Understanding the Basics of BLDC Drivers
A BLDC driver is an electronic device that manages the power, speed, and direction of a BLDC motor. It determines the rotor's position using either sensor-based or sensorless techniques. It is widely used in applications requiring high efficiency and nd precise speed control such as robotics, electric vehicles, drones.

BLDC motors are widely used in modern applications due to their high efficiency, reliability, and low maintenance requirements. However, to operate smoothly, BLDC motors require dedicated electronic drivers. BLDC drivers play a crucial role in controlling the BLDC motor’s speed, torque and direction by managing the commutation process electronically.
In this blog, we will explore the fundamental aspects of BLDC drivers, their working principles, types, and key considerations for selection.
What is a BLDC Driver?
A BLDC driver is an electronic device that controls the operation of a BLDC motor by managing its power, speed, and direction. Unlike brushed DC motors, which rely on brushes and commutators, BLDC motors require electronic commutation making the driver an essential component for proper functioning.
The BLDC driver regulates the motor’s performance by switching the direction of current in stator windings in synchronisation with the rotor position. It is achieved using control algorithms such as trapezoidal, sinusoidal, or field-oriented control (FOC), ensuring smooth and efficient operation.
The BLDC drivers operate using either sensor-based or sensorless techniques to determine the rotor’s position. Hall effect sensors or encoders provide feedback in a sensor-based system, while sensorless drivers detect position using back-EMF which reduces cost and complexity.
BLDC drivers are widely used in applications requiring high efficiency, precise speed control, and minimal maintenance, such as industrial automation, robotics, electric vehicles, drones, and household appliances.
Components of BLDC Driver
A BLDC driver consists of several key components that work together to control the motor’s operation efficiently. Key components include:
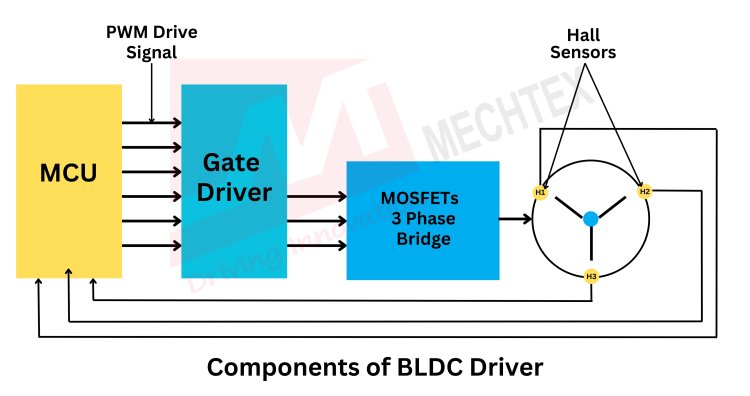
- Microcontroller (MCU) / Digital Signal Processor (DSP)
It acts as the brain of the driver and executes control algorithms such as trapezoidal, sinusoidal, or field-oriented control (FOC). It processes sensor feedback or back-EMF signals to determine the rotor position and adjust the commutation accordingly.
- Gate Driver Circuit
It amplifies the control signals received from microcontrollers to drive the power switches such as MOSFETs or IGBTs. It also ensures proper switching timing and voltage levels for efficient operation.
- Power Stage (MOSFETs / IGBTs)
It handles the high-power switching to control current flow through the BLDC motor windings. They typically consist of a three-phase inverter bridge to energize the motor coils in the correct sequence.
- Current and Voltage Sensors
They monitor the BLDC motor’s parameters to ensure proper operation and protection against overcurrent or Under-voltage conditions. They are used in closed-loop control systems for precise speed and torque regulation.
- Position Sensors
They detect the rotor position for accurate commutation in a sensor-based system. In sensorless drivers, back-EMF detection or other algorithms are used to estimate the rotor position.
Working Principle of BLDC Driver
The BLDC driver controls the operation of the brushless DC motor by electronically commutating the stator windings in synchronisation with the rotor position. Since BLDC motors lack brushes and commutators, the BLDC driver plays a crucial role in switching the current flow to achieve continuous rotation.
The first step in working the BLDC driver is rotor position detection. The BLDC driver detects the rotor position using hall effect sensors or other sensorless control techniques such as back-EMF detection. This information helps to decide which stator coil needs to energise next to ensure proper commutation.
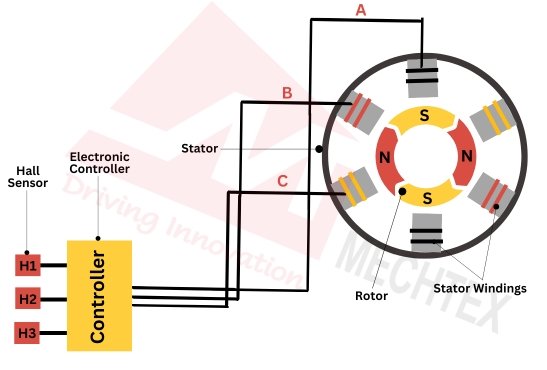
Next, the BLDC driver performs electronic commutation. Based on the rotor’s position, it activates specific MOSFETs or IGBTs in a three-phase inverter bridge. This process generates a rotating magnetic field in the stator.
In trapezoidal control, current switching follows a six-step sequence while in sinusoidal and field-oriented control (FOC), current is applied smoothly for improved efficiency and torque performance.
For speed and torque control, the BLDC driver adjusts the PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) duty cycle to regulate the speed of the LDC motor. It also uses current feedback to ensure optimal torque delivery based on load conditions.
Lastly, the BLDC driver incorporates protection and efficiency optimisation features. It includes overcurrent, overvoltage, and thermal protection to prevent damage. Advanced BLDC drivers further optimise energy efficiency by dynamically adjusting power delivery.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a BLDC Driver
When selecting a BLDC driver, several factors must be considered to ensure compatibility, efficiency, and optimal performance. Some of the key factors are:\
- Voltage and Current Ratings
The BLDC driver must match the operating voltage and current requirements of the BLDC motor. Overrated or underrated drivers can lead to inefficiencies or damage.
- Control Method
Trapezoidal control offers simpler implementation but may cause torque ripple. Sinusoidal and Field-Oriented Control (FOC) provide smoother operation and better efficiency.
- Sensor-Based vs. Sensorless Operation
Hall sensor-based drivers provide precise control but add cost and complexity. Sensorless drivers rely on back-EMF detection which reduces wiring but requires sophisticated algorithms.
- Application-Specific Requirements
Compact size, thermal management, and programmability play a role in selecting the right driver for applications like drones, robotics, or industrial automation.
Conclusion
BLDC drivers are essential components that enable efficient and precise control of brushless DC motors. By understanding their components, working principles, and selection criteria, engineers and designers can choose the right driver for their specific applications.
Whether it’s a sensor-based or sensorless driver, proper integration and tuning can significantly enhance motor performance and overall system efficiency. As advancements in power electronics and microcontrollers, BLDC drivers are becoming smarter, more efficient, and increasingly indispensable in modern applications.