Why Pole Count Matters in Stepper Motor Design
Pole count in a stepper motor refers to the number of magnetic poles in the stator. It is based on the stator and its winding pattern. It plays a crucial role in determining the resolution, torque, and speed characteristics of a stepper motor.
Stepper motors are widely used in automation, robotics and precision control applications due to their ability to move in discrete steps. One of the key design parameters influencing the performance of stepper motors is pole count. The number of poles in the stepper motor affects resolution, torque and efficiency.
In this blog, we will understand the role of pole count in stepper motor design, which will help us to select the right stepper motor for our application.
What is a Stepper Motor?
A stepper motor is an electric motor that converts the electrical pulses into precise mechanical movements. Unlike conventional motors, it does not rotate continuously but moves in discrete steps, which makes it ideal for applications that require precise movements.
Construction of the stepper motor includes two main components: Stator and Rotor. The stator is made up of multiple windings arranged in specific patterns, while the rotor is made up of permanent magnets. When electrical signals are applied to the stator windings, they generate a magnetic field and cause the stepper motors to move from one step to another.
Watch the YouTube Video by "The Engineering Mindset" to get a deep insight into the working of stepper motors.
The working of stepper motors is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When electrical pulses are sequentially applied to stator windings, the rotor moves in discrete steps and aligns with the changing magnetic field.
The number of pulses determines the step angle, and the pulse frequency controls the speed. This allows for precise control over movements without any feedback system.
Stepper motors offer various advantages such as high precision, an open-loop control system, and excellent torque at low speed, which makes them ideal for applications such as robotics, CNC machines, 3D printers and medical devices.
Also Read
What is the Pole Count in the Stepper Motor?
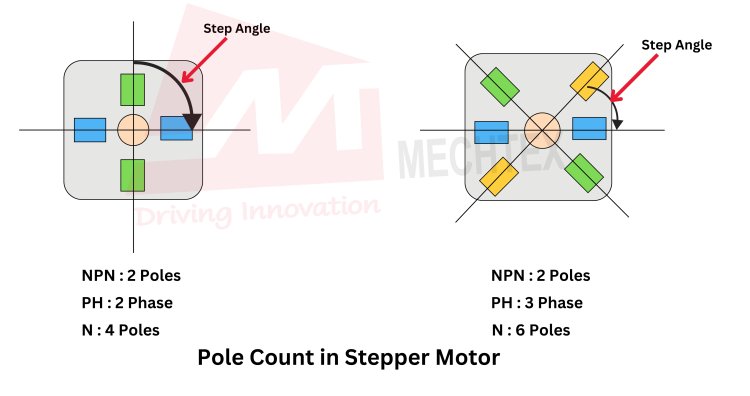
The pole count in a stepper motor refers to the number of magnetic poles in the stator. Each pole consists of a north and south magnetic field, which interacts with the rotor to create step movements. The pole count determines the speed of the stepper motor.
The pole count is based on the stator and its winding pattern. A 2-pole stepper motor has one north and one south pole, while a 4-phase stepper motor has two north and two south poles. Stepper motors with higher pole counts have more switching points in the stator, which affects the step angle of the motor.
The step angle is calculated as
Step Angle = 360° / Number of steps per revolution
A higher pole count results in smaller step angles and leads to finer positioning.
Hybrid stepper motors usually have a high pole count, i.e. 50 to 200 poles, which offer a step angle of 1.8° per step.
Based on pole count, stepper motors are classified into variable reluctance stepper motors, permanent magnet stepper motors and hybrid stepper motors.
Variable reluctance stepper motors rely on rotor teeth aligning with stator poles. Permanent magnet stepper motors are where the rotor has permanent magnets, and hybrid stepper motor is a combination of both stepper motors for high precision.
How Pole Count Affects Stepper Motor Performance
The pole count in a stepper motor plays a crucial role in determining its resolution, torque, and speed characteristics. Here are some parameters of the stepper motor that are affected by pole counts:
- Step Resolution
A higher pole count results in more steps per revolution, which improves the stepper motor resolution. For instance, a stepper motor with 50 poles offers finer positioning than a stepper motor with 20 poles.
- Torque Production
A higher pole count in a stepper motor generally enhances the torque generation, particularly at low speeds. More poles create a strong magnetic field between the stator and rotor, which improves its ability to hold its position and resist external force.
- Speed Considerations
A high pole count improves resolution and torque but reduces the stepper motor's operating speed. This occurs because stepper motors require electrical pulses to switch poles, and a greater number of poles means more frequent switching, limiting speed capabilities.
- Smoothness of Motion
Stepper motors with higher pole counts provide smoother motion due to a smaller step angle. It is particularly beneficial in applications requiring high-precision movements, such as CNC machines and medical devices.
- Efficiency and Heating
A higher pole count in the stepper motor leads to more losses due to the frequent switching of currents. This may cause heating issues and require proper thermal management.
Conclusion
The pole count in a stepper motor design significantly impacts resolution, torque, speed, and efficiency. Engineers must carefully consider these factors to optimise motor performance for specific applications. A balance between pole count and operating requirements ensures efficient and reliable stepper motor operation, enhancing performance in diverse industrial and commercial applications.