets and produces torque.
Watch the YouTube Video by "Jantzen Lee" to learn more about commutation in BLDC motor.
In sensorless BLDC motors, back-EMF detection is used to determine the rotor position by eliminating the need for hall sensors. Electronic commutation offers higher efficiency, reduced noise, and a longer lifespan compared to mechanical commutation.
Also Read
Understanding Commutation in BLDC Motors
What is a Hall Sensor BLDC Driver?
A hall sensor BLDC driver is an electronic controller designed to operate a BLDC motor equipped with hall sensors. These sensors detect the rotor position by measuring changes in the magnetic field as the rotor spins. The hall sensor BLDC driver uses this feedback to control the motor commutation electronically to ensure smooth and precise motion.
As the rotor of the BLDC motor rotates, the hall sensor detects its position and sends signals to the driver. The driver processes these signals and determines which stator winding needs to energise.
By applying the current to the appropriate windings in sequence, the driver generates a rotating magnetic field that interacts with the rotor magnet and produces motion.
The hall sensor feedback ensures correct timing and synchronisation of commutation to enable stable and efficient operation of the BLDC motor.
This makes Hall sensor BLDC drivers ideal for applications requiring consistent performance and smooth motion.
What is a Sensorless BLDC Driver?
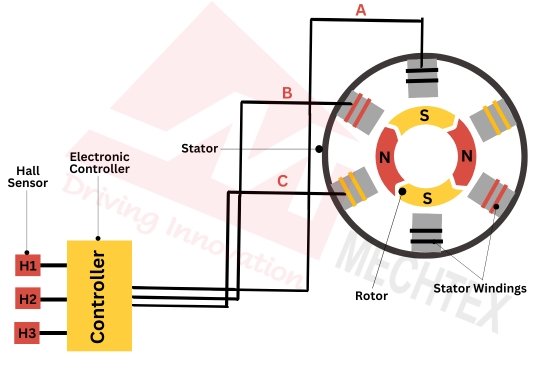
A sensorless BLDC driver is an electronic controller used to operate BLDC motors without hall sensors or other position feedback devices. Instead of relying on physical sensors, it uses the motor's back-EMF (back electromotive force) to determine the rotor position.
As the rotor spins, the stator windings generate back -EMF which is proportional to the rotor's speed and position. The driver monitors back-EMF voltage to estimate the rotor’s position. It then uses this information to commutate the BLDC motor by energising the appropriate stator windings in the sequence.
A sensorless BLDC driver requires initial start-up algorithms since back-EMF is absent when the motor is stationary. Once the motor gains speed, the back-EMF signals are used for precise commutation.
Also Read
Sensorless Control Techniques for BLDC Motors
Hall Sensor Drivers vs. Sensorless BLDC Drivers
Choosing the right BLDC driver is crucial for optimising motor performance in various applications. The hall sensor drivers offer precise rotor position feedback, while sensorless drivers reduce complexity by relying on back-EMF signals.
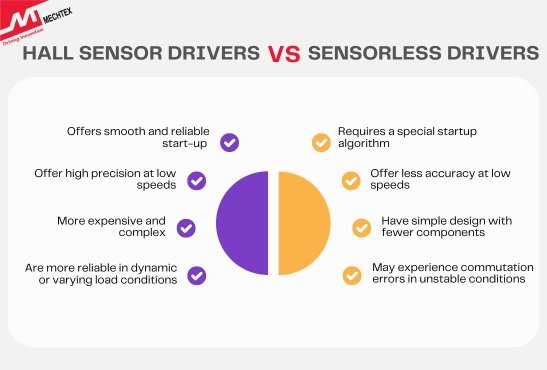
Understanding the fundamental differences between these two driver types is essential for selecting the most suitable option for your needs. Here are some key differences between both types of drives:
- Startup Performance
Hall Sensor Driver: It offers a smooth and reliable start-up as the sensors provide accurate position feedback.
Sensorless Driver: It requires a special startup algorithm since back-EMF is absent when the motor is stationary.
- Accuracy at Low Speed
Hall Sensor Driver: These drivers offer high precision at low speeds, as the sensors consistently detect the rotor position. This makes them suitable for robotics, industrial automation, and other low-speed applications.
Sensorless Driver: These drivers offer less accuracy at low speeds since back-EMF signals are weak at low RPM, making commutation less precise.
- Cost and Complexity
Hall Sensor Driver: These drivers are more expensive and complex due to the hardware, including sensors and wiring. However, they offer greater reliability in dynamic conditions.
Sensorless Driver: These drivers have a simple design with fewer components, making them more cost-effective and lightweight.
- Reliability and Efficiency
Hall Sensor Driver: These drivers are more reliable in dynamic or varying load conditions as they provide consistent feedback regardless of change in speed.
Sensorless Driver: These drivers may experience commutation errors in unstable conditions. However, they offer higher efficiency due to reduced component count and lower power consumption.
Conclusion
Both Hall sensor and sensorless BLDC drivers have their own advantages and trade-offs. Hall sensor drivers offer precise control and low-speed stability, making them ideal for industrial and precision applications. On the other hand, sensorless drivers are cost-effective, lightweight, and highly efficient for high-speed applications like drones and fans.
By understanding the differences, you can select the appropriate driver technology to maximize the performance and efficiency of your BLDC motor systems


















