Types of Stepper Motors: PM, VR, Hybrid, Unipolar & Bipolar
Discover the different types of stepper motors: permanent magnet (PM), variable reluctance (VR), and hybrid motors with unipolar and bipolar winding configurations and their applications.

What is Stepper Motor?
A stepper motor is a brushless synchronous electric motor engineered to convert digital input (pulses) into mechanical rotation. Unlike conventional electric motors, stepper motors divide a full rotation (360°) into a series of equal steps. This results in a step angle of 1.8°, which means each electrical pulse moves the shaft by exactly that amount.
The construction (parts) of a stepper motor consists of stator and rotor. Stator is the stationary part of the motor equipped with multiple windings arranged in specific phases. Rotor is the rotating part of the motor equipped with permanent magnets, which interact with the magnetic field and cause rotation.
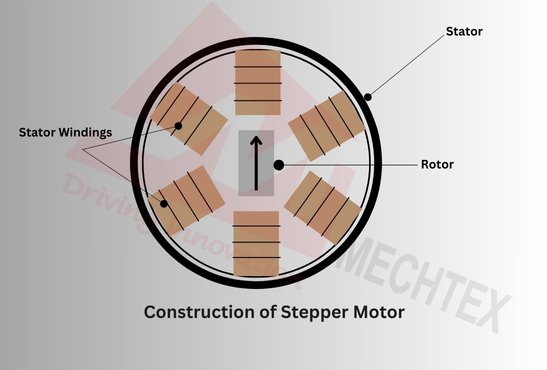
When current flows through the windings in a controlled sequence, magnetic fields are produced that pull the rotor into the precise step position. The number of stator poles and rotor teeth determines the step angle and resolution of the stepper motor.
As stepper motor is a DC motor that operates using a DC supply. The switching of current through various windings creates a rotating magnetic field that minimises the AC operation and makes the stepper motor function as a digital control-driven motor.
Because of these discrete step movements, stepper motors offer precise open-loop control without requiring a position feedback system. As the pulse increases, the stepper motor transitions from individual steps to continuous motion. The speed of rotation directly correlated with the input pulse rate, making stepper motors ideal for applications demanding consistent speed and positioning.
Stepper motors are widely used in robotics, 3D printing, CNC machines, and printers. Their ability to move in discrete steps and provide precise positioning and control makes them an ideal choice for these applications.
Working Principle of Stepper Motor
The working principle of stepper motor is based on electromagnetic attraction. When the stator coils are energised, they produce a magnetic field that aligns the rotor with the stator pole. By energising stator coils in a specific sequence, the rotor moves incrementally from one position to the next at a specific angle. Each electrical pulse advances the rotor by one step.
The below stepper motor diagram will help us to visualise how stepper motors work.
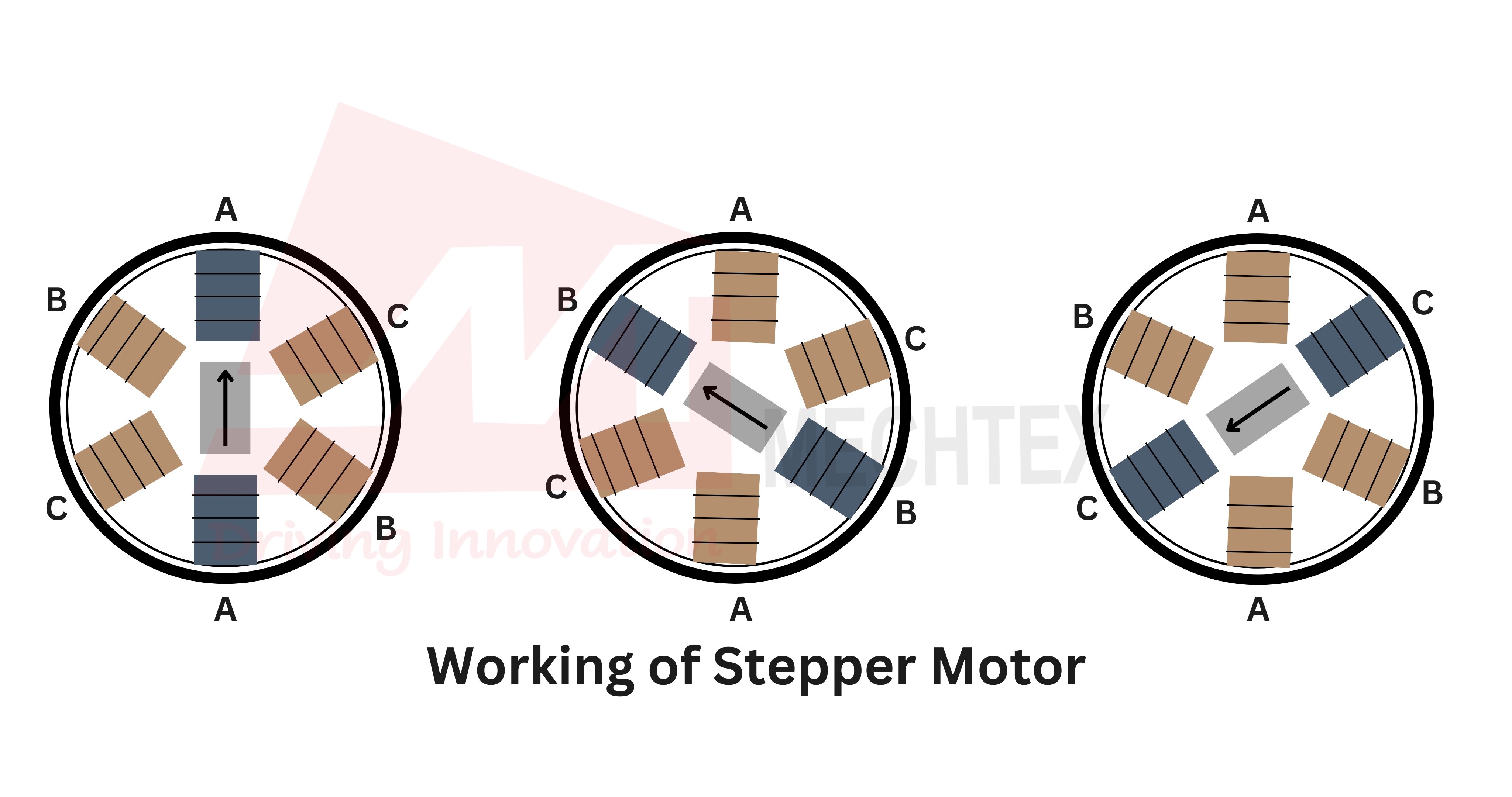
Here are the different modes of the stepper motor:
-
Full-step mode: It is the mode where one winding (or a pair of windings) is energised at a time.
- Half-step mode: In this mode, the motor alternates between energising one winding and two windings at a time. It creates more steps in one full rotation and results in smooth and morev accurate movement than full-step mode.
-
Microstepping or half-step mode, where multiple windings are partially energised to achieve smoother and more precise motion.
As the frequency of pulses increases, the stepping becomes faster and transitions into continuous rotation. Since the movement is pulse-driven, the motor’s position and speed can be precisely controlled without needing feedback sensors.
Different Types of Stepper Motor
Stepper motors are the type of electric motor that moves with precision and accuracy as compared to other traditional motors. These motors are widely used in various applications that require precise positioning and accuracy in operation.
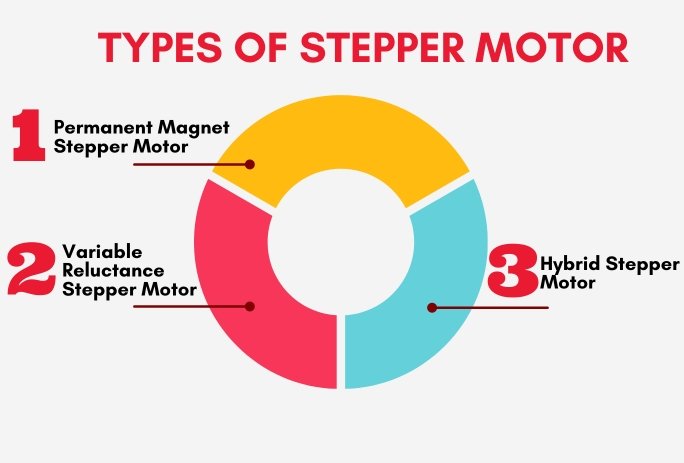
There are three different types of stepper motors: Permanent Magnet (PM) Stepper Motor, Variable Reluctance (VR) Stepper Motor, and Hybrid Synchronous or Hybrid Stepper Motor.
Permanent Magnet (PM) Stepper Motor
A permanent Magnet (PM) Stepper Motor is an electric motor that converts electrical pulses into precise movements through the use of magnetic fields. PM stepper motors are determined with the use of their permanent magnets embedded in the rotor. These magnets create a magnetic field that interacts with the magnetic field of the stator and causes the stepper motor to move in precise angular steps.
One of the key advantages of permanent magnet stepper motors is their ability to provide precise positioning without feedback devices. PM stepper motors use their permanent magnets within the rotor and stator to achieve precise positioning even when the external force is applied. This simplifies the design of the PM stepper motor and enhances reliability by reducing the potential errors caused by the sensors.
Another key advantage of the PM stepper motor is to maintain high torque at low speed. Unlike traditional motors, which depend on electromagnetic fields created by energised coils, PM stepper motors use permanent magnets to generate the magnetic field. This magnetism allows PM stepper motors to maintain high torque at low speed and ensure accurate positioning and smooth operation.
While it also has some drawbacks, such as having a low power requirement and producing more torque for precision movement.
PM stepper motors are valuable components in various applications such as robotics, automated manufacturing machines, and medical devices, where precise positioning and high torque at low speed are essential.
Also Read
Basics of Permanent Magnet Stepper Motor
Working of PM Stepper Motor
A permanent magnet (PM) stepper motor operates at the principle of electromagnetism, where electrical pulses are converted into mechanical movements. These motors consist of two main components: stator and rotor. The stator is the stationary part of the motor and consists of electromagnets arranged in a specific pattern. The rotor is the rotating part of the motor and consists of permanent magnets with slotted surfaces.
When electrical current is supplied to the electromagnets of the stator, they create a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the permanent magnets of the rotor and causes the rotor to rotate at a specific angle. The direction of rotation depends upon the sequence of electrical current supplied to the electromagnets of the stator.
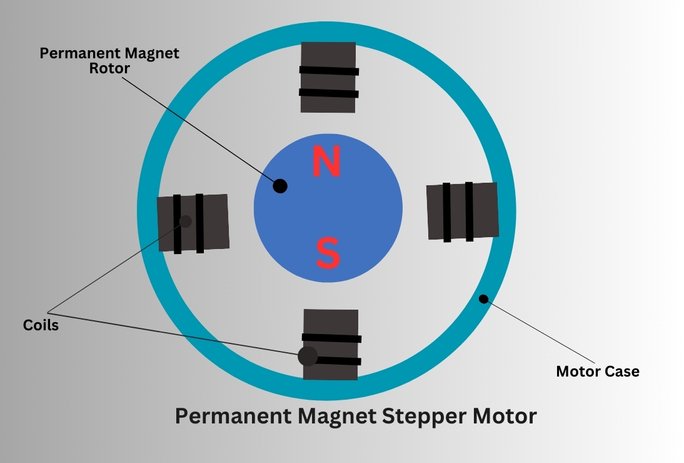
The rotation of the rotor is controlled with the help of a digital controller. This digital controller controlled the timing and sequence of the electrical pulses applied to the stator electromagnets. Each permanent magnet of the rotor aligns with the corresponding electromagnets of the stator and causes the rotor to move forward and backward making it ideal for various applications.
Mechtex MTS3a is a 12V Bipolar Stepper Motor with a 7.5° step angle, holding torque of 1.6 Ncm with a simple mechanical structure which makes it ideal for applications such as Level Switches, Valve Actuators.
Variable Reluctance (VR) Stepper Motor
Variable reluctance stepper motor is also known as “reluctance stepper motor”. It has a plain iron rotor and a wound stator. The stator is made up of multiple teeth, and each tooth has a winding. When current is applied to the windings, it creates a magnetic field that interacts with the soft iron rotor and causes the rotor to rotate.
One of the key advantages of variable reluctance (VR) stepper motors is they offer low cogging torque as compared to other stepper motors. It is achieved through their unique design. Unlike other stepper motors, which use permanent magnets to generate the magnetic field, variable reluctance stepper motors use soft magnetic material in the rotor to generate the magnetic field.
It helps VR stepper motors to produce smoother motion and reduce the risk of vibration and noise, resulting in smoother and more precise operation.
Another key advantage of variable reluctance stepper motors is they offer high torque at low speed. VR stepper motors use the rotor with a salient pole and stator with winding to achieve high torque at low speed. When stator windings are energised in sequence, they create a magnetic field and interact with the poles of the rotor.
This magnetic interaction between the stator and rotor is the strongest and provides the necessary torque to the VR stepper motor to overcome the load and maintain rotation even at low speeds.
Variable reluctance stepper motors are widely used in high-power applications such as industrial machinery, robotics, and CNC machines due to their precise positioning and low-cogging torque for smooth operation.
Working of VR Stepper Motor
A variable reluctance stepper motor is a stepper motor that operates in the principle of magnetic reluctance. This motor consists of a stator with a winding and a rotor with poles. When stator windings are energised, it creates a magnetic field and attracts the poles of the rotor causing it to rotate.
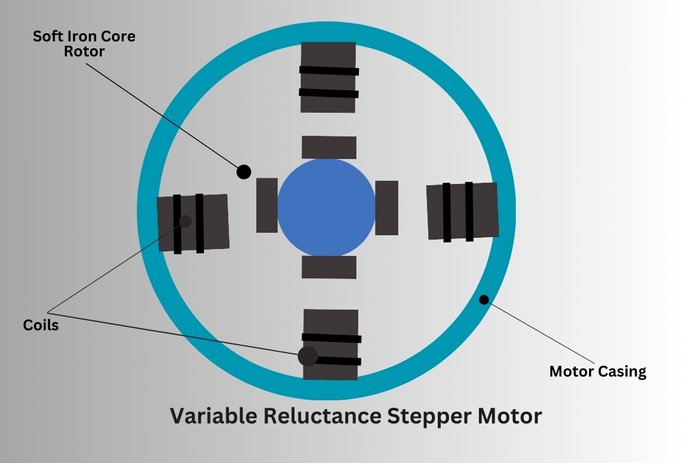
The VR stepper motors are controlled using unipolar and bipolar drives. In unipolar drives, the stator winding is connected to a single power supply, while in bipolar drives, windings are connected to two power supplies. The direction of the rotation is controlled by reversing the polarity of the current in windings.
VR stepper motors also operate in open loop mode and close loop mode. In open-loop mode, the motor is controlled by a fixed sequence of pulses, while in closed-loop mode, the motor’s position is monitored using feedback devices such as encoders.
Hybrid Synchronous (HS) Stepper Motor
The hybrid synchronous stepper motor is also known as a hybrid stepper motor. This motor combines the features of both a permanent magnet (PM) stepper motor and a variable reluctance (VR) stepper motor. A hybrid stepper motor has a hybrid design consisting of a permanent magnet rotor and variable reluctance stator.
The permanent magnet rotor provides high torque and holding torque to ensure the motor can maintain its position even when power is off. Simultaneously, the variable reluctance stator allows for precise control over the speed and position of the motor.
One of the key advantages of hybrid stepper motors is their ability to provide high torque or holding torque at low speeds. The rotor in the hybrid stepper motor is constructed with permanent magnets and interacts with the stator's electromagnets. When the stator coils are energised in specific sequences, the rotor aligns itself with the magnetic field produced by the stator. This interaction creates holding torque and resists the external force that trying to rotate the rotor.
Another key advantage of hybrid stepper motors is their ability to maintain a precise position. Unlike other stepper motors, which completely rely on the open-loop system, a hybrid stepper motor consists of a permanent magnet rotor and tooth stator to create a closed-loop system.
In the closed-loop system, the magnetic field produced with the help of the interaction of the stator and rotor allows for precise control over the position of the rotor without any feedback device. It results in exceptionally small steps in the range of 0.9 degrees to 1.8 degrees to enable precise positioning and smooth operation. The standard step angle of a hybrid stepper motor is 1.8 degrees and has become the most popular type of stepper motor
Mechtex Nema 17 Stepper Motor is a versatile and powerful stepper motor. It has a step angle of 1.8 degrees with an in-built driver that ensures seamless integration with different types of applications.
Hybrid stepper motors are widely used in applications such as 3D printers, CNC machines, and medical equipment due to their abilities such as precise positioning and maintaining high torque at low speed.
Also Read
Working of Hybrid Stepper Motor
The hybrid stepper motor is a brushless synchronous motor that divides the full rotation into small steps. A hybrid stepper motor consists of two main components: stator and rotor. The stator has multiple electromagnets while the rotor has permanent magnets.
The stator’s electromagnets are arranged in circular patterns with specific winding configurations. The motor controller sends electrical pulses to the stator’s electromagnets and creates a magnetic field.
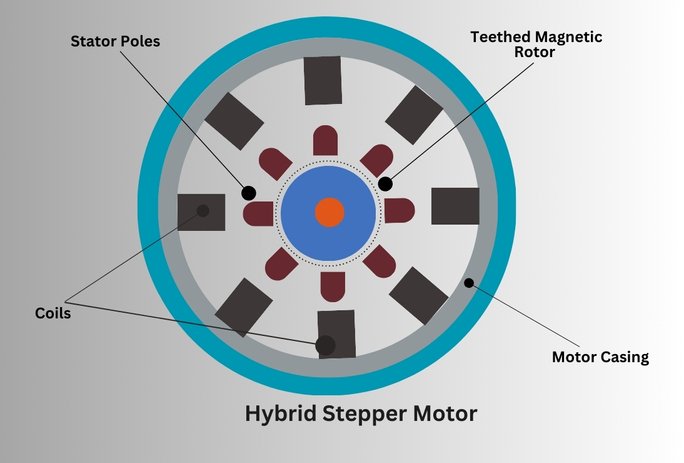
The rotor’s permanent magnet attracts and repels by the stator electromagnets and causes the rotor to rotate in small and discrete steps. The number of steps depends upon the hybrid stepper motor’s design. The common configuration includes 200, 400, and 720 steps per revolution. By controlling the sequence and timing of electrical pulses, the motor controller precisely controls the rotor's position and speed.