Exploring the Role of Rotor Inertia in Stepper Motor Performance
Rotor inertia refers to the resistance of a stepper motor’s rotor to the change in its rotational motion. The performance of the stepper motor is directly influenced by its rotor inertia. To optimise stepper motor performance, it is crucial to consider the impact of rotor inertia during the selection and design phase.

Stepper motors are indispensable components in applications that require precise motion control such as robotics, CNC machines, and medical devices. A critical but often overlooked parameter which affects its performance is rotor inertia. Understanding rotor inertia and its impact is essential for optimising the stepper motor’s functionality and achieving reliable operation.
In this blog, we will understand the concept of rotor inertia, its effect on stepper motor performance, and consideration for choosing the right stepper motor.
What is Rotor Inertia?
Rotor inertia refers to the resistance of a stepper motor’s rotor to the change in its rotational motion. It is a physical property of the rotor, defined as the mass distribution around its axis of rotation and expressed in units of kg·m².
Higher rotor inertia means the rotor requires more torque to accelerate or decelerate, while low rotor inertia allows for faster changes in speed and motion.
It can be calculated as:
I = ½ mr2
Where:
I = Rotor inertia (e.g., g·cm², kg·m²)
M = Rotor mass (in grams or kilograms)
R = Radius of the rotor (in centimetres or meters)
Stepper motors are characterised by their ability to move in precise increments. Rotor inertia plays a significant role in determining the motor’s responsiveness to these incremental movements.
How Rotor Inertia Affects Stepper Motor Performance
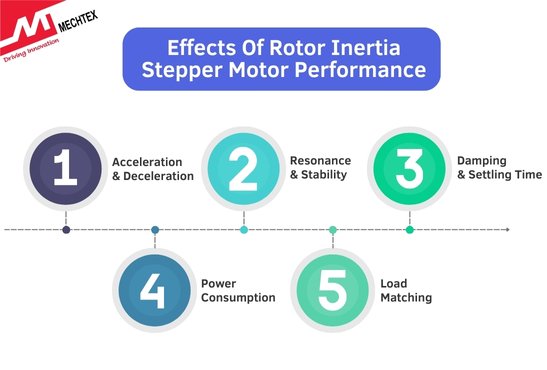
The performance of the stepper motor is directly influenced by its rotor inertia. Key areas of impact include:
- Acceleration and Deceleration
Rotor inertia dictates how quickly a stepper motor can accelerate or decelerate. A rotor with higher inertia requires more torque to achieve a given acceleration.
Higher inertia can limit the motor’s ability to respond to rapid changes in speed or direction making it less suitable for high-dynamic applications.
- Resonance and Stability
Stepper motors require resonance, particularly at certain step frequencies. Rotor inertia influences the system's natural frequency. A mismatch between the rotor inertia and the load inertia can exacerbate resonance issues, leading to vibration, noise, and loss of step accuracy.
- Damping and Settling Time
Higher rotor inertia can increase the time required for the stepper motor to settle into its final position after a move. This is especially critical in applications requiring high-speed operation and rapid positioning.
- Power Consumption
A stepper motor with rotor inertia demands more power to initiate motion. This increased power requirement can lead to higher energy consumption and reduced efficiency, especially in battery-operated systems.
- Load Matching
Rotor inertia must be carefully matched with the load inertia for optimal performance. An improperly matched system can result in overshooting, undershooting, or even motor stalling.
Practical Considerations for Managing Rotor Inertia
To optimise stepper motor performance, it is crucial to consider the impact of rotor inertia during the selection and design phase. Here are some practical guidelines:
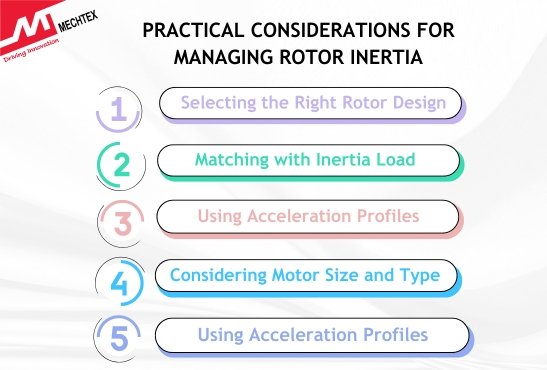
- Selecting the Right Rotor Design
Rotor designs vary across the stepper motor. For example, a hybrid stepper motor typically has a higher rotor inertia due to its robust design. Permanent magnet stepper motors, on the other hand, tend to have low inertia and are better suited for high-speed applications.
- Matching with Inertia Load
A general rule of thumb is used to match the rotor inertia to the load inertia as closely as possible. If the load inertia is significantly higher using a gearbox or coupling can help achieve a better match.
- Using Acceleration Profiles
Implementing controlled acceleration and deceleration profiles can help mitigate the impact of high rotor inertia. Gradual speed changes reduce the torque demand and minimise the risk of resonance.
- Considering Motor Size and Type
Large stepper motors generally have high rotor inertia. If your application requires quick responsiveness consider choosing a small stepper motor with low inertia with an optimised rotor design.
- Incorporating Damping Mechanisms
Damping techniques such as adding a viscous damper or using electronic damping through a microcontroller can help manage resonance and improve stability in systems with high rotor inertia.
Conclusion
Rotor inertia is a fundamental parameter influencing stepper motor performance. Whether you need rapid acceleration, precise positioning, or energy efficiency, understanding and managing rotor inertia is key to achieving your goals. By carefully selecting the motor type, matching load and rotor inertia, and leveraging modern control techniques, you can optimize your system for peak performance.
In the ever-evolving world of motion control, rotor inertia remains a pivotal factor in ensuring that stepper motors meet the demands of diverse and challenging applications.