Role of Synchronous Motors in Power Factor Correction and Reactive Power Management
Power factor correction is the process of improving the power factor of an electrical system and reactive power is an AC system component that maintains the magnetic field necessary for operation. Synchronous motors are an indispensable component of maintaining system efficiency and ensuring reliable power.

In modern electrical power systems, efficient energy utilisation and stable operation are critical concerns. Power factor correction and reactive power management are fundamental aspects of maintaining system efficiency and ensuring reliable power. Among the various technologies, synchronous motors play a vital role in addressing these challenges.
In this blog, we will explore the importance and benefits of synchronous motors in power factor correction and reactive power management.
What is Power Factor Correction?
Power factor correction is the process of improving the power factor of an electrical system, which measures how effectively electrical power is converted into motion. Unity power factor signifies maximum efficiency, whereas a low power factor indicates loss of energy. Synchronous motors are widely used for power factor correction in industries because of their inherent characteristics.
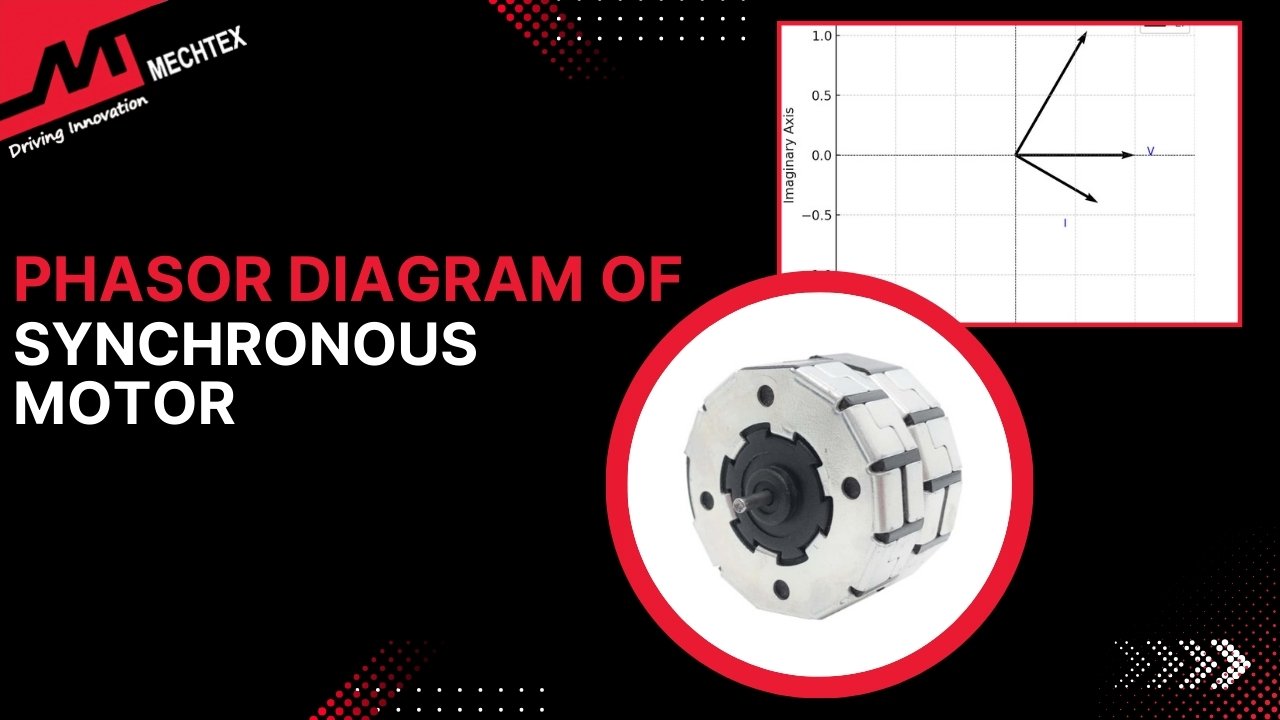
Synchronous motors operate at a constant speed regardless of load and reactive power capabilities which allow them to either absorb or supply reactive power needs. By doing so, they can counteract the reactive power demand of inductive loads. When a synchronous motor is added to any electrical system it helps balance the reactive power and improve the overall power factor of the system.
Watch the YouTube Video by "The Engineering Mindset" to learn about the Power Factor.
Improved power factor reduces energy losses in the system and optimises the capacity of power equipment. Additionally, it minimises voltage drops in electrical work which leads to better voltage regulation.
Using synchronous motors for power factor correction is particularly advantageous in large industrial settings where significant inductive loads are present. Their ability to provide stable and adjustable power factor correction contributes to energy efficiency and cost savings, making them a critical component in modern electrical systems.
Also Read
Understanding Power Factor Correction Using Synchronous Motors
Role of Synchronous Motor in Power Factor Correction
Synchronous motors play a significant role in power factor correction, making them essential in industrial applications where reactive power compensation is needed. Here's an overview of their role:
- Operate at Leading Power Factor Mode
When synchronous motors are over-excited, they generate reactive power in the form of a leading power factor. This compensates for the lagging power factor created by inductive loads such as motors and transformers. It results in power balance which helps to minimise the total reactive power demand and improve the overall system’s power factor.
- Enhanced System Efficiency
A high power factor means less reactive power flow through the system. This results in low current flow thereby reducing energy losses of the system. This low energy loss translates into improved energy efficiency and allows the system to operate more effectively.
- Stabilisation of Voltage Levels
Synchronous motors play a key role in stabilising voltage levels in electrical systems. By supplying reactive power, they support the voltage regulation ensuring that the system voltage level remains steady.
- Dynamic Response to Load Changes
Synchronous motors provide a quick dynamic response to load variations making them ideal for systems with fluctuating reactive power demand.
Unlike induction motors, which require external capacitors to adjust the power factor, synchronous motors can actively adjust their excitation levels instantly changing from lagging to leading power factor mode.
What is Reactive Power?
Reactive power is an AC system component that maintains the magnetic field necessary for operation. In a synchronous motor, reactive power plays a critical role in supporting the operation of other inductive and capacitive loads.
Synchronous motors are essential for reactive power because they can consume or supply reactive power depending on the system’s needs.
For systems with a lagging power factor caused by inductive loads, synchronous motors can supply reactive power to offset the demand, improving the power factor. Conversely, in systems with a leading power factor due to capacitive loads, synchronous motors can absorb reactive power, balancing the network.
The ability of synchronous motors to manage reactive power enhances system stability, reduces energy losses, and ensures better voltage regulation. It is particularly beneficial in industrial and utility settings where maintaining a balanced and efficient electrical system is critical.
Role of Synchronous Motor in Reactive Power
Synchronous motors play a crucial role in managing reactive power in electrical systems, primarily due to their ability to operate at various power factors (lagging, unity, or leading). Here are the roles of synchronous motor:
- Variable Power Factor Operation
Synchronous motor can adjust their excitation to operate at a desired power factor:
-
- Under Excited: Synchronous motor operates at a lagging power factor and consumes reactive power.
- Over Excited: Synchronous motor operates at a leading power factor and supplies reactive power.
- Normal Excitation: Synchronous motor operates at a unity power factor and neither consumes nor supplies reactive power.
- Reactive Power Compensation
By operating in an over-excited mode, the synchronous motor acts as a capacitive load and supplies reactive power to the grid or other inductive loads. This reduces the burden on external reactive power sources like capacitors or synchronous condensers, helping maintain voltage stability.
- Voltage Regulation
By supplying reactive power, the synchronous motor helps stabilise and regulate the voltage in the power system, especially during load fluctuation.
- Improving Power System Efficiency
Managing reactive power through synchronous motors reduces energy losses and improves the overall efficiency of the power system.
Conclusion
Synchronous motors are indispensable in modern electrical systems for their ability to enhance power factor and manage reactive power. Their dual role as mechanical drivers and reactive power compensators makes them a cost-effective and efficient solution for industries and power grids alike.
For industries and utilities aiming to optimise their energy usage and ensure reliable power delivery, investing in synchronous motors is a strategic choice that pays dividends in efficiency and sustainability.