Category: Blog
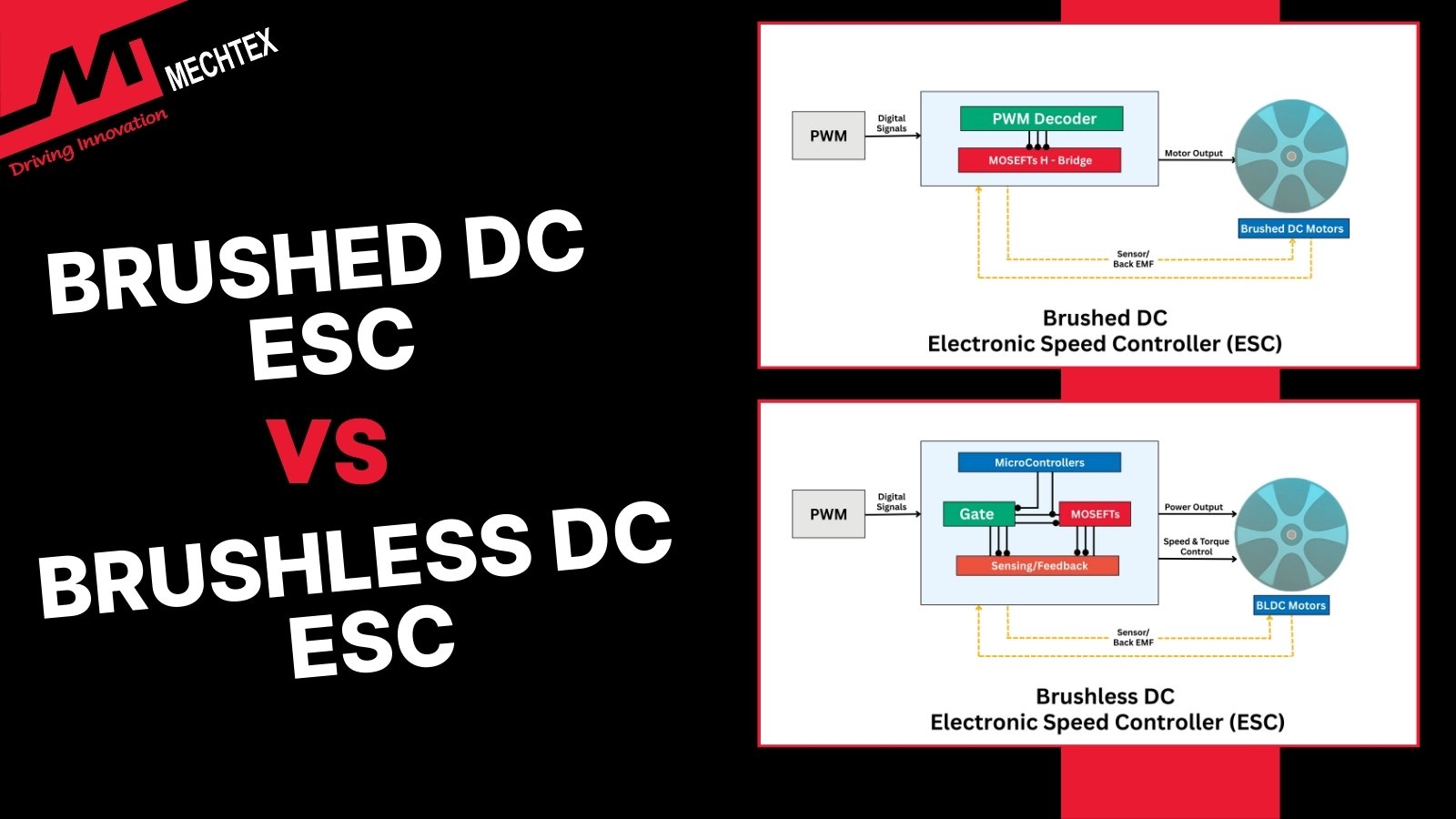
Brushed ESC vs. Brushless ESC - Key Differences Wo...
Learn what an electronic speed controller (ESC) is and explore the key differences between brushed ESC and brushless ESC, includin...
BLDC Motor Driver Circuit Design
A BLDC driver is an electronic control unit that regulates the flow of electric power delivered to stator windings. It consists of...
Tripod Turnstiles A Comprehensive Overview
A tripod turnstile is a three-arm control gate designed to regulate pedestrian/crowd entry by allowing only one person to pass at ...
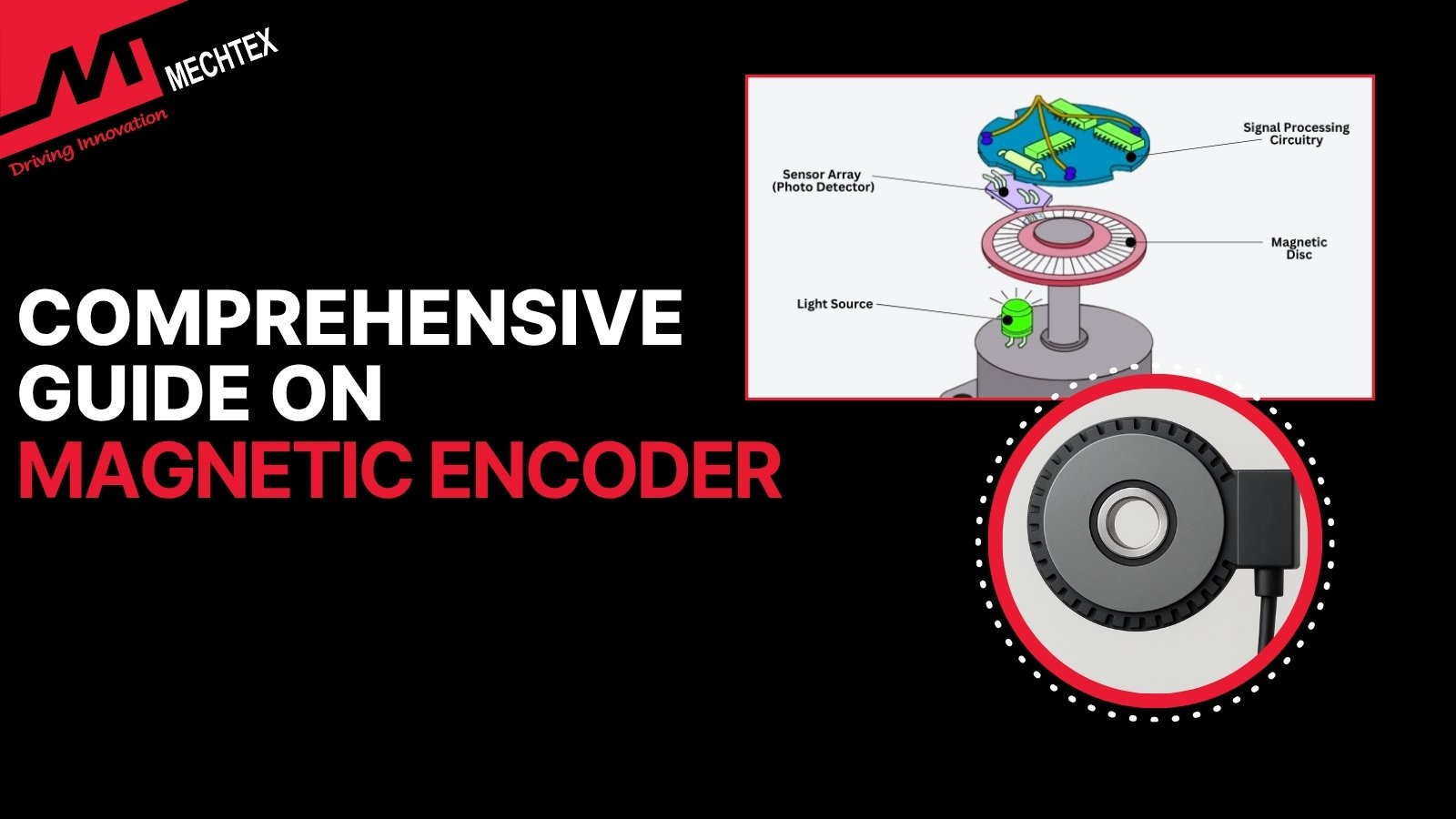
Comprehensive Guide on Magnetic encoder
A magnetic encoder is an electromechanical device which converts motion into digital signals using a magnetic field. It provides f...
Understanding Different Types of Encoders
Different types of encoders like Incremental, Absolute, Linear, Rotary, and Optical encoders work on a distinct working principle ...
How Hall Effect Sensors Work in BLDC Motors: Posit...
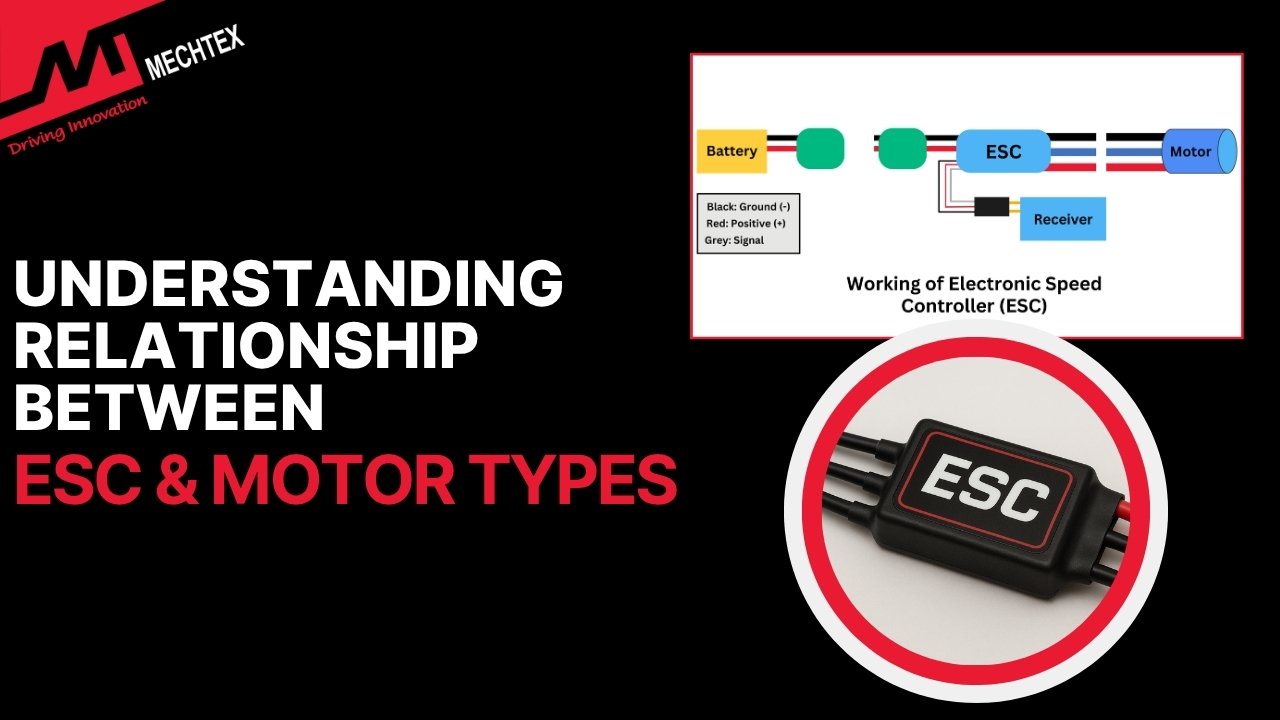
An ESC (Electronic Speed Controller) is an electronic device used to control speed, direction and braking of the electric motor. L...
Mechtex’s Innovative Motor and Gearbox Solutions a...
REI 2025 brings together leaders and innovators in renewable energy. Mechtex showcases BLDC motors, synchronous motors, and gearbo...
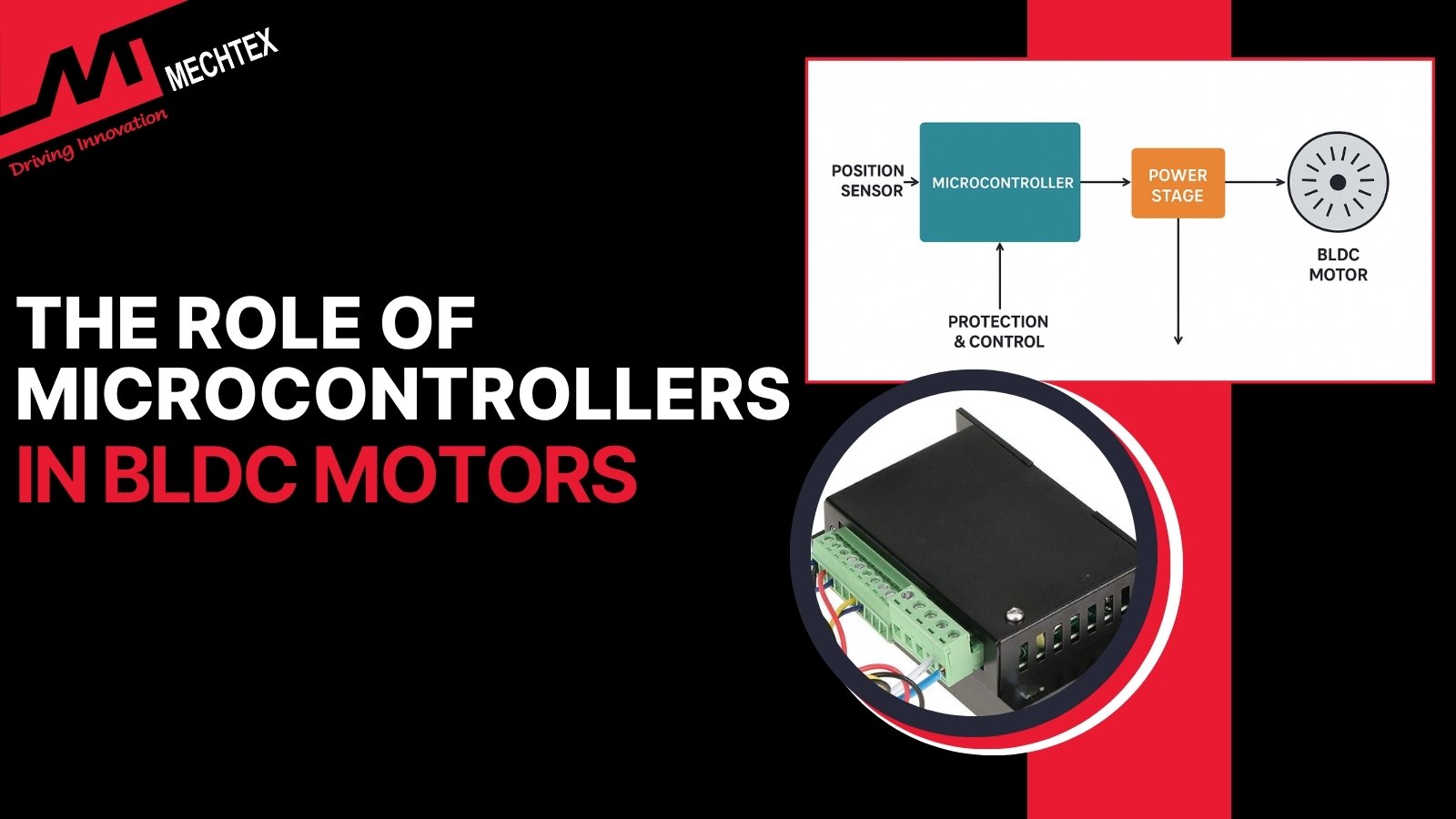
The Role of Microcontrollers in BLDC Driver
A microcontroller (MCU) is a compact integrated circuit designed to perform specific control tasks with electronic control devices...
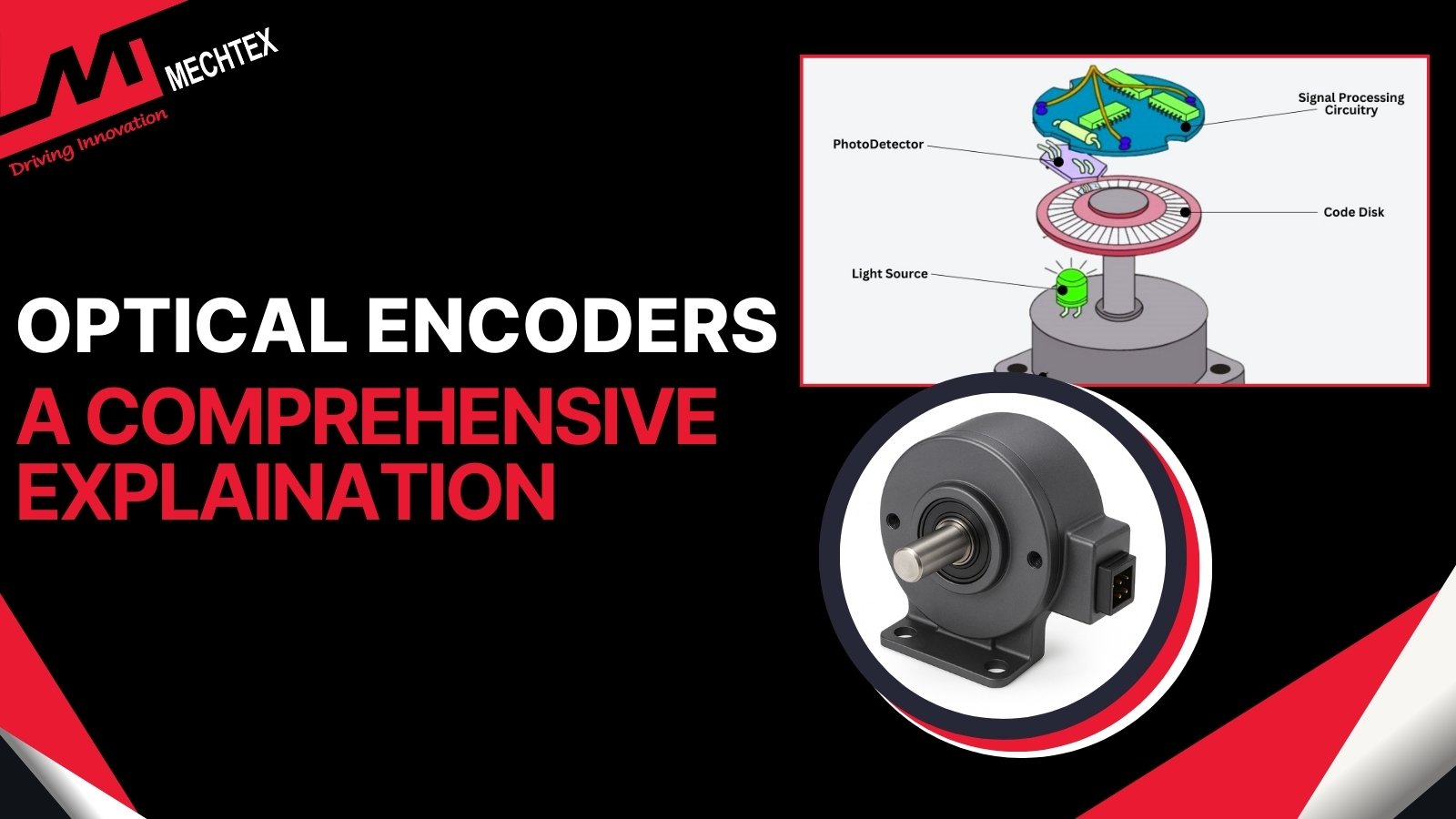
Optical Encoders: A Comprehensive Guide
An optical encoder is an electromechanical device used to convert the angular position of a shaft into electrical signals. Its mai...
Stepper Motors for Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs...
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are self-driven vehicles designed to transport materials from one area to another, especially in ...
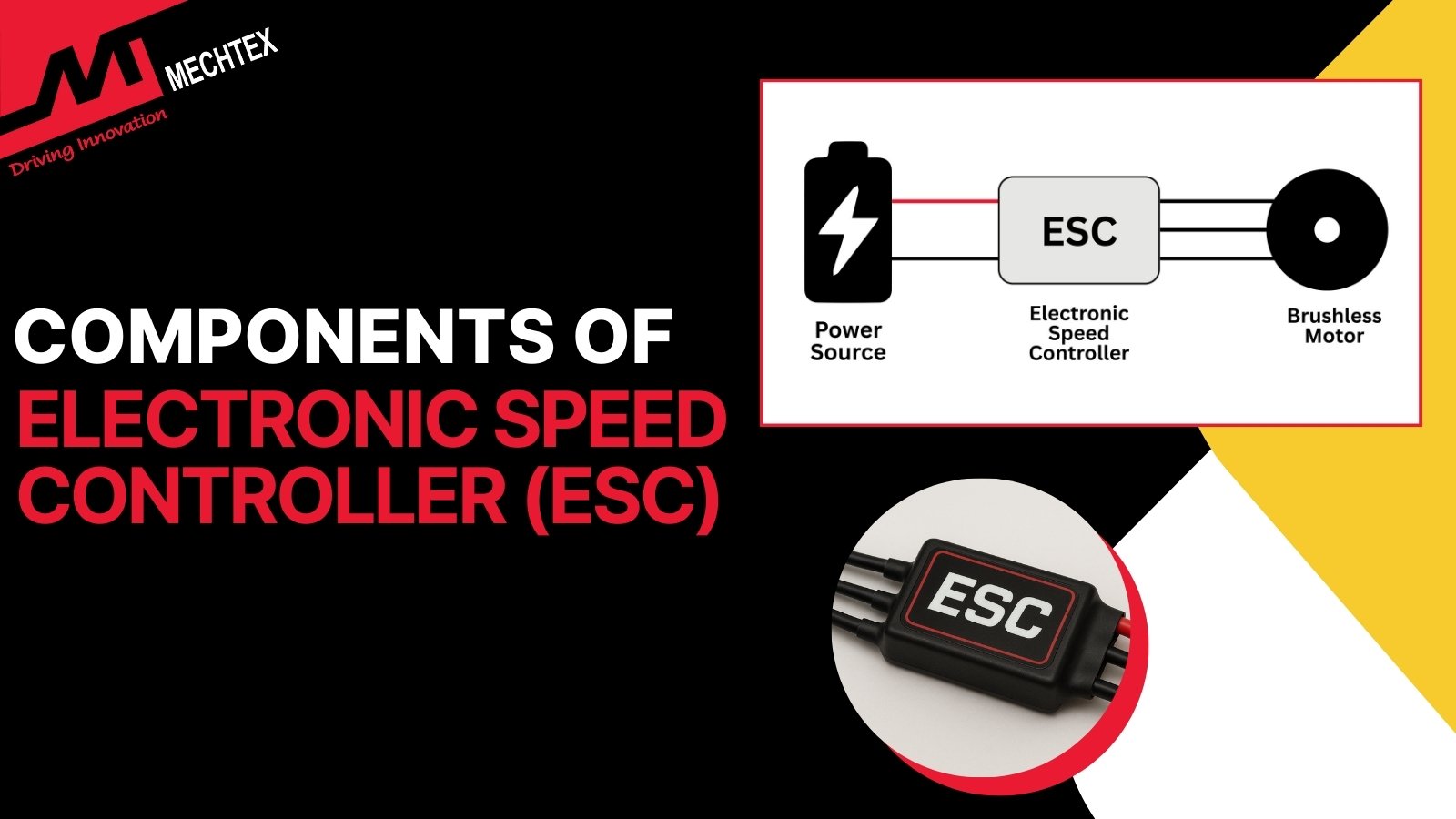
Key Components of an ESC: A Complete Breakdown
The ESC is built with a combination of hardware and software components. Hardware components manage the power supply, signal gener...
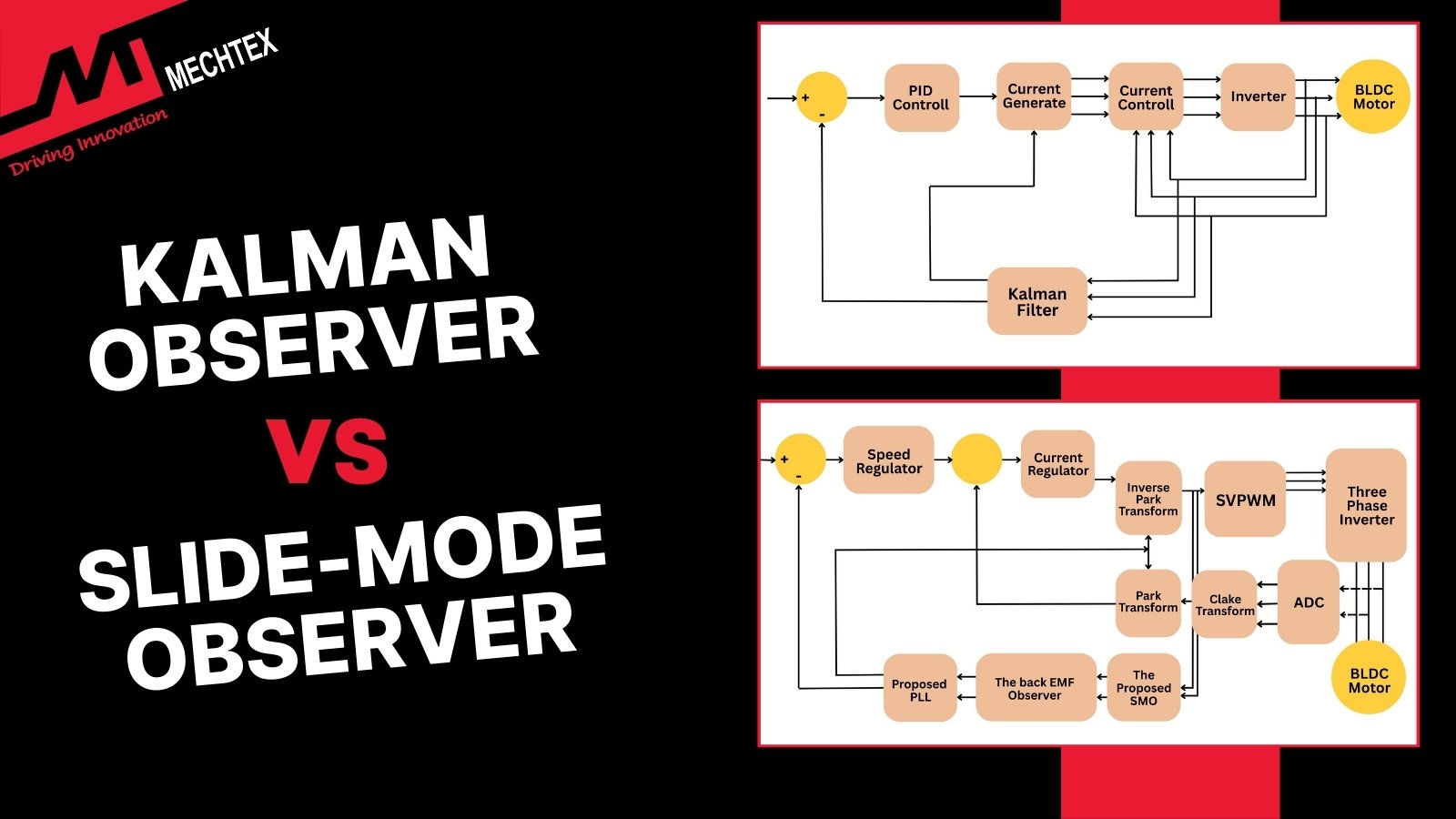
Kalman Observer & Sliding-Mode Observers in BLDC M...
Kalman observer estimates BLDC rotor position using statistical prediction, while the Sliding-Mode observer uses nonlinear control...