The Significance of Synchronous Motors - Working, Applications, and Industrial Importance
A synchronous motor is a type of electric motor, where the rotational speed of the motor is synchronised with the frequency of electrical current. It consists of a stator and a rotor. Common applications include HVAC systems, medical devices, valves, actuators, pumps, compressors, wind turbines, etc.

"Synchronous motors work well at a constant speed, following a precise rhythm with the electrical current to ensure smooth and efficient performance."
Have you ever wondered how your appliances maintain a constant speed and operate so smoothly? It is all thanks to the synchronous motors that keep things running efficiently and consistently. Synchronous motors are a fundamental type of AC motor that runs at a continuous speed regardless of load. They are widely used in Industrial automation, power factor correction, and precision equipment due to their efficiency and controllability.
In this blog, we will explore everything about synchronous motors - from what they are, how they work, their uses, applications, and importance in modern industries.
What is a Synchronous Motor?
A synchronous motor is an AC motor that operates at a constant speed, synchronised with the frequency of the current supply. In this motor, the rotor rotates in sync with the stator's magnetic field and maintains a constant speed regardless of load. Unlike induction motors, where the rotor lags behind the magnetic field, in synchronous motors, the rotor spins along with the magnetic field, which makes it ideal for applications where precise speed control is required.
A synchronous motor consists of two main components: the stator and the rotor. The stator is a stationary part of the motor. It consists of three-phase windings energised by an AC supply to create a rotating magnetic field. The rotor is the rotating part of the motor. It consists of electromagnets or permanent magnets and often requires DC excitation to produce its magnetic field. It requires an external DC source to energise and create a magnetic field.
These AC motors are categorised into non-excited (e.g., permanent magnet) and electromagnetically excited types, depending upon how the rotating magnetic field is generated.
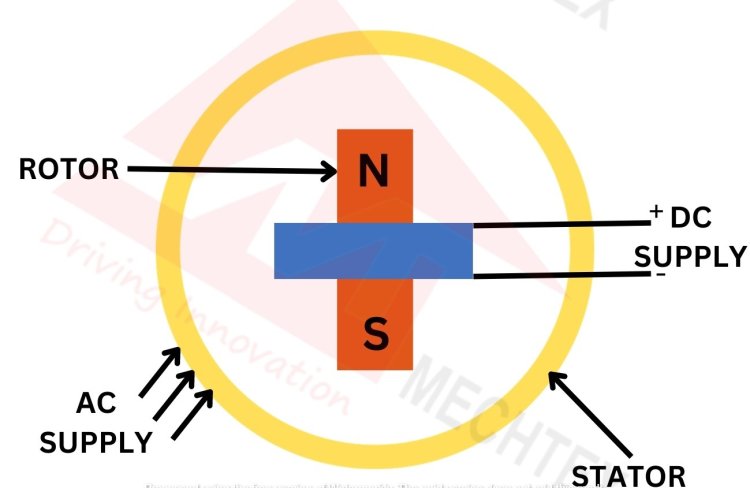
Synchronous motor operates on the principle of rotating magnetic field. When AC power is supplied to the stator it creates a rotating magnetic field (RMF). The rotor interacts with this magnetic field and starts to spin. Once the rotor reaches the synchronous speed it locks into the same frequency as the stator magnetic field and rotates at synchronous speed.
Synchronous motors are widely used in applications requiring high efficiency and constant speed, such as in industrial machinery, power generation, and robotics. Their ability to maintain consistent speed under varying loads makes them suitable for tasks that demand high precision, such as timekeeping devices, automation systems and many more.
Construction of Synchronous Motor
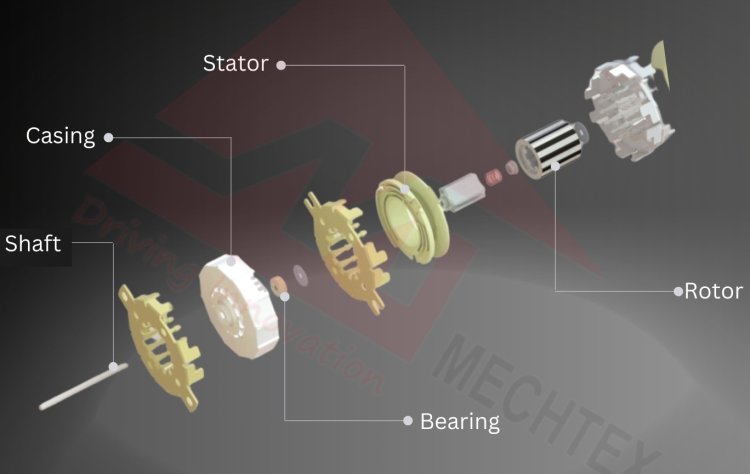
A synchronous motor consists of various parts such as a stator, rotor, excitation system, bearings, and many more. All these parts work together to rotate the rotor at a synchronised speed with the help of an AC supply. The key components of the synchronous motor are :
-
Stator
It is the stationary part of the motor. It consists of a stack of thin, insulated laminated sheets and other magnetic materials. These laminations are stacked to form the core of the stator. The core of the stator consists of coils of wire wound around the slots, which form the winding of the motor. It includes 3-phase windings. When an AC current is supplied through this winding, it produces a rotating magnetic field to rotate the rotor.
-
Rotor
It is the rotating part of the motor. It consists of steel lamination, copper conductors, and permanent magnets. When AC current is supplied through the winding of the stator, it generates the magnetic field, then the rotor interacts with the magnetic field and rotates the motor at a synchronised speed.
The rotor is excited by DC supply or fitted with permanent magnets, depending on the motor type. In a DC-excited synchronous motor, slip rings and brushes are used to deliver the excitation current to the rotor winding.
-
Exciter
It is a crucial component of a synchronous motor. It is responsible for maintaining the synchronous speed of the motor. Adjusting the phase of direct current (DC) supplies to the rotor, ensures that the rotors rotate at the same speed as stator winding. It helps the motor to rotate at its constant speed and to maintain its stability.
-
Bearing
It plays a critical role in a synchronous motor. It provides support to the rotor shaft to maintain its position and allows it to rotate freely. There are 3 types of bearings such as sleeve bearings, roller bearings, and ball bearings.
Sleeve bearings made up of bronze allow smooth rotation of the rotor by providing low friction. Roller bearings use cylindrical and tapper rollers to reduce friction and handle high radial loads. Ball bearing uses balls to minimise friction.
They are efficient in handling the axial loads. Bearings need timely inspection to avoid wear and tear, maintenance, and potential failures to improve the efficiency of the motor.
Other Components
-
Shaft
It connects the rotor with the external load of the motor. It helps to transmit the rotational force produced by the motor to the application.
-
Housing or Frame
It protects the internal components of synchronous motors, provides structural support and consists of a bearing, stator, rotor, and exciter.
Working Principle of Synchronous Motor
The working principle of a synchronous motor is based on the interaction between the stator and the rotor’s magnetic field. It involves the interlocking between the rotor and stator field, which ensures that the rotor rotates synchronously with the frequency of supply. When the stator is powered by an AC supply, it generates a rotating magnetic field (RMF). This magnetic field rotates at a speed which is directly proportional to the frequency of the AC supply.
The rotor which consists of permanent magnets or electromagnets is excited with an external DC supply and creates its own magnetic field. The rotor interacts with the stator’s rotating magnetic field (RMF) and starts rotating.
Once the rotor reaches this speed, it continues to rotate at the same speed as the stator's magnetic field. This synchronous operation allows the motor to maintain a constant speed regardless of variations in the load, as long as the load does not exceed the motor's torque capacity. If the load surpasses this limit, known as the pull-out torque, the rotor will lose synchronization and the motor may stop.
Also Read
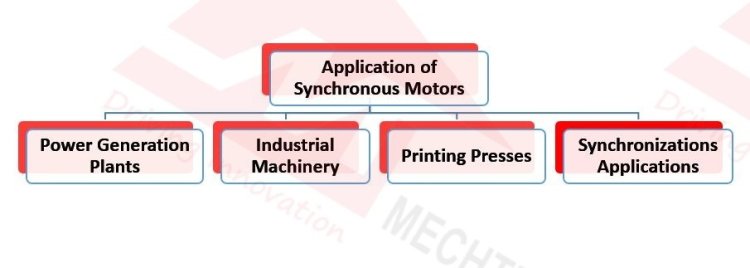
Applications of Synchronous Motor
-
Power Generation Plant
Synchronous motors are used in power generation plants as synchronous generators. They convert the mechanical energy into electrical energy. They are connected to turbines and driven by steam, wind, and water. As a synchronous generator, it rotates at a synchronous speed and produces electricity.
Synchronous motors are also used for power factor correction in the plants. They regulate the power factor by adjusting the exciter and allowing it to absorb or supply reactive power, regulating the voltage supply and overall efficiency of the system.
They are also employed in electrical substations for power factor correction, improving grid stability and system performance.
-
Industrial Machinery
Synchronous motors are used in industrial applications to perform various tasks that demand constant speed and reliability. These motors are used in machine tools such as lathes, milling machines, and grinders, where constant speed is required for precise cutting and finishing of the materials.
Synchronous motors play a pivotal role in the conveyor systems of factories and warehouses. These motors provide constant speed and precise control, which allows the smooth movement of goods from the assembly line to the packaging area.
They are also widely used in pumps and compressors in water treatment and HVAC systems, where steady and controlled operation is essential. In addition, they drive industrial fans and blowers for consistent air movement in ventilation systems.
Mechtex 24V AC Synchronous Motor with a power of 3.1 W, a speed of 250 RPM, and a torque of 3.6 Ncm is well-suited for Industrial Machinery.
- Printing Presses
Synchronous motors are important components in printing presses by facilitating constant speed and accurate control in the printing operation. These motors help in maintaining the accurate alignment of printing plates. This alignment helps in aligning each colour and element properly.
These motors offer constant speed and rotation, which is crucial for aligning colour, text, and design accurately on paper. Printing presses print different types of formats and designs. The motor's constant speed and precise control help to control the printing speed and improve the flexibility of the printing process.
Mechtex MTR4b is a 3.6 W synchronous motor with speed 500 RPM speed and 2.7 Ncm torque which make it well suited for printing presses where constant speed is required.
-
Synchronisation Applications
Synchronous motors are used in various synchronisation applications such as clock and timing devices, industrial automation, Audio and broadcast systems, and telecommunication devices.
These motors are the driving force in clocks and timing devices. The devices function with the help of the synchronised speed of the motor. This synchronisation helps in accurate timekeeping and the continuous functioning of devices. It is commonly found in public clocks and industrial timekeeping systems.
Synchronous motors are used in multiple industrial automation applications such as CNC machines, printing presses, packaging machines, and many more. The motor’s precise speed and accurate control help CNC machines and automated manufacturing processes in repeatable movement. The motor's constant speed and accuracy help packaging machines and printing presses perform tasks with accuracy.
They are also extensively used in textiles and paper machinery for their ability to provide uninterrupted, stable performance. In heavy industries, synchronous motors drive rolling mills and crushers in mining applications where constant torque and high power are crucial.
Mechtex is a permanent magnet synchronous motor manufacturer in India since 1967. Our synchronous motors are used in various synchronisation applications such as CNC machines, printing presses, packaging machines, textile machines, and many more.
Why Synchronous Motors Are Crucial in Industries?
In recent times, the world has experienced a shift toward new motor technology due to various factors such as the advancement in technology, changing consumer preferences, the need for efficient and sustainable solutions, and an increase in environmental standards and regulations.
This shift led to the adoption of brushless DC motors and permanent magnet motors. These motors are key in driving progress and fulfilling the demand for efficient and sustainable solutions. Their ability to control speed and torque caters to the requirements of modern industrial technology.
Despite advancements in technology and new types of motors, synchronous motors are still crucial components for various industrial applications. One of the key reasons to continue the use of synchronous motors is their constant speed and high efficiency. Their constant speed makes them ideal for applications that require stable and continuous rotation for their operations.
They are particularly favoured in industries for their long-term operational stability and excellent performance in synchronised systems.
Another key reason to use synchronous motors in today's industrial applications is their ability to operate in both motor and generator modes. In the motor mode, it converts the electrical energy into mechanical energy, while in generator mode, it converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy. This ability makes them a reliable solution for applications such as wind turbines, power generation plants, and hybrid vehicles.
Synchronous motors also offer customisable speed-torque characteristics, making them suitable for high-inertia machinery like compressors, mills and crushers. Their seamless integration with digital control systems (PLC/SCADA) enhances monitoring, diagnostics, and automation, essential in smart manufacturing environments.





















